Day - 3 | Exploring Data Transformation with Google Cloud
 Aditya Khadanga
Aditya Khadanga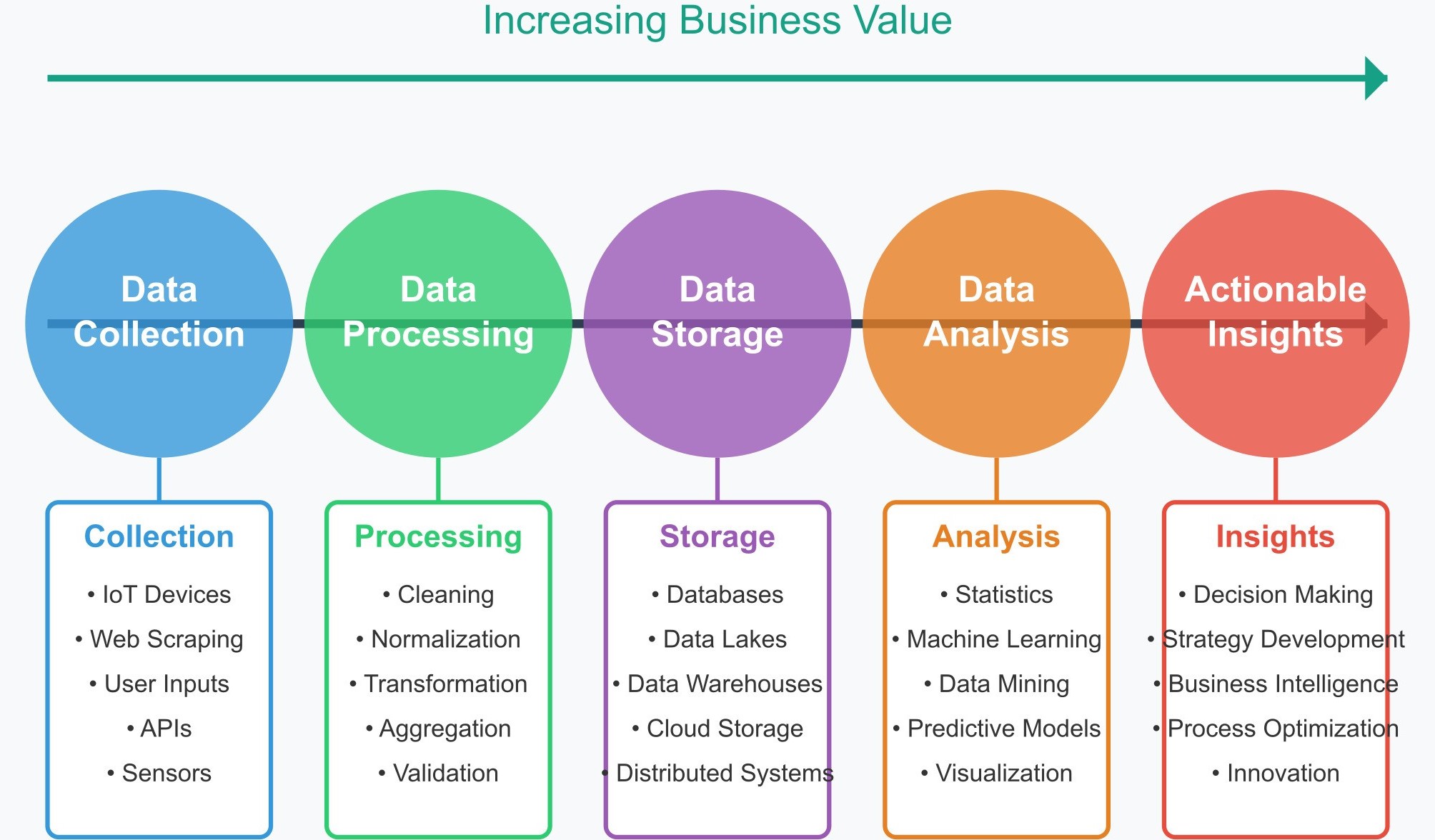
In today's digital age, data is the lifeblood of business. Capturing, managing, and extracting value from data is paramount to redefining customer experiences and driving innovation across industries. Whether it's understanding customer behavior, optimizing operations, or developing new products, data is the key. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of data transformation with Google Cloud, exploring fundamental concepts and practical applications.
