Cybersecurity: Distribution of Responsibility and Security Culture
 Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn
Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn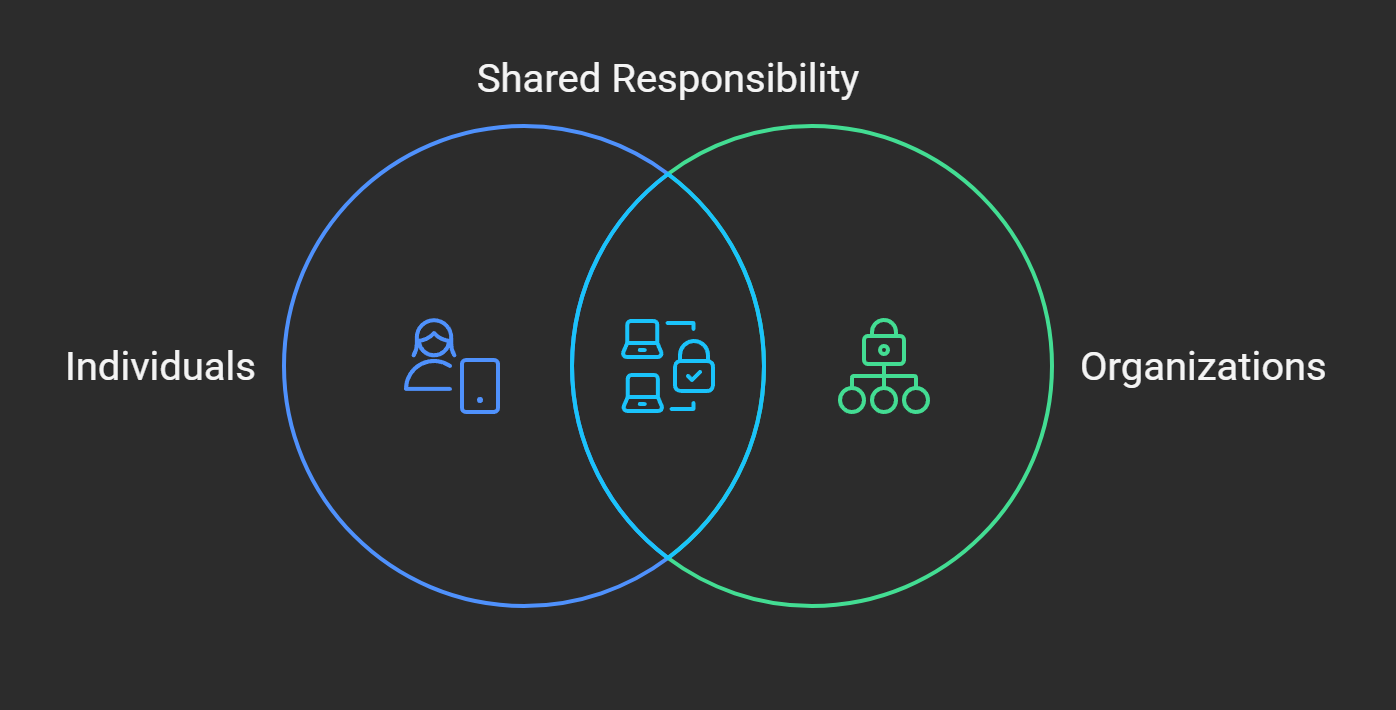
In today's digital environment, cybersecurity is a critical topic that encompasses both technological aspects and social and organizational issues. The common belief that cybersecurity is solely about technical measures is, in fact, incomplete. Technology plays a vital role, but the success of protection also depends on people, their behavior, their awareness of threats, and their understanding of responsibility. One of the most effective ways to encourage people to care about their online safety is to instill a sense of responsibility for others. This can apply not only to family members or colleagues but also to any individuals whose safety may be linked to our online actions.
