Which AI Should You Use to Prep for Your AP Exam?
 Shawn Sullivan
Shawn SullivanTable of contents
- TLDR – Best AI Models for AP Test Prep
- Choosing the Right AI for AP Test Prep
- AI isn’t Designed to Take AP Exams
- What You’ll Learn
- How We Tested the AIs
- AP Biology: AI Model Recommendation
- AP U.S. History: AI Model Recommendation
- AP World History Modern: AI Model Recommendation
- So is Any AI Model OK to Use for AP Test Prep?
- Sneak Peek: Incept Outperforms Every Other Model
- Final Takeaways

We Tested the Top Models So You Don’t Have To!
TLDR – Best AI Models for AP Test Prep
If you just want the recommendations, here they are:
🧬 AP Biology → Use LearnLM (don’t miss Google’s prompt recommendations!)
🏛️ AP U.S. History → Use LearnLM
🌍 AP World History: Modern → Use Gemini 2.0 Flash
🌀 Other AP Subjects → Experiment with LearnLM, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and Claude Sonnet 3.7
Want to know why these are the best? Keep reading—we tested them all and have the benchmarks to prove it.
Choosing the Right AI for AP Test Prep
You might think all the AI models out there are more or less all equally helpful for getting ready for your AP exam. ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok. Whatever. Ask them to help you prep for an AP test, and they’ll happily quiz you on topics literally forever. But if you dig into what these models actually do, you’ll discover some are much better than others — and the ones that are bad are really, really bad.
In this article, you’ll learn which models work best for AP test prep, why the best models are the best, and how you can pick the right path to use AI to get that 5 on your AP exam.
AI isn’t Designed to Take AP Exams
Most AI models aren’t built to help you ace an AP test! They are generalists who give a great impression of knowing how to help, but fall short in reality.
If you're prepping for an AP exam, you’ve probably turned to an AI model like ChatGPT, Claude, or Grok for help. Some of the answers seem useful. Others are way off. And unless you're already an expert, it's hard to tell which is which.
That’s where EduBench comes in.
EduBench is the first benchmarking system built to evaluate how well AI models actually help students learn, not just how fluent or confident their answers appear. In this post, we used EduBench to test leading AI models on one very specific task: creating high-quality AP-style quizzes.
What You’ll Learn
This post will show you:
Which AI model is best for AP Biology, AP U.S. History, AP World History: Modern, and other AP subjects
What a great quiz looks like—and what a terrible one looks like
A sneak peek at Incept, our upcoming model that outperforms everything else
A comprehensive option if you want a real AI-powered AP test prep platform, not just raw models
Whether you're a student trying to self-study or a teacher looking for the best tools, this is your evidence-based guide to choosing the right AI.
How We Tested the AIs
The Two Benchmark Scores That Matter Most for AP Students
To make our recommendations, we used the EduBench Quiz Composition benchmark—a structured evaluation that measures the quality of AI-generated multiple-choice quizzes in five areas (benchmarks for other AP exam components like free-response questions coming soon!).
For AP test prep, two of those benchmarks matter most:
Concept Coverage: Does the AI give you quizzes that review the most important topics and ideas from the course? A high score here means the AI hits more of the content you'll actually be tested on.
Standardized Testing Preparedness: Does the AI make quizzes that look and feel like the real AP test? This benchmark checks for question format, cognitive demand, distractor quality, and how closely the AI mimics the real AP exam style.
Both benchmarks are scored on a scale of 0-5, with 0 meaning the AI is essentially useless and 5 meaning it is as good as the best human tutors. Together, these benchmarks tell us how well each model can help you study smarter and score higher—not just memorize trivia or regurgitate surface-level facts.
AP Biology: AI Model Recommendation
Best Model: LearnLM (Runner Up: Gemini 2.0 Flash)
Why LearnLM wins: Strongest combined performance on both Concept Coverage and Standardized Testing Preparedness
If you’re using AI to prep for AP Biology, LearnLM is the winner. That said, none of the tested models performed amazingly well for AP Biology.
