Cyber Unicorns Reverse Engineered (CSPM & XDR): JSON, Cypher, Graphs, Embeddings, and Intruders
 Amit Sides
Amit Sides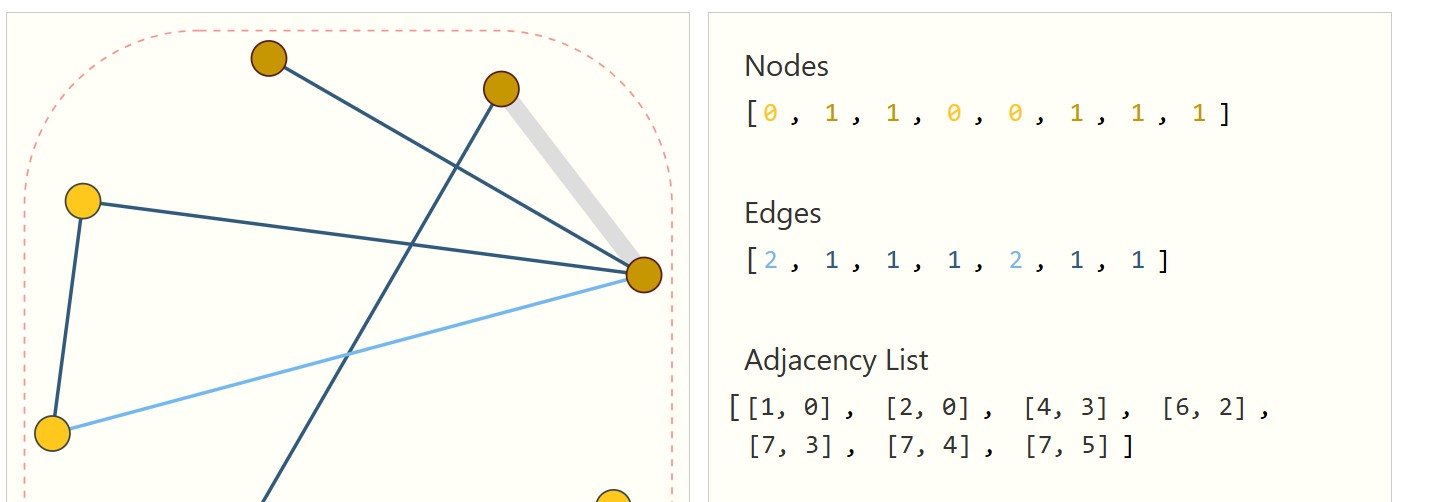
Tags: AI, Cyber, CSPM, XDR, GraphMap, GNN, Cypher, XGBoost, Python
What’s the technology behind Cybersecurity Unicorns? What are the complexities of building AI First XDR/CSPM Products? Multiple Use Cases, Misconfigurations, Datatypes, and Cyber Ontologies are involved. Converting Cloud Infrastructure to JSONs & Graphs, Embedding?
How do they detect real-time anomalies and trigger response mechanisms?
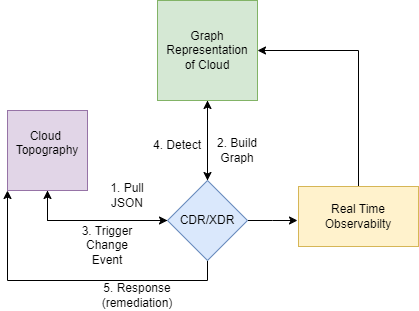
The Challenge of Graph XDR/CDR
Cloud JSON Parsing → Graph Map → Change Events Observability → Remap → Response
Real-Time Detection — Every Event in the Cloud Reshape the Graph and searches for Edges Anamolly
Respond — Automated response to detected intruders in the Graph SIEM- Trigger a Change Event on every Cloud Change (Real-time Observability)
The Data
JSON ←→ Cypher ←→ Graphs
GraphDb (Neo4j) / Neptune / Cypher for representing the cloud (IaC/JSON)
Python & XGBOOST for processing the graph (Graph Neural Network)
The Data Transformation Flow Strategy
Generate JSON from your Cloud
Ask LLM to Build a Cypher “Create Graph” Query or using Python to Generate Cypher from JSON
Store Graph in GraphDb
Train GNN
Embedding
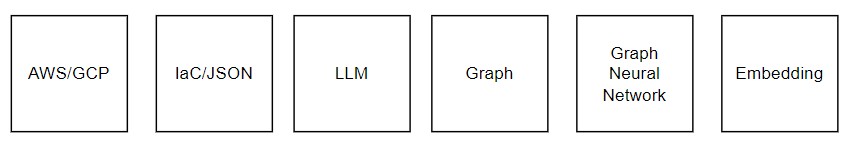
Generate Cloud Graph Map with JSON 2 Cypher using Python (or LLM), Train GNN, and Save Embedding.
