NAT Gateway in AWS — The Complete Guide
 Soumo Sarkar
Soumo SarkarTable of contents
- 🚀 What is a NAT Gateway in AWS?
- ✅ Why do we need a NAT Gateway?
- 📅 When should you use a NAT Gateway?
- ⚙️ How NAT Gateway works (Simple Flow)
- 📊 Quick Example Architecture
- 🚀 Terraform Code
- 📌 Folder Structure
- 1️⃣ provider.tf (Set up AWS provider)
- 2️⃣ variables.tf (Define variables for flexibility)
- 3️⃣ main.tf (Infrastructure Setup)
- 4️⃣ outputs.tf (Display Useful Information)
- 5️⃣ terraform.tfvars (Custom Values - Optional)
- 📌 How to Deploy
- 🎯 Key Features of this Setup
- 💰 Estimated Costs (As of 2025)
- 🎯 Next Steps
- ⚖️ Pros and Cons of NAT Gateway
- ☑️ Important Notes
- 🎯 Summary
- ✅ Conclusion
In modern cloud architecture, security and scalability are critical. AWS offers NAT Gateway (Network Address Translation Gateway) as a fully managed service that allows instances in private subnets to securely access the internet or other AWS services without exposing them directly to the public internet.
In this guide, we will explore what NAT Gateway is, how it works, when to use it, and solve real-world problems using it.
🚀 What is a NAT Gateway in AWS?
NAT Gateway (Network Address Translation Gateway) in AWS is a highly available, managed network service that allows instances (like EC2) in a private subnet to access the internet or other AWS services for outbound connections, without receiving inbound connections from the public internet.
➡️ NAT stands for Network Address Translation, which means it translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses to allow outbound traffic.
🔑 Key Features
Outbound-only internet (one-way) connectivity for private subnets.
Fully managed and auto-scalable by AWS.
Highly available within an Availability Zone (AZ).
✅ Why do we need a NAT Gateway?
When you have EC2 instances or other resources in a private subnet, they don't have direct internet access for security reasons (because they don't have public IPs).
However, sometimes, these private instances need to connect to the internet for:
Downloading updates, patches, packages (e.g., apt-get, yum)
Accessing external APIs
Connecting to AWS services like S3, DynamoDB (if VPC endpoints are not used)
🔑 NAT Gateway allows this outbound communication while still keeping those instances private.
📅 When should you use a NAT Gateway?
| Scenario | Need NAT Gateway? |
| EC2 instances in private subnet need internet | ✅ Yes |
| EC2 instances in public subnet with public IP | ❌ No (they have direct internet) |
| Accessing S3/DynamoDB from private subnet | ⚠️ Optional (VPC endpoint preferred, but NAT possible) |
| Private subnet resources needing security patches | ✅ Yes |
⚙️ How NAT Gateway works (Simple Flow)
Private EC2 instance (in Private Subnet, No Public IP) makes a request to the Internet.
Traffic is routed to NAT Gateway through the Route Table.
NAT Gateway (in Public Subnet, with Elastic IP) translates private IP to public IP.
Response from the internet returns to NAT Gateway, which then forwards it back to the private EC2 instance.
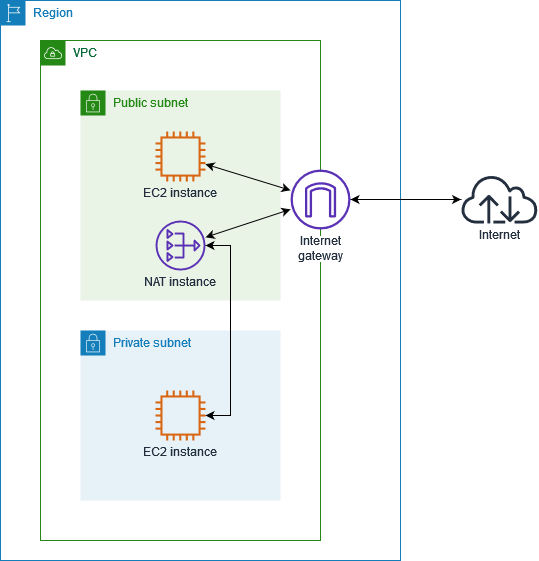
📊 Quick Example Architecture
Architecture Components
| Component | Description |
| VPC | Your private network |
| Public Subnet | Hosts NAT Gateway, has route to Internet Gateway |
| Private Subnet | Hosts EC2 instances, no direct internet access |
| NAT Gateway with Elastic IP | Provides outbound internet for private subnet |
| Internet Gateway | Connected to VPC, provides public internet access |
| Route Tables & Associations | Route traffic correctly between components |
🚀 Terraform Code
📌 Folder Structure
nat-gateway-terraform/
│── main.tf # Main Terraform config
│── variables.tf # Input variables
│── outputs.tf # Outputs (Elastic IP, NAT Gateway ID, etc.)