Advantages of Distributed Responsibility
Enhanced Awareness of Consequences: When individuals understand that their online actions can affect not only themselves but also others, it significantly increases their awareness and responsibility. For example, choosing a strong password, being cautious of suspicious emails, or using two-factor authentication becomes important not only for personal security but also for the security of others, such as colleagues, family members, or even strangers whose information may be at risk.
Formation of a Security Culture: Distributing responsibility for cybersecurity fosters a collective culture where everyone is obliged to assist others in data protection matters. This principle applies not only within families or organizations but also in a broader context, such as educational institutions, public agencies, or business structures, where people interact, share knowledge, and actively support each other in security matters.
Mutual Assistance and Learning: Responsibility for others not only stimulates increased caution but also promotes mutual assistance. When one employee or family member teaches another the basic principles of security, they better assimilate them. This raises the overall level of awareness and creates more reliable protection for all participants.
Companies that distribute responsibilities in the field of cybersecurity typically experience significantly fewer security incidents. This approach improves an organization's protection against cyber threats, as each employee or department has defined duties and roles, enabling faster responses to potential threats. A clear definition of responsibility increases the effectiveness of security measures at all levels.
Risk Management and Business Continuity: Distributing responsibility is crucial for risk management, as clear role definition allows for better resource management and prompt responses to potential threats. It also ensures business continuity, as cybersecurity incidents do not result in attempts to shift responsibility, enabling faster problem localization.
Potential Drawbacks
Shifting Responsibility: One potential risk of distributed responsibility is that some individuals may shift their responsibility to more experienced participants or technologies, leading to a decline in overall awareness. This attitude can lower the overall security level, as everyone must be responsible for their online actions.
Conflicts and Misunderstandings: Unclear distribution of responsibility can lead to conflicts, especially in organizations with varying levels of security awareness. This can reduce the effectiveness of measures and threaten the presence of vulnerable points in protection.
Legal and Ethical Aspects: Legal and ethical issues regarding the protection of personal data and confidential information also become important in cases of distributed responsibility. For example, if one person delegates their duties to others, it can create a situation where violations of security standards lead to legal consequences or information misuse.
Strategies for Risk Minimization
To minimize negative consequences, it is important to develop a clear strategy for distributing responsibility, considering organizational needs and potential threats. This includes:
Regular checks.
Training.
Automated systems for access control and auditing.
Using the RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) for clear definition of roles and responsibilities.
Implementing the Zero Trust model: Which assumes that no user or device is automatically trusted, minimizing internal threat risks.
Key Factors for Success
Responsibility Distribution Model: Distribution of responsibility depends on the organization's specifics and threat level. Large corporations may have specialized cybersecurity departments, while small companies may have more universal responsibility, involving broader employee participation in the security process.
Control and Audit: Control and audit mechanisms are integral to the effective distribution of responsibility. They allow organizations to detect violations promptly and adjust actions to prevent incidents.
Technology as a Support Tool: Modern technologies play a crucial role in ensuring security. Usage of:
Password management tools (e.g., LastPass, 1Password).
Antivirus software (e.g., Norton, NOD32).
Two-factor authentication.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS).
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems for centralized collection and analysis of security events.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) platforms for detecting and responding to threats on endpoints.
Data Actualization:
Cybersecurity is a rapidly changing field. It is important to consider modern threats such as ransomware, phishing, supply chain attacks, DDoS attacks, and attacks on IoT devices.
Regular employee training is necessary to raise awareness of cyber threats and teach basic security rules.
Simulating cyber attacks (penetration testing) is recommended to test an organization's readiness for real threats and identify weaknesses.
The Role of Organizations in Cybersecurity: Challenges and Opportunities for Business
According to a recent PwC study, organizations in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) recognize cybersecurity as critical for maintaining trust with their business and partners. Most regional executives believe that enhancing cybersecurity is an important element of their digital transformation strategy. However, only 2% of companies have fully implemented company-wide cybersecurity programs, indicating a need for greater investment and improved strategies in this area.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a complex process that includes not only technical tools but also social and organizational factors. Distributing responsibility among all participants is an important element in achieving a high level of security. Clear role definition, training, and technology application are the foundation for effective data protection and business continuity. Considering potential risks and implementing a control strategy helps ensure security at all levels.