The Cloud
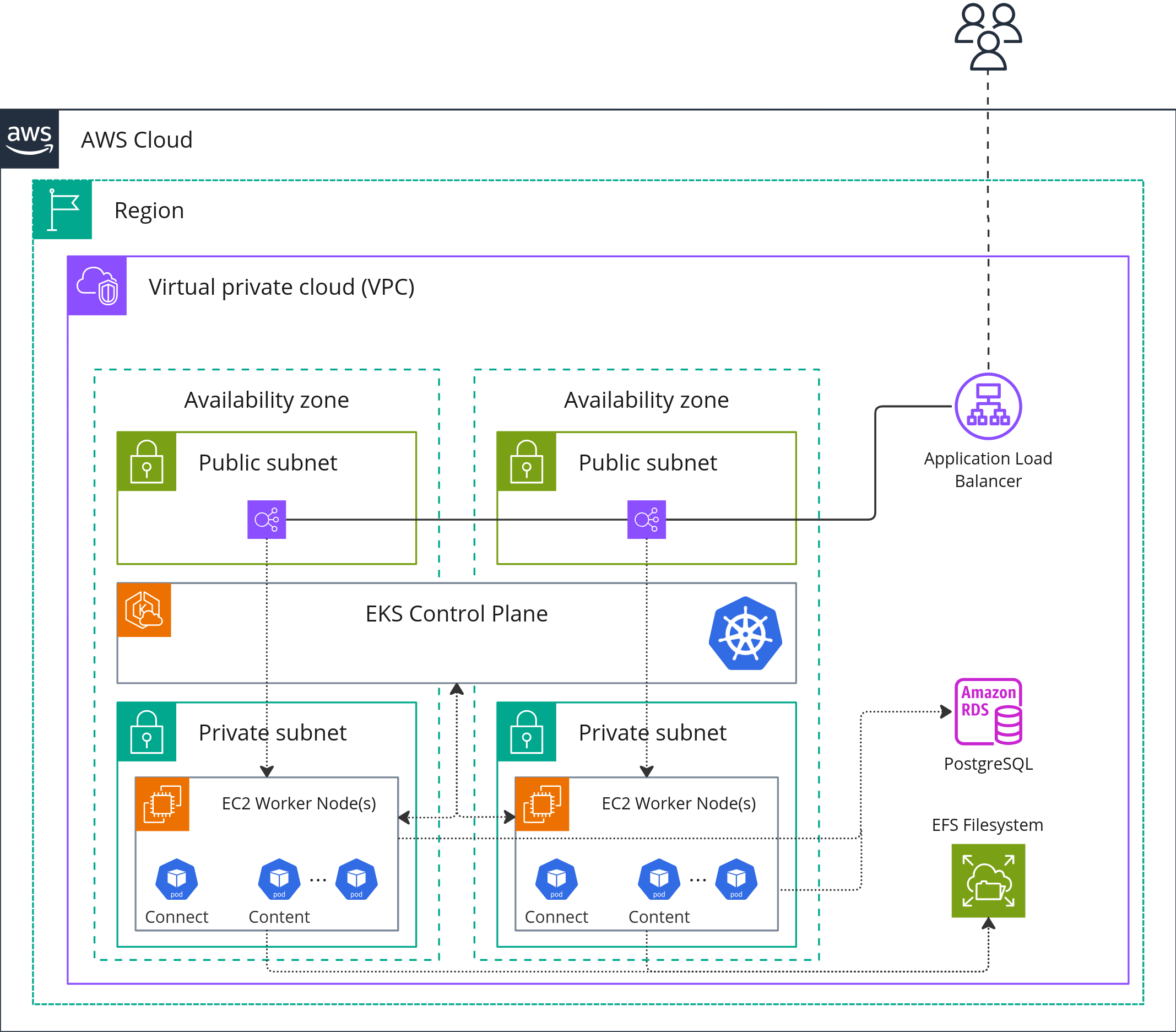
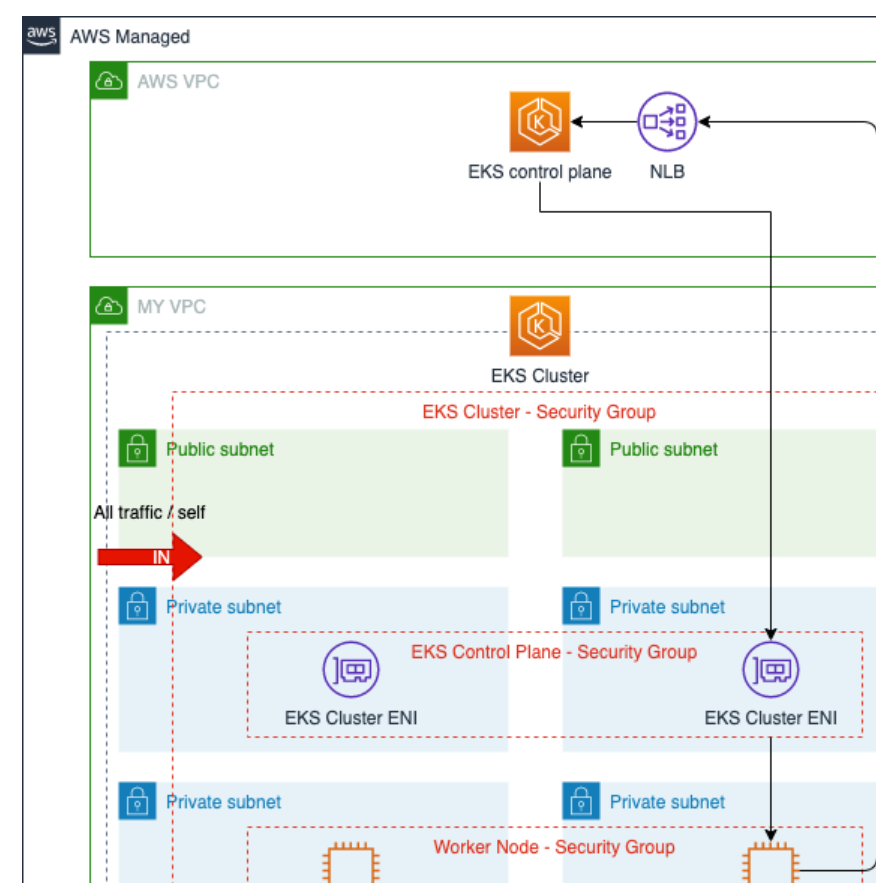
module "vpc" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws"
version = "5.8.1"
name = "education-vpc"
cidr = "10.0.0.0/16"
azs = slice(data.aws_availability_zones.available.names, 0, 3)
private_subnets = ["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24", "10.0.3.0/24"]
public_subnets = ["10.0.4.0/24", "10.0.5.0/24", "10.0.6.0/24"]
enable_nat_gateway = true
single_nat_gateway = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
public_subnet_tags = {
"kubernetes.io/role/elb" = 1
}
private_subnet_tags = {
"kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb" = 1
}
}
The Input: JSON
Search the cloud for JSONS of Policies, IAM Conf, Terraform State File, AWS Describe, AWS List.
