Cyber Security (Day-1)
 Balaji Patil
Balaji PatilWHAT IS CYBER SECURITY?
Cyber security is the practice of defending computer system, networks, and data from malicious attacks and unauthorized access.
It involves a range of of techs, processes and practices designed to protect sensitive info, maintain data integrity and ensure the availability of digital resources.
THIS INCLUDES :-
Firewalls
Encryption
Intrusion detection system
Antivirus software
Security policies
Conducting regular venerability assessments
Educating the users to prevent from common threats like phishing and social engineering
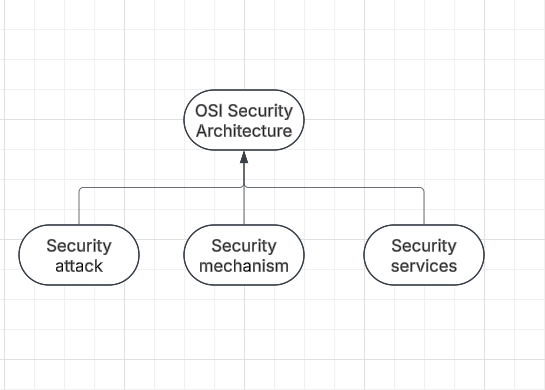
OSI Security (Open system interconnection)
It is a set of protocols, standards, and techniques used to ensure the security of the data and communication in a network environment based on OSI model. The international organization for standardization (ISO) established by model to provide a framework how different network protocol interact with layered architecture.
Security Attack
Security attack is an attempt by a person or a entity to gain unauthorized access to disrupt or compromise the security of a system, network or device. These are defined as actions that put at risk an organization’s safety.
They are further classified into 2 categories
Passive attack :- Attack in which third party intruder tries to access the message/ content / Data being shared by sender and receiver by keeping a close watch on the transmission or eave-dropping the transmission is called passive attack.
— Focuses on gathering information rather then direct attack.
— Neither the sender nor the receiver has any clue about the attack making it risky.
Passive attack is further divided into 2 sub-categories
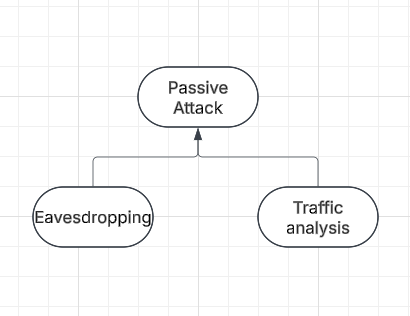
Eaves-dropping
— Involves the attacker intercepting and listening to communication based on their behaviour between 2 or more parties
— can be performed by techniques such as packet sniffing, middle- in - midde attack
Packet Sniffing :- The act of caputering data packets across the computer network is called packet sniffing
IT TRACKS : Who is the sender
Who is the reciver
What you download
Sites you visit
What you looked on the website
Download from the site
Streaming events like videos, audios, etc.
Traffic analysis
This involves the attacker analyzing network traffic patterns and metadata to gather information about the system, network or device. Here intruder cant read the message but only understand the pattern and length of encryption. Traffic analysis can be performed using a variety of techniques such as network flow analysis or protocol analysis.
Active Attacks :- Refers to types of attacks that involves the attacker actively disrupting or altering system, network or device activity. Active attacks are typically focused on causing damage or disruption rather than gathering information
— The message transmitted dosen’t remain in usual form and shows deviation form its original behavior
— It is dangerous as now sender or receiver does not know if the message or information they are receiving are by the original or has been altered somewhere in between.
Types of Active Attacks
Masquerade: This is a type of attack in which the attacker pretends to be an authentic sender in order to gain unauthorized access to a system.
Replay: A type of attack in which the attacker intercepts a transmitted message through a passive channel and then maliciously or fraudulently replays or delays it at a later time.
Modification of message: Attacker modifying the transmitted message and making the final message received by the receiver look like its not safe or non- meaningful. This type of attack can be used to manipulate the content of the message or to disrupt the communication process.
Denial of service: The attacker sending a large volume of traffic to a system network, or device in an attempt to overwhelm it and make it unavailable to user.
Security mechanism
The mechanism that is built to identify any breach of security or attack on the organization is called a security mechanism. These are also responsible for protecting a system, network, or device against unauthorized access, tempering or other security threats
Encryption: Involves the use of algorithm to transform data into a form that can only be read by someone with the appropriate decryption key. encryptions can be used to protect data in it transmitted over a network, or to protect data when it is stored on a device.
Digital padding : This is a security mechanism that involves the use of cryptography techniques to create a unique, verifiable identifier for digital document or message.
Traffic padding: This is a technique used to add data to a network traffic stream in an attempt to obscure the true content of the traffic and make it more difficult to analyze.
Routing control: Allows the selection of specific physically secure router for specific data transmission and enables routing changes particularly when a gap in security is suspected.
Security service
Refers to the different services available for maintaining the security and safety of an organization. They help in preventing any potential risks to security.
Security services are divided into 5 categories
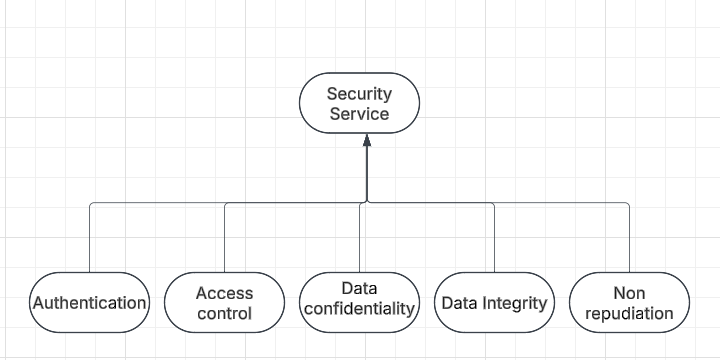
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device in order to grant or deny access to a system or device.
Access Control involves the use of policies and procedures to determine who is allowed to access specific resources within a system.
Data Confidentiality is responsible for the protection of information from being accessed or disclosed to unauthorized parties.
Data Integrity is a security mechanism that involves the use of techniques to ensure that data has not been tampered with or altered in any way during transmission or storage.
Non-repudiation involves the use of techniques to create a verifiable record of the origin and transmission of a message which can be used to prevent the sender from denying that they sent the message.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Balaji Patil directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
