Tutorial on Real Estate Investment App
 Saurav Bhowmick
Saurav Bhowmick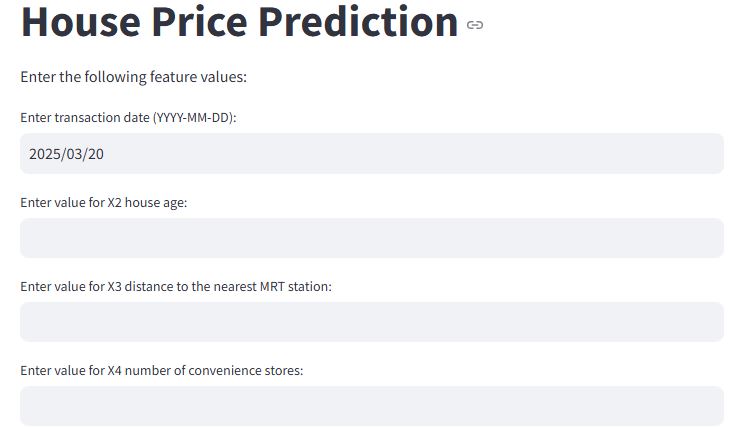
Building a House Price Prediction App with Streamlit and Bagging Regressor
Predicting house prices is a popular problem in the real estate industry, and machine learning can provide valuable insights. In this tutorial, we’ll build an interactive web app using Streamlit and Bagging Regressor from Scikit-Learn to predict house prices based on real estate data.
Step 1: Install the Required Libraries
Before we start coding, ensure you have the required libraries installed. You can install them using pip:
pip install streamlit pandas numpy scikit-learn
Step 2: Load and Preprocess the Data
We will use real estate data from a public dataset available on GitHub. Let’s load it using Pandas:
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import datetime
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Load the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tushuli396/Real-estate-investment/refs/heads/main/data/Real-estate.csv")
df = data
# Convert transaction timestamp
df['X1 transaction timestamp'] = pd.to_datetime(df['X1 transaction date'], unit='s')
df.set_index('X1 transaction timestamp', inplace=True)
# Feature engineering
df['day_of_year'] = df.index.dayofyear
df['time_of_day'] = df.index.hour + df.index.minute / 60
# Select features and target variable
features = df.drop(columns=['No', 'day_of_year', 'time_of_day', 'Y house price of unit area'])
target = df['Y house price of unit area']
# Split the data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, target, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Standardize features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Train Bagging Regressor
model = BaggingRegressor(random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
Step 3: Create the Streamlit App
Now, let’s build the Streamlit web app to make predictions interactively.
# Streamlit UI
st.title("House Price Prediction")
st.write("Enter the following feature values:")
# Convert input date to fractional year
def convert_to_fractional_year(date):
year = date.year
start_of_year = pd.Timestamp(f'{year}-01-01')
next_year = pd.Timestamp(f'{year + 1}-01-01')
fraction = (date - start_of_year).days / (next_year - start_of_year).days
return year + fraction
# User input for transaction date
transaction_date_input = st.date_input("Enter transaction date (YYYY-MM-DD):")
transaction_date_fractional = convert_to_fractional_year(pd.to_datetime(transaction_date_input))
# User input for other features
feature_names = ['X2 house age',
'X3 distance to the nearest MRT station',
'X4 number of convenience stores', 'X5 latitude', 'X6 longitude']
input_data = [transaction_date_fractional]
for feature in feature_names:
value = st.text_input(f"Enter value for {feature}:", "")
input_data.append(value)
# Predict button
if st.button("Predict"):
try:
input_data = [float(val) for val in input_data]
except ValueError:
st.error("Please enter valid numeric values for all features.")
st.stop()
input_data_scaled = scaler.transform([input_data])
prediction = model.predict(input_data_scaled)
st.success(f"Predicted House Price: {prediction[0]:.2f}")
# Display location on map
latitude = input_data[4]
longitude = input_data[5]
map_data = pd.DataFrame({'lat': [latitude], 'lon': [longitude]})
st.map(map_data)
Step 4: Run the Streamlit App
To launch the Streamlit app, save the script as app.py and run:
streamlit run app.py
This will open a local web app where you can enter feature values and get a house price prediction.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we built a machine learning-powered house price prediction web app using Streamlit and Bagging Regressor. This is a great starting point for exploring real estate price predictions, and you can improve it by using different models, adding more features, or optimizing hyperparameters. 🚀
If you found this tutorial helpful, don’t forget to share it with fellow data enthusiasts! 😊
Also, you can check the app here: https://real-estate-prediction-app-by-tas.streamlit.app/
Happy coding!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Saurav Bhowmick directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Saurav Bhowmick
Saurav Bhowmick
👋 Hey there! I'm Saurav Bhowmick 💡 Passionate about web development, open-source, and data science, I love turning ideas into impactful projects. I specialize in frontend & backend development, working with modern technologies to create seamless digital experiences. 🚀 Currently built Portfolio and exploring time series forecasting (ARIMA models). 📝 Sharing insights on coding, software engineering, and tech trends. Follow along for tips, tutorials, and deep dives into development!