{
"nodes": [
{ "id": "UserA", "type": "User" },
{ "id": "UserB", "type": "User" },
{ "id": "AdminRole", "type": "Role" },
{ "id": "CrossAccount", "type": "Role" }
],
"relationships": [
{ "source": "UserA", "target": "s3:ListBucket", "type": "ALLOW" },
{ "source": "UserB", "target": "ec2:StartInstances", "type": "ALLOW" },
{ "source": "AdminRole", "target": "*", "type": "ALLOW" },
{ "source": "CrossAccount", "target": "iam:PassRole", "type": "ALLOW" }
]
}
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"eks:DescribeNodegroup",
"eks:DeleteNodegroup",
"eks:ListClusters",
"eks:CreateCluster"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "eks:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:eks:*:*:cluster/*"
}
]
}
# Example JSON Graph Route of Intruder
json_graph = json.dumps({
"nodes": [
{
"id": "A",
"features": {
"type": "Service",
"externalAccess": true,
"dnsResolved": ["example.com"]
}
},
{
"id": "B",
"features": {
"type": "Service",
"externalAccess": false,
"dnsResolved": []
}
},
{
"id": "C",
"features": {
"type": "Service",
"externalAccess": true,
"dnsResolved": ["api.example.com"]
}
}
],
"edges": [
{
"source": "A",
"target": "B",
"type": "HTTP",
"features": {
"requests": 100,
"blocked": true,
"reason": "NetworkPolicy"
}
},
{
"source": "B",
"target": "C",
"type": "HTTP",
"features": {
"requests": 50,
"blocked": false
}
},
{
"source": "A",
"target": "C",
"type": "HTTP",
"features": {
"requests": 75,
"blocked": false
}
},
{
"source": "external",
"target": "A",
"type": "HTTP",
"features": {
"requests": 200,
"blocked": false
}
},
{
"source": "external",
"target": "C",
"type": "HTTP",
"features": {
"requests": 150,
"blocked": false
}
}
]
}
)
Future Directions: Converting “infrastructure as code” to Graph: Take the terraform State file and Build a Graph.
The Code
Generate Cypher Queries from JSON with Python
def generate_cypher_queries(self) -> List[str]:
"""
Generate Cypher queries to insert the IAM policy into Neo4j.
Returns:
List of Cypher queries for creating nodes and relationships
"""
queries = []
# Create Policy node
policy_props = {
'id': self.policy_id,
'type': 'IAMPolicy',
'version': self.policy.get('Version', '')
}
queries.append(self._create_node_query('AWSPolicy', policy_props))
# Process each statement in the policy
for i, statement in enumerate(self.policy.get('Statement', [])):
statement_id = f"{self.policy_id}_statement_{i}"
# Create Statement node
statement_props = {
'id': statement_id,
'effect': statement.get('Effect', ''),
'position': i
}
queries.append(self._create_node_query('PolicyStatement', statement_props))
# Create relationship between Policy and Statement
queries.append(self._create_relationship_query(
'AWSPolicy', {'id': self.policy_id},
'CONTAINS',
'PolicyStatement', {'id': statement_id}
))
# Process Actions
self._process_actions(statement, statement_id, queries)
# Process Resources
self._process_resources(statement, statement_id, queries)
return queries
def build_aws_policy_graph(policy_json):
"""
Builds a graph from AWS policy JSON, focusing on relationships between resources.
Args:
policy_json (dict): The AWS policy JSON as a dictionary.
Returns:
networkx.Graph: A graph representing the policy relationships.
"""
graph = nx.Graph()
if "Alarms" in policy_json:
for alarm in policy_json["Alarms"]:
alarm_name = alarm.get("AlarmName")
alarm_arn = alarm.get("AlarmARN")
if alarm_name and alarm_arn:
# Add alarm node
graph.add_node(alarm_arn, type="Alarm", name=alarm_name)
# Extract relevant information from ARN (e.g., service, region, account)
arn_parts = alarm_arn.split(":")
if len(arn_parts) >= 6:
service = arn_parts[2]
region = arn_parts[3]
account_id = arn_parts[4]
resource_type_and_name = arn_parts[5].split(":")
# Add service, region, account nodes and edges
graph.add_node(service, type="Service")
graph.add_node(region, type="Region")
graph.add_node(account_id, type="Account")
graph.add_edge(alarm_arn, service, relationship="part_of")
graph.add_edge(alarm_arn, region, relationship="located_in")
graph.add_edge(alarm_arn, account_id, relationship="owned_by")
if len(resource_type_and_name) >= 2:
resource_type, resource_name = resource_type_and_name[0], resource_type_and_name[1]
graph.add_node(resource_type, type="ResourceType")
graph.add_node(resource_name, type="ResourceName")
graph.add_edge(alarm_arn, resource_type, relationship="type")
