Text Analysis
 Swati Verma
Swati Verma
1. wc
It is used to count the number of lines, words, and characters (bytes) in a text file. Its name stands for "word count”.
file1.txt
wc file-name
To check lines only
wc -l
2.sort
sort fileName
It sorted the capital letters and the small letters separately
3. uniq
It is used to filter out or report duplicate lines in a sorted file. It's often used in combination with the sort command because uniq only removes adjacent duplicate lines.
4. How to split and combine the files
- Combine: cat file1.txt file2.txt > combined.txt
Split
The
splitcommand is used to divide large files into smaller chunks based on lines, size, or custom patterns. It is useful for handling large logs, datasets, or files that need to be processed in parts.split -l 1 file-name1 -> number of lines
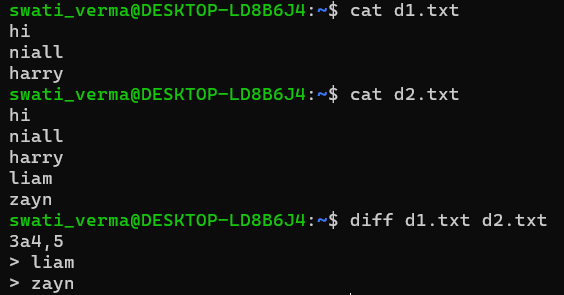
5. diff
diff [options] file1 file2
6.Cut
cut Command – Extract Specific Columns
The cut command is used to extract specific sections of each line from a file based on bytes, characters, or fields.
Use Cases
Extract Specific Columns (
-f)cut -f1,3 data.txt- Extracts columns 1 and 3 from a tab-separated file.
Specify a Delimiter (
-d)cut -d',' -f2 data.csvExtracts the 2nd column from a CSV file (comma
,as delimiter).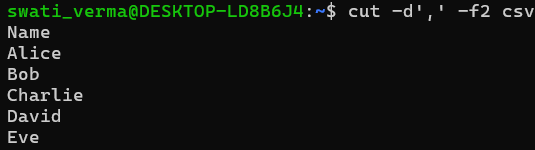
Extract First 5 Characters (
-c)cut -c1-5 file.txt- Prints the first 5 characters of each line.
Extract First Two Words (Space as Delimiter)
cut -d' ' -f1,2 file.txt- Extracts the first and second word from each line.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Swati Verma directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Swati Verma
Swati Verma
Growing in DevOps, together! 🤝 | Associate Software Engineer at Tech Mahindra | Enthusiastic about automation, cloud solutions, and efficient software delivery. | Let's connect, collaborate, and learn from each other!