The Value of Data: From Raw Information to Actionable Insights
Data comes in various forms, from structured financial spreadsheets to unstructured social media posts. While some data is easily accessible, others require sophisticated tools and techniques for extraction. The goal is to transform raw data into actionable insights that can drive strategic decisions.
Understanding Data Types
To effectively manage data, it's essential to understand its different categories:
Structured Data
Organized in a tabular format with rows and columns, like a spreadsheet or database.
Easily searchable and analyzable.
Example: Financial transactions, customer demographics in a CRM.
Semi-Structured Data
Falls between structured and unstructured, with some organizational hierarchy.
Examples: JSON, XML, HTML files.
Useful for data exchange.
Unstructured Data
Lacks a predefined data model and isn't organized in a traditional format.
Examples: Images, audio files, videos, social media posts.
Requires advanced tools for analysis.
Unlocking Business Value from Data
Imagine a marketing team analyzing social media posts to gauge customer sentiment towards a brand. This is an example of extracting value from unstructured data.
Cloud tools like Google Cloud's Vision API, which uses machine learning, can analyze images to detect and label objects. This turns unstructured image data into structured, actionable information.
By leveraging APIs, and Machine Learning, any unstructured data can be turned into structured data.
Data Management Concepts
Google Cloud offers a range of data management solutions:
Relational Databases
Store data in tables with defined relationships.
Examples: Cloud SQL, Spanner.
Good for transactional data.
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
Offer flexible data models for various data types.
Examples: Datastore, Bigtable.
Good for high volume, and flexible data.
Data Warehouses
Centralized repositories for structured data, optimized for analysis.
Example: BigQuery.
Good for business intelligence.
Data Lakes
Store vast amounts of raw data in various formats.
Example: Cloud Storage.
Good for data exploration and experimentation.
Data Warehouses vs. Data Lakes:
These are complementary tools.
Data warehouses are used by business intelligence analysts for structured data insights.
Data lakes are used by data engineers and scientists for raw data exploration and experimentation.
The Role of Data in Digital Transformation
Organizations have access to unprecedented amounts of data, both internal (first-party) and external (second and third-party).
First-party data: data collected directly from your customers.
- Example: web site activity.
Second-party data: First party data from another trusted source.
- Example: Data shared from a business partner.
Third-party data: Data purchased from outside sources.
- Example: Market research data.
Google Cloud Marketplace provides access to third-party data.
The Data Value Chain
The data value chain involves transforming raw data into actionable insights.
It includes data collection, storage, processing, analysis, and visualization.
The optimal value chain evolves as technologies and business needs change.
NoSQL for fast read/write, Data warehousing for quick analysis, and Object storage for unstructured data, all play a role in the value chain.
Data Governance
Data governance involves establishing policies and procedures for data management.
It ensures data quality, security, and compliance.
It builds trust with customers and partners.
It protects sensitive data from unauthorized access.
It helps organizations remain compliant with regulations.
Conclusion
Data transformation is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age. Google Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of tools and services to help organizations capture, manage, and extract value from their data. By understanding data types, data management concepts, and the importance of data governance, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data and drive meaningful innovation.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aditya Khadanga directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aditya Khadanga
Aditya Khadanga
A DevOps practitioner dedicated to sharing practical knowledge. Expect in-depth tutorials and clear explanations of DevOps concepts, from fundamentals to advanced techniques. Join me on this journey of continuous learning and improvement!