graph.add_edge(alarm_arn, resource_name, relationship="name")
The Graph: A Use Case
A. HAS_CREDENTIALS_TO
Nodes [ DB, ServiceAccount, KubernetesPod ]
Edges [ HAS_CREDENTIALS_TO, CONNECTS_TO, ASSUMES]
Three nodes representing your AWS cloud components:
A Database node (RDS PostgreSQL)
A ServiceAccount node with ARN details
A KubernetesPod node with cluster information
Three relationships show the connections between them:
The service account HAS_CREDENTIALS_TO the database
The pod CONNECTS_TO the database
The pod ASSUMES the service account (using IAM Roles for Service Accounts)
// Create nodes for AWS cloud components
CREATE (db:Database {
name: 'aws-database-1',
type: 'RDS',
engine: 'PostgreSQL',
version: '13.4',
region: 'us-west-2',
instanceType: 'db.m5.large'
})
CREATE (sa:ServiceAccount {
name: 'app-service-account',
arn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/app-service-account',
created: datetime('2025-01-15'),
managed_by: 'Terraform'
})
CREATE (pod:KubernetesPod {
name: 'app-backend-pod',
namespace: 'production',
clusterName: 'eks-cluster-01',
region: 'us-west-2',
image: 'app-backend:v1.3.2',
status: 'Running'
})
// Create relationships between nodes
CREATE
(sa)-[:HAS_CREDENTIALS_TO {
accessType: 'read-write',
credentialType: 'IAM Role',
expiryDate: datetime('2025-12-31')
}]->(db),
(pod)-[:CONNECTS_TO {
protocol: 'TCP',
port: 5432,
encrypted: true,
connectionPoolSize: 10
}]->(db),
(pod)-[:ASSUMES {
method: 'IRSA',
configuredOn: datetime('2025-02-01')
}]->(sa);
The Unit Testing
test_detect_misconfigurations
test_privilege_escalation_paths
test_anomaly_detection
import unittest
class TestIAMPolicySecurity(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
"""Setup a sample IAM policy graph."""
self.iam_graph = {
"UserA": {"Allow": ["s3:ListBucket"], "Deny": []},
"UserB": {"Allow": ["ec2:StartInstances"], "Deny": []},
"AdminRole": {"Allow": ["*"], "Deny": []}, # Potential Privilege Escalation
"CrossAccount": {"Allow": ["iam:PassRole"], "Deny": []}, # Cross-account risk
}
def test_detect_misconfigurations(self):
"""Check for overly permissive policies."""
for entity, permissions in self.iam_graph.items():
with self.subTest(entity=entity):
self.assertNotIn("*", permissions["Allow"], f"{entity} has overly permissive access")
def test_privilege_escalation_paths(self):
"""Detect privilege escalation risks."""
risky_permissions = ["iam:PassRole", "iam:CreatePolicyVersion"]
for entity, permissions in self.iam_graph.items():
with self.subTest(entity=entity):
self.assertFalse(any(p in permissions["Allow"] for p in risky_permissions),
f"{entity} can escalate privileges")
def test_anomaly_detection(self):
"""Identify unexpected permission changes."""
known_safe = {
"UserA": {"Allow": ["s3:ListBucket"], "Deny": []},
"UserB": {"Allow": ["ec2:StartInstances"], "Deny": []},
}
for entity, permissions in self.iam_graph.items():
with self.subTest(entity=entity):
if entity in known_safe:
self.assertEqual(permissions, known_safe[entity],
f"Unexpected permission change detected for {entity}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
The Future: Cloud Graph Neural Network for XDR
From Graphs to ML Model: Graph to XGBOOST Searches
Converting the Graph and training a Neural Network based on the Weights between the nodes/edges can detect an anomaly of an intruder.
Tokenization of Graphs shouldn’t be different from Tokenization of Text in LLMs. So, why not train a GNN yourself based on your SIEM data in your ElasticSearch/OpenSearch?
Graph Representation: Input graph as JSON (nodes, edges, features).
Feature Extraction: Convert nodes/edges into a feature matrix.
XGBoost Model: Train on past traversal data (or heuristically assign edge weights).
Search Algorithms: Use XGBoost predictions as weights for Dijkstra/A*.
The detection of an anomaly could be when there’s a new Edge HAS_CREDENTIALS of a new Pod to a Database which never before existed.
import json
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
from queue import PriorityQueue
class XGBoostGraphSearch:
def __init__(self, json_graph):
"""
Initialize the graph from a JSON representation.
"""
self.graph = self.load_graph(json_graph)
self.model = None # XGBoost model for edge weighting
def load_graph(self, json_graph):
"""
Load a JSON graph representation into a NetworkX graph.