Call to Action:
In today's digital world, cybersecurity is an integral part of our lives. Whether you are a large company executive, a small firm employee, or a regular Internet user, each of us has a role to play in ensuring online safety.
- For Executives: Develop and implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes clear distribution of responsibilities, regular employee training, and the use of modern technologies.
For Employees: Be attentive and cautious online, follow security rules, report suspicious activities, and continuously improve your cybersecurity awareness.
For Everyone: Use strong passwords, do not open suspicious emails, update software, and be vigilant about potential cyber threats.
Remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Only by joining forces can we create a safe digital world for all.
Sources and Related Сontent:
7 reasons why security awareness training is important in 2023. CybSafe. URL: https://www.cybsafe.com/blog/7-reasons-why-security-awareness-training-is-important/#:~:text=Security%20awareness%20programs%20are%20essential,threats%20and%20best%20practices%20for (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Building cybersecurity through C-suite collaboration. 2025 Global Digital Trust Insights Survey: insights for Retail. PwC. URL: https://www.pwc.com/ua/en/survey/2025/cee-findings-from-the-2025-global-digital-trust-insights-survey/retail.html#:~:text=Cyber%20risks%20are%20top%20of,over%20the%20next%2012%20months%20( (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Cyber Security Strategy - How to plan and develop it?. Data Privacy & Information Security - DataGuard. URL: https://www.dataguard.com/cyber-security/strategy/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
IBM. What Is Cybersecurity? | IBM. IBM - United States. URL: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/cybersecurity (date of access: 14.03.2025).
In an organisation, who is responsible for cyber security?. TSC. URL: https://thesecuritycompany.com/the-insider/in-an-organisation-who-is-responsible-for-cyber-security/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Information Security Policies: 10 Examples, Features, and Benefits | Syteca. Syteca. URL: https://www.syteca.com/en/blog/information-security-policies (date of access: 14.03.2025).
ISO 27001 Roles and Responsibilities | Compyl. Compyl. URL: https://compyl.com/blog/iso-27001-roles-and-responsibilities-explained/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
One Size Does Not Fit All Organizations. Security Intelligence. URL: https://securityintelligence.com/articles/cybersecurity-one-size-organization/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Psychology of Cybersecurity and Human Behavior. URL: https://identitymanagementinstitute.org/psychology-of-cybersecurity-and-human-behavior/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
The impact of unclear responsibilities and expectations on people | More Than Motivation. More Than Motivation. URL: https://morethanmotivation.co.uk/the-impact-of-unclear-responsibilities-and-expectations-on-people/ (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Understanding the Zero Trust Security Model to Safeguard Digital Infrastructure. Enterprise IP and DLP Software | Digital Guardian. URL: https://www.digitalguardian.com/blog/understanding-zero-trust-security-model-safeguard-digital-infrastructure#:~:text=Dealing%20with%20Insider%20Threats:%20By,detect%20and%20prevent%20insider%20threats. (date of access: 14.03.2025).
What is a RACI Chart? | Wrike. Blog Wrike. URL: https://www.wrike.com/blog/what-is-a-raci-chart/#:~:text=So,%20what%20does%20RACI%20stand,accountable,%20consulted,%20and%20informed. (date of access: 14.03.2025).
What is EDR? Endpoint Detection & Response Defined | CrowdStrike. CrowdStrike: We Stop Breaches with AI-native Cybersecurity. URL: https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/cybersecurity-101/endpoint-security/endpoint-detection-and-response-edr/#:~:text=Endpoint%20Detection%20and%20Response%20(EDR),%20also%20referred%20to%20as,endpoint%20security%20solution%20that%20continuously (date of access: 14.03.2025).
What Is SIEM? | Microsoft Security. URL: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/security-101/what-is-siem#:~:text=SIEM%20systems%20collect%20and%20analyze,other%20security%20solutions,%20and%20cloud (date of access: 14.03.2025).
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
