MERN Stack Overview
 Dhanraj Chopade
Dhanraj Chopade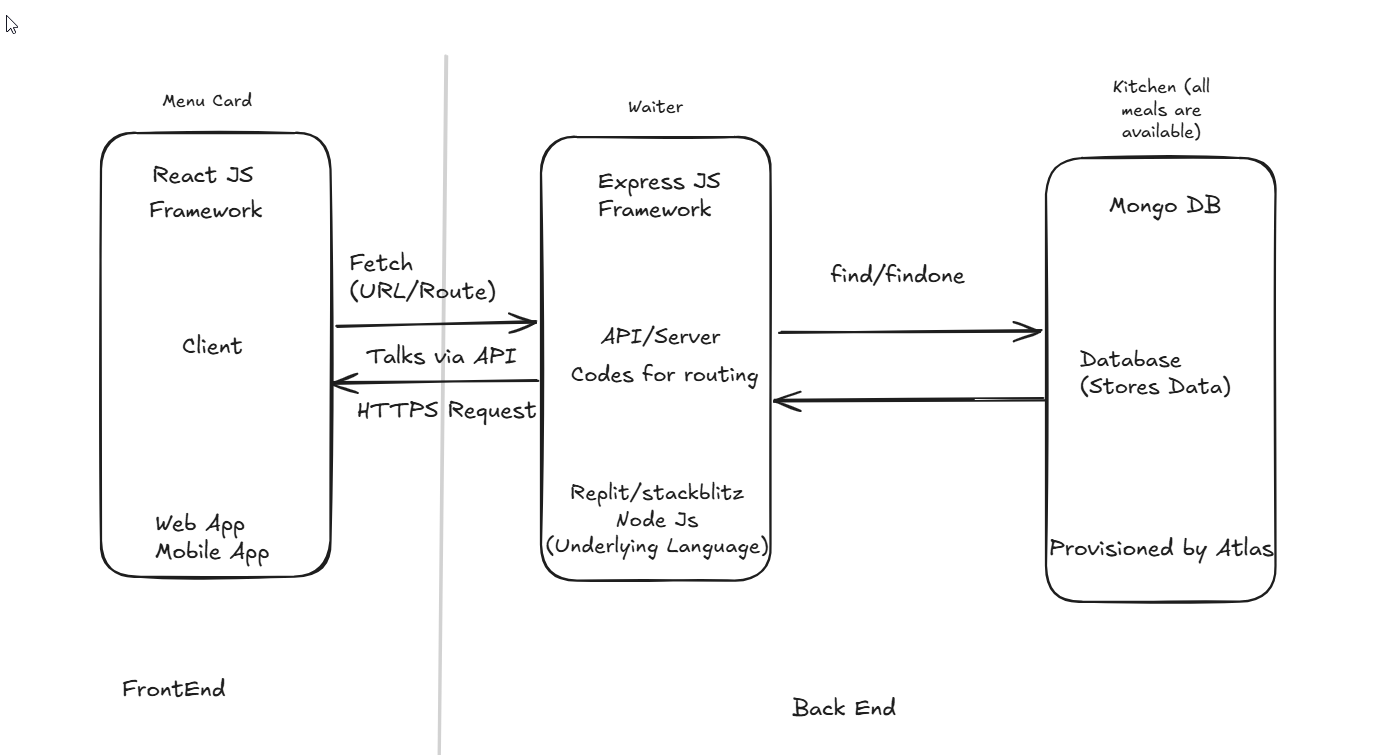
Unlocking Efficient Web Development: The MERN Stack’s Frontend-Backend Interaction
The MERN stack is a popular JavaScript-based framework for building modern web applications. It consists of four main technologies:
MongoDB: A NoSQL database for storing data.
Express.js: A web application framework for handling server-side logic.
React.js: A front-end library for creating user interfaces.
Node.js: The runtime environment for executing server-side JavaScript code.
MERN Stack Architecture
The MERN stack follows a three-tier architecture:
Frontend (Client-Side): React.js is used to build the user interface and handle client-side logic. It renders the UI and interacts with the server via APIs.
Backend (Server-Side): Node.js and Express.js work together to handle server-side logic. Express.js is used to create API endpoints that interact with the frontend and the database.
Database: MongoDB stores and manages data. The server interacts with MongoDB using queries like
find,findOne,get,delete, andpost.
Interaction Between Frontend and Backend
The frontend and backend interact through APIs. Here’s how it works:
Frontend (React.js): Sends HTTP requests (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to the server using
fetchcalls or libraries.Backend (Express.js): Receives these requests, processes them, and interacts with the database (MongoDB) as needed.
API Endpoints: Defined in Express.js, these endpoints handle CRUD operations and return responses to the frontend.
Waiter Concept Analogy
Imagine a restaurant where:
Menu (UI): Built with React.js, it represents the user interface.
Waiter (Server): Express.js running on Node.js acts as the waiter, taking orders (requests) from the client and communicating with the kitchen (database).
Kitchen (Database): MongoDB stores and prepares data (food), which the waiter retrieves or updates based on orders.
MERN Flow for a Web App
Client Request: The user interacts with the React.js UI, triggering a request to the server.
Server Processing: Express.js receives the request, processes it, and interacts with MongoDB if necessary.
Database Interaction: MongoDB stores or retrieves data based on the server’s queries.
Server Response: The server sends the processed data back to the client via API responses.
Client Rendering: React.js updates the UI with the received data.
Infrastructure
Static/CDN Server: Hosts static frontend files (JS, CSS, images).
API Server: Handles backend logic and API requests.
Database Server: Stores and manages data.
This setup allows for efficient, scalable web application development using a single language, JavaScript.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dhanraj Chopade directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
