Zero Trust Security: Why Traditional Network Defenses Are No Longer Enough
 Scribesquad
Scribesquad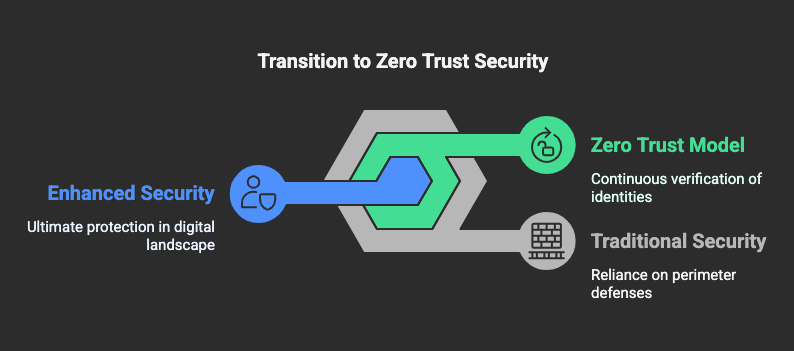
The Problem with Traditional Security Models
Cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented pace. By 2026, global cybercrime will cost businesses over $10.5 trillion annually (Cybersecurity Ventures). Traditional security models persist among numerous organizations even though they fail to acknowledge threats that can emerge from within the protected area of their networks. Undertaking security with this approach permits critical weaknesses to remain open, generating extensive breaches.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a “never trust, always verify” approach that eliminates implicit trust within networks. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, which grant broad access once inside, Zero Trust requires continuous verification of every user, device, and connection attempting to access sensitive data.
Key Principles of Zero Trust
Verify Every User & Device: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and device validation ensure that only authorized users gain access.
Least Privilege Access: Users receive the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks, reducing exposure to insider threats.
Micro-Segmentation: Networks are divided into secure zones, limiting lateral movement in case of a breach.
Continuous Monitoring & Analytics: AI-driven monitoring detects and responds to anomalies in real-time.
Assume Breach Mentality: Organizations operate under the assumption that breaches will happen and prepare accordingly.
Why Traditional Security Is No Longer Enough
🔴 Perimeter-Based Defenses Are Obsolete
Traditional security relies on firewalls and VPNs to keep attackers out. However, 75% of breaches occur due to compromised credentials (Verizon Data Breach Report). Attackers bypass perimeter defenses by exploiting weak passwords, phishing, and insider threats.
🔴 Remote Work & Cloud Adoption Increase Risk
With 70% of employees working remotely at least once a week (Gartner), traditional security models fail to protect data outside corporate networks. Cloud services, IoT devices, and BYOD policies expand the attack surface, making Zero Trust necessary.
🔴 Ransomware & Insider Threats Are Rising
Ransomware attacks surged 150% in 2024, with average recovery costs exceeding $4.5 million per incident (IBM Security Report). Zero Trust limits damage by restricting unauthorized access and detecting threats before they spread.
Implementing Zero Trust: Where to Start
✅ Assess Your Security Posture
Conduct a risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities, privileged accounts, and critical assets.
✅ Enforce Strong Identity & Access Management
Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and enforce least privilege access policies to minimize risks.
✅ Segment Your Network
Use micro-segmentation to isolate critical systems and prevent lateral movement during an attack.
✅ Leverage AI & Automation
Deploy AI-driven threat detection tools to monitor user behavior and detect anomalies continuously.
✅ Adopt a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Follow the NIST Zero Trust framework (NIST 800-207) to build a robust security model that adapts to modern threats.
The Future of Cybersecurity Is Zero Trust
Cybercriminals will continue developing more sophisticated attacks in 2025 and beyond. Organizations must move beyond outdated security models and embrace Zero Trust to protect their data, customers, and reputation.
🚀 Don’t wait for a breach—secure your organization with Zero Trust today.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Scribesquad directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Scribesquad
Scribesquad
Writing is a lifestyle. I am about everything research and technology