Syncing Existing GitHub Repositories to Fabric with Semantic Link Labs / Sempy
 Nalaka Wanniarachchi
Nalaka Wanniarachchi
Managing and syncing Microsoft Fabric workspaces with GitHub repositories is an essential practice for ensuring proper version control, seamless collaboration, and efficient data management. Previously, Sandeep Pawar blogged about how to sync Fabric Workspace artifacts to GitHub programmatically.
All good. But what if you need to do the reverse—sync existing GitHub repositories back into Fabric? In this blog, as a sequel to Sandeep’s post, I am explaining how I achieved that.
💡This approach is particularly beneficial when an organization undergoes changes, such as onboarding new users or setting up a new capacity. Instead of manually identifying and syncing each repository one by one, this automated solution ensures that all relevant Fabric artifacts from GitHub are seamlessly restored.
Thanks to the power of Michael Kovalsky’s Semantic Link Labs and Sempy, we can automate this process and make it efficient. In this blog, we’ll walk through how to accomplish this in a structured and automated way.
What I have done previously
In my case, I previously synced my existing Fabric Workspaces to GitHub with the ‘Bkp_' prefix (Refer to Sandeep’s previous article )
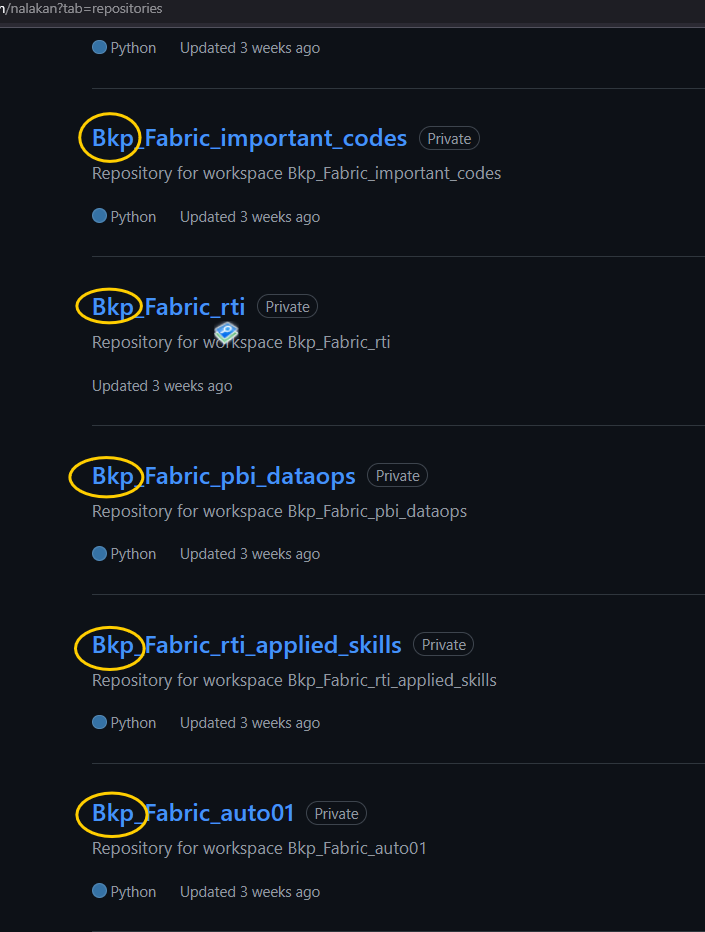
Now, I can easily filter out these repositories and sync them into Fabric without the prefix (I created the new Workspaces with the same name in Github repos without the ‘Bkp_’ prefix programmatically). If a workspace already exists, I simply skip creating it and proceed with Git initialization.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the process, ensure you have:
GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT): Required for authentication with the GitHub API. Create a classic token with appropriate scopes.
Microsoft Fabric Connection ID: This is generated when setting up a GitHub connection in Fabric.
Administrative Rights: You must have admin access to Fabric workspaces to sync repositories.
pip install PyGithub semantic-link-labs
Key Functions used in Semantic Link Labs and Sempy
To effectively sync Fabric workspaces with GitHub, we rely on several key functions from Semantic Link Labs and Sempy:
Semantic Link Labs Functions
labs.admin.list_git_connections()
- Fetches all existing GitHub connections linked to Fabric workspaces.
labs.connect_workspace_to_github(owner_name, repository_name, branch_name, directory_name, connection_id, workspace)
- Establishes a Git connection between a Fabric workspace and a GitHub repository.
labs.initialize_git_connection(workspace)
- Initializes the GitHub connection for a Fabric workspace and returns the latest commit hash.
labs.update_from_git(workspace, remote_commit_hash, conflict_resolution_policy='PreferRemote')
- Synchronizes the Fabric workspace with the latest version from GitHub.
Sempy Functions
fabric.list_workspaces()
- Retrieves a list of existing workspaces in Microsoft Fabric.
fabric.create_workspace(display_name, description, capacity_id)
- Creates a new Fabric workspace with the specified name, description, and capacity.
These functions form the backbone of our automation, enabling us to efficiently manage workspaces and maintain synchronization between GitHub and Fabric.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Initialize GitHub and Fabric Connections
First, we set up our connections to GitHub and Microsoft Fabric:
from github import Github
import sempy.fabric as fabric
import sempy_labs as labs
import time
# GitHub Personal Access Token and Connection ID
g = Github("your_github_pat")
conn_id = "your_connection_id"
capacity_id = "your_capacity_id"
2. Fetch Existing GitHub Repositories
To retrieve all repositories associated with your GitHub account:
user = g.get_user()
repos = list(user.get_repos()) # Convert iterator to list
print(f"ℹ️ Total repositories found: {len(repos)}")
3. List Existing Workspaces and Git Connections
Before creating new Fabric workspaces, check which ones already exist:
existing_workspaces_df = fabric.list_workspaces()
git_connections_df = labs.admin.list_git_connections()
4. Automate Workspace Creation and connect WS to Git
For each repository (With “Bkp_”), we check if a corresponding workspace exists. If not, we create it and sync it with GitHub.
# Initialize counters
total_repos_processed = 0
workspaces_created = 0
workspaces_skipped = 0
workspaces_already_exist = 0
git_connections_created = 0
git_connections_skipped = 0
workspaces_synced_from_github = 0
for repo in repos:
total_repos_processed += 1
try:
if not repo.name.startswith("Bkp_"):
print(f"⚠️ Skipping '{repo.name}', does not match 'Bkp_' prefix.")
workspaces_skipped += 1
continue
workspace_name = repo.name.replace("Bkp_", "")
print(f"Processing repo: {repo.name} -> Workspace name: {workspace_name}")
existing_workspace = existing_workspaces_df[existing_workspaces_df['Name'] == workspace_name]
if not existing_workspace.empty:
workspace_id = existing_workspace.iloc[0]['Id']
print(f"ℹ️ Workspace '{workspace_name}' already exists with ID: {workspace_id}.")
workspaces_already_exist += 1
if workspace_id in git_connections_df['Workspace Id'].values:
print(f"⚠️ Workspace '{workspace_name}' already has a Git connection. Skipping.")
git_connections_skipped += 1
continue
else:
workspace_id = fabric.create_workspace(
display_name=workspace_name,
description=f"Workspace for {repo.name} synced from GitHub",
capacity_id=capacity_id
)
print(f"🟢 Workspace '{workspace_name}' created with ID: {workspace_id}.")
workspaces_created += 1
labs.connect_workspace_to_github(
owner_name=user.login,
repository_name=repo.name,
branch_name="main",
directory_name="/",
connection_id=conn_id,
workspace=workspace_id
)
print(f"🟢 Connected workspace '{workspace_name}' to GitHub repository '{repo.name}'.")