│── provider.tf # AWS provider config
│── terraform.tfvars # Variable values
1️⃣ provider.tf (Set up AWS provider)
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1" # Change as needed
}
2️⃣ variables.tf (Define variables for flexibility)
variable "vpc_cidr" {
description = "VPC CIDR Block"
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
variable "public_subnet_cidr" {
description = "Public Subnet CIDR"
default = "10.0.1.0/24"
}
variable "private_subnet_cidr" {
description = "Private Subnet CIDR"
default = "10.0.2.0/24"
}
variable "availability_zone" {
description = "AWS Availability Zone"
default = "us-east-1a"
}
3️⃣ main.tf (Infrastructure Setup)
# Create VPC
resource "aws_vpc" "main_vpc" {
cidr_block = var.vpc_cidr
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "Main-VPC"
}
}
# Create Internet Gateway
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "igw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "Main-IGW"
}
}
# Create Public Subnet
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet_cidr
availability_zone = var.availability_zone
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
tags = {
Name = "Public-Subnet"
}
}
# Create Private Subnet
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.private_subnet_cidr
availability_zone = var.availability_zone
tags = {
Name = "Private-Subnet"
}
}
# Allocate an Elastic IP for NAT Gateway
resource "aws_eip" "nat_eip" {
domain = "vpc"
}
# Create NAT Gateway in Public Subnet
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "nat_gw" {
allocation_id = aws_eip.nat_eip.id
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet.id
tags = {
Name = "Main-NAT-Gateway"
}
}
# Public Route Table (Allows outbound to Internet Gateway)
resource "aws_route_table" "public_rt" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.igw.id
}
tags = {
Name = "Public-Route-Table"
}
}
# Associate Public Subnet with Public Route Table
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_assoc" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.public_rt.id
}
# Private Route Table (Routes Internet Traffic via NAT Gateway)
resource "aws_route_table" "private_rt" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
nat_gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.nat_gw.id
}
tags = {
Name = "Private-Route-Table"
}
}
# Associate Private Subnet with Private Route Table
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private_assoc" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.private_subnet.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.private_rt.id
}
4️⃣ outputs.tf (Display Useful Information)
output "vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.main_vpc.id
}
output "public_subnet_id" {
value = aws_subnet.public_subnet.id
}
output "private_subnet_id" {
value = aws_subnet.private_subnet.id
}
output "nat_gateway_id" {
value = aws_nat_gateway.nat_gw.id
}
output "nat_gateway_ip" {
value = aws_eip.nat_eip.public_ip
}
5️⃣ terraform.tfvars (Custom Values - Optional)
vpc_cidr = "10.0.0.0/16"
public_subnet_cidr = "10.0.1.0/24"
private_subnet_cidr = "10.0.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "us-west-2a"
📌 How to Deploy
1️⃣ Initialize Terraform
terraform init
2️⃣ Validate the Configuration
terraform validate
3️⃣ Plan the Deployment
terraform plan
4️⃣ Apply the Deployment
terraform apply
5️⃣ Get Outputs
terraform output
🎯 Key Features of this Setup
✅ Secure Design – Private instances have outbound-only internet access.
✅ Flexible – Uses variables to easily change subnet CIDRs, region, and AZ.
✅ Fully Managed – Uses AWS-managed NAT Gateway for auto-scaling.
✅ Cost-Efficient – Private subnets avoid unnecessary public exposure.
💰 Estimated Costs (As of 2025)
| Resource | Estimated Cost |
| NAT Gateway (per hour) | ~$0.045 per hour |
| Data transfer (per GB) | ~$0.045 per GB |
| Elastic IP (while in use) | Free |
Tip: To optimize cost, use VPC endpoints for AWS services like S3 and DynamoDB instead of NAT Gateway.
🎯 Next Steps
✅ Deploy an EC2 instance in the private subnet to test outbound internet access.
✅ Attach a security group to control outbound traffic.
✅ Deploy a Lambda in the private subnet and test calling external APIs.
🔥 Now you have a fully functional Terraform setup for NAT Gateway!
⚖️ Pros and Cons of NAT Gateway
| Pros | Cons |
| Fully managed, auto-scalable | Additional cost (per hour + traffic) |
| Highly available (one AZ) | Limited to single AZ (HA needs multiple NAT Gateways) |
| Secure way for private subnet to go out | Cannot handle inbound traffic |
| Simple to set up | Requires public subnet setup |
☑️ Important Notes
Chargeable Service: NAT Gateway costs money for usage and data transfer.
High Availability: Managed by AWS, scales automatically, highly available within an AZ.
Regional/AZ Scope: NAT Gateway is specific to an Availability Zone, so for high availability, deploy in multiple AZs.
🎯 Summary
NAT Gateway = Private subnet → Internet (outbound only, securely)
When needed: When private instances need updates, external communication.
Cost: Yes, but fully managed, scalable, and secure.
✅ Conclusion
In a world where security and connectivity must go hand in hand, AWS NAT Gateway serves as a powerful solution to enable private instances to securely access the internet. Whether it's for fetching updates, interacting with third-party APIs, or connecting to AWS services, NAT Gateway ensures outbound traffic is handled smoothly while keeping your resources private and secure.
Pro Tip: Combine NAT Gateway with VPC Endpoints and Security Groups for cost-efficient and secure architecture.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Soumo Sarkar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Soumo Sarkar
Soumo Sarkar
Aspiring DevOps Engineer