"""
G = nx.DiGraph() # Directed Graph
data = json.loads(json_graph)
# Add nodes
for node in data["nodes"]:
G.add_node(node["id"], **node["features"])
# Add edges
for edge in data["edges"]:
G.add_edge(edge["source"], edge["target"], type=edge["type"], **edge["features"])
return G
def extract_features(self):
"""
Convert graph edges into feature vectors for XGBoost.
"""
X, y = [], []
for u, v, attr in self.graph.edges(data=True):
# Example features: edge type (one-hot), node degrees, custom attributes
feature_vector = [
self.graph.degree[u], # Source node degree
self.graph.degree[v], # Target node degree
int(attr.get("type", 0)), # Edge type (assume integer encoding)
attr.get("weight", 1) # Default weight
]
X.append(feature_vector)
y.append(attr.get("target_score", 1)) # Supervised label (if available)
return np.array(X), np.array(y)
def train_xgboost(self):
"""
Train an XGBoost model on the extracted graph features.
"""
X, y = self.extract_features()
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X, label=y)
params = {
"objective": "reg:squarederror",
"max_depth": 3,
"learning_rate": 0.1,
"n_estimators": 100
}
self.model = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_boost_round=10)
def predict_edge_weights(self):
"""
Use the trained XGBoost model to assign edge weights.
"""
if not self.model:
raise ValueError("Model not trained. Call train_xgboost() first.")
X, _ = self.extract_features()
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X)
predicted_weights = self.model.predict(dtest)
# Assign predicted weights to edges
for i, (u, v, _) in enumerate(self.graph.edges(data=True)):
self.graph[u][v]["weight"] = predicted_weights[i]
def bfs(self, start, goal):
"""
Breadth-First Search (BFS) to find the shortest path.
"""
queue = [(start, [start])]
visited = set()
while queue:
node, path = queue.pop(0)
if node in visited:
continue
visited.add(node)
if node == goal:
return path
for neighbor in self.graph.neighbors(node):
queue.append((neighbor, path + [neighbor]))
return None
def dijkstra(self, start, goal):
"""
Dijkstra’s Algorithm using XGBoost-predicted weights.
"""
self.predict_edge_weights()
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.put((0, start, [start])) # (cost, node, path)
visited = {}
while not pq.empty():
cost, node, path = pq.get()
if node in visited and visited[node] <= cost:
continue
visited[node] = cost
if node == goal:
return path
for neighbor in self.graph.neighbors(node):
weight = self.graph[node][neighbor].get("weight", 1)
pq.put((cost + weight, neighbor, path + [neighbor]))
return None
def a_star(self, start, goal, heuristic=lambda x, y: 0):
"""
A* Search using XGBoost-predicted weights and heuristic.
"""
self.predict_edge_weights()
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.put((0, start, [start]))
g_scores = {start: 0}
while not pq.empty():
_, node, path = pq.get()
if node == goal:
return path
for neighbor in self.graph.neighbors(node):
weight = self.graph[node][neighbor].get("weight", 1)
new_g = g_scores[node] + weight
f_score = new_g + heuristic(node, neighbor)
if neighbor not in g_scores or new_g < g_scores[neighbor]:
g_scores[neighbor] = new_g
pq.put((f_score, neighbor, path + [neighbor]))
return None
# Usage
graph_search = XGBoostGraphSearch(json_graph)
graph_search.train_xgboost() # Train the model
print(graph_search.dijkstra("A", "C")) # Find the best path
Summery
In this blog post, I have tried to lay out the core flow, data types, structures, functions, ontologies, architecture, and potentialities of developing a cyber product with graphs and AI in mind while taking into consideration the idea that we are looking for intruders by the event-driven changes in the cloud.
About the Author
I am a cyber security researcher, DevOps, python developer, data scientist, AI Engineer and Machine Learning Architect.
Further Investigation & Related Resources:
https://github.com/cilium/hubble
https://distill.pub/2021/gnn-intro/
https://blog.kuzudb.com/post/unstructured-data-to-graph-baml-kuzu/
https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/cybersecurity-mesh
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Amit Sides directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Amit Sides
Amit Sides
Amit Sides is a AI Engineer, Python Backend Developer, DevOps Expert, DevSecOps & MLOPS GITHUB https://github.com/amitsides