git_connections_created += 1
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Unexpected error processing '{repo.name}': {e}")
4. Initialize Git Connection and Git pull
# Wait for Git connection to initialize
time.sleep(10) # Adjust as necessary
try:
commit_hash = labs.initialize_git_connection(workspace=workspace_id)
print(f"🟢 Git connection initialized for '{workspace_name}'. Commit: {commit_hash}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Error initializing Git for '{workspace_name}': {e}")
continue # Move to the next repo
# Automatically update workspace from Git
try:
update_status = labs.update_from_git(workspace=workspace_id, remote_commit_hash=commit_hash, conflict_resolution_policy='PreferRemote')
print(f"🟢 Updated workspace '{workspace_name}' from Git. Status: {update_status}")
workspaces_synced_from_github += 1
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Error updating workspace '{workspace_name}' from Git: {e}")
# Sync all content from GitHub repo
print(f"🟢 Workspace '{workspace_name}' setup completed. Moving to next repo.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Unexpected error processing '{repo.name}': {e}"
Output of the code
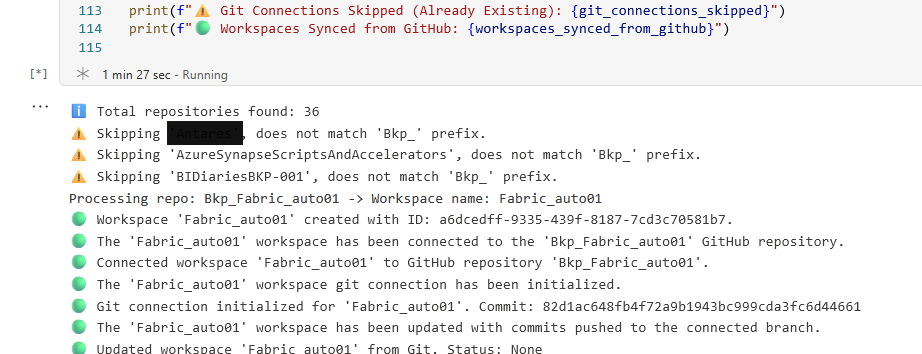
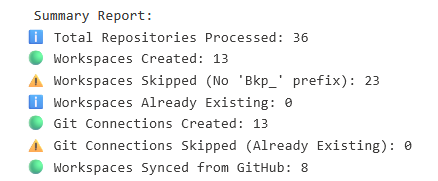