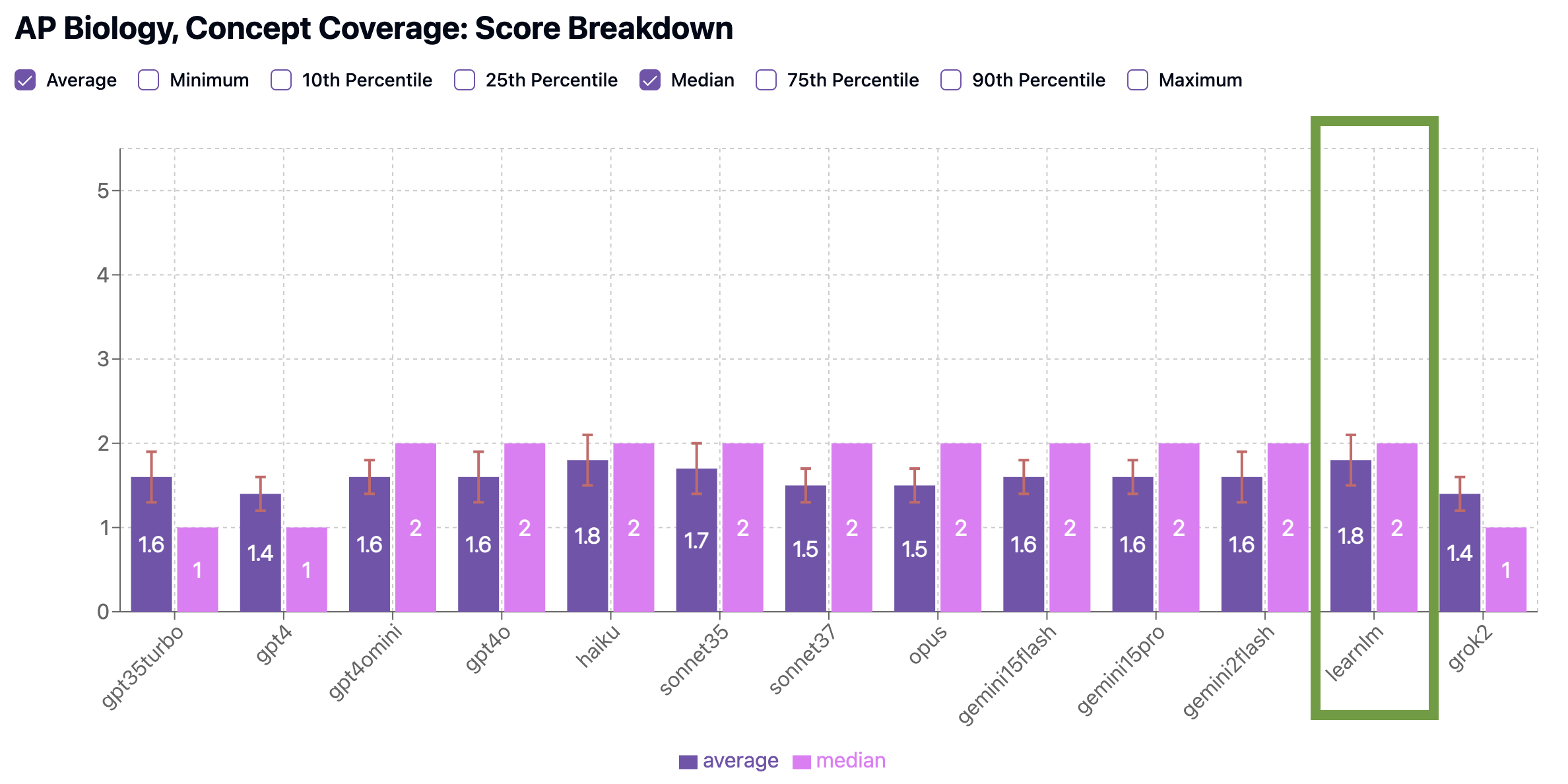