Workspaces are now automatically created and content is synced in Fabric.
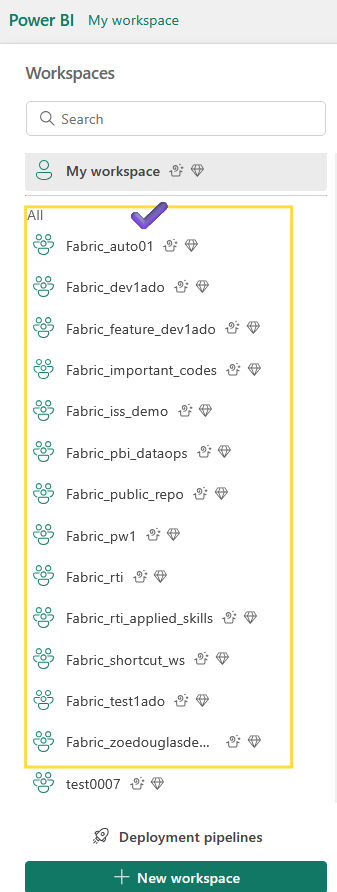
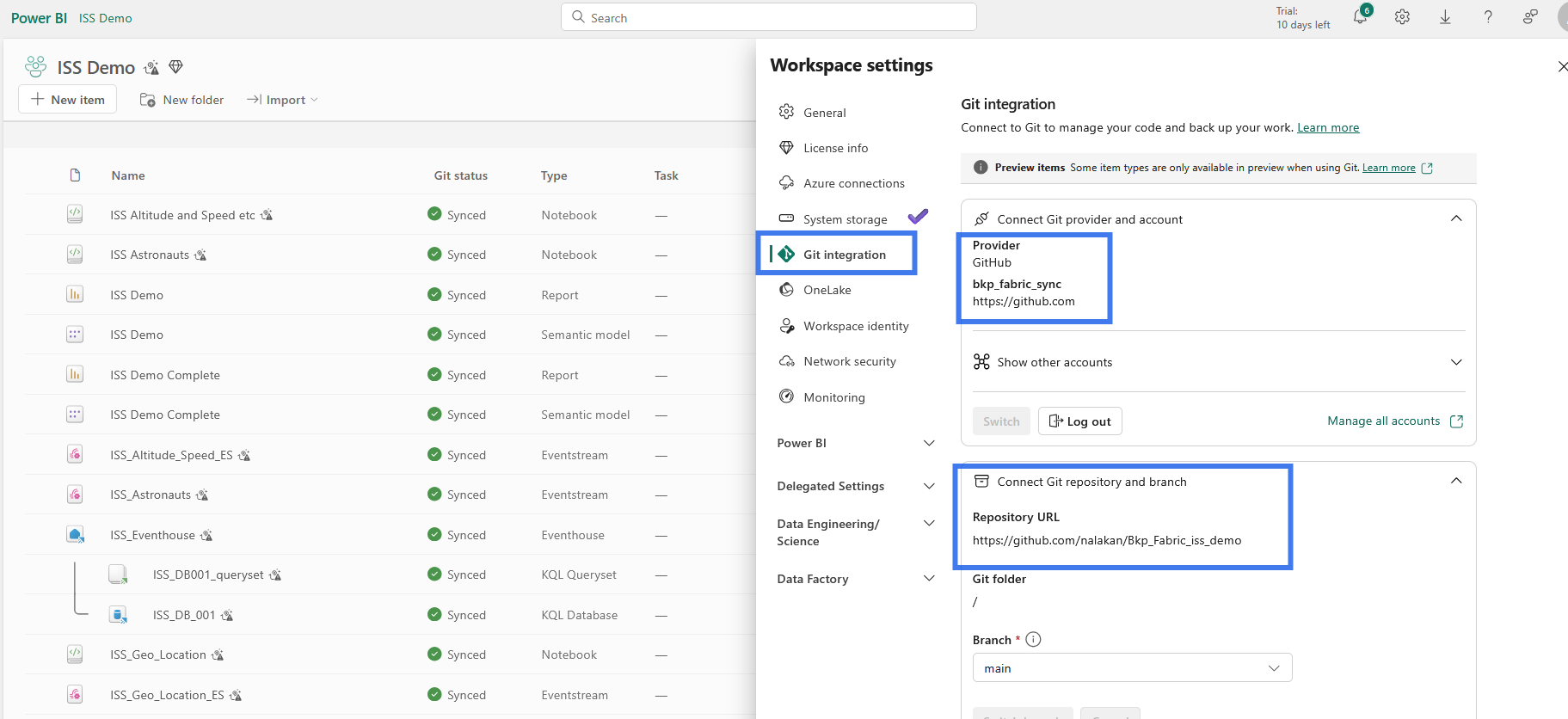
Following Workspace pulled the content from Github Repo and now it is connected with Github automatically.
Conclusion
With these steps, you can now integrate previously synced Github artifacts into Microsoft Fabric with minimal effort.(No manual configuration). For Azure DevOps repos the process would be the same.
Full code is available in this GitHub Gist.
Happy syncing - Thanks for Reading!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nalaka Wanniarachchi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nalaka Wanniarachchi
Nalaka Wanniarachchi
Nalaka Wanniarachchi is an accomplished data analytics and data engineering professional with over 20 years of working experience. As a CIMA(ACMA/CGMA) UK qualified ex-banker with strong analytical skills, he transitioned into building robust data solutions. Nalaka specializes in Microsoft Fabric and Power BI, delivering advanced analytics and engineering solutions. He holds a Microsoft certification as a Fabric Analytic Engineer and Power BI Professional, combining technical expertise with a deep understanding of financial and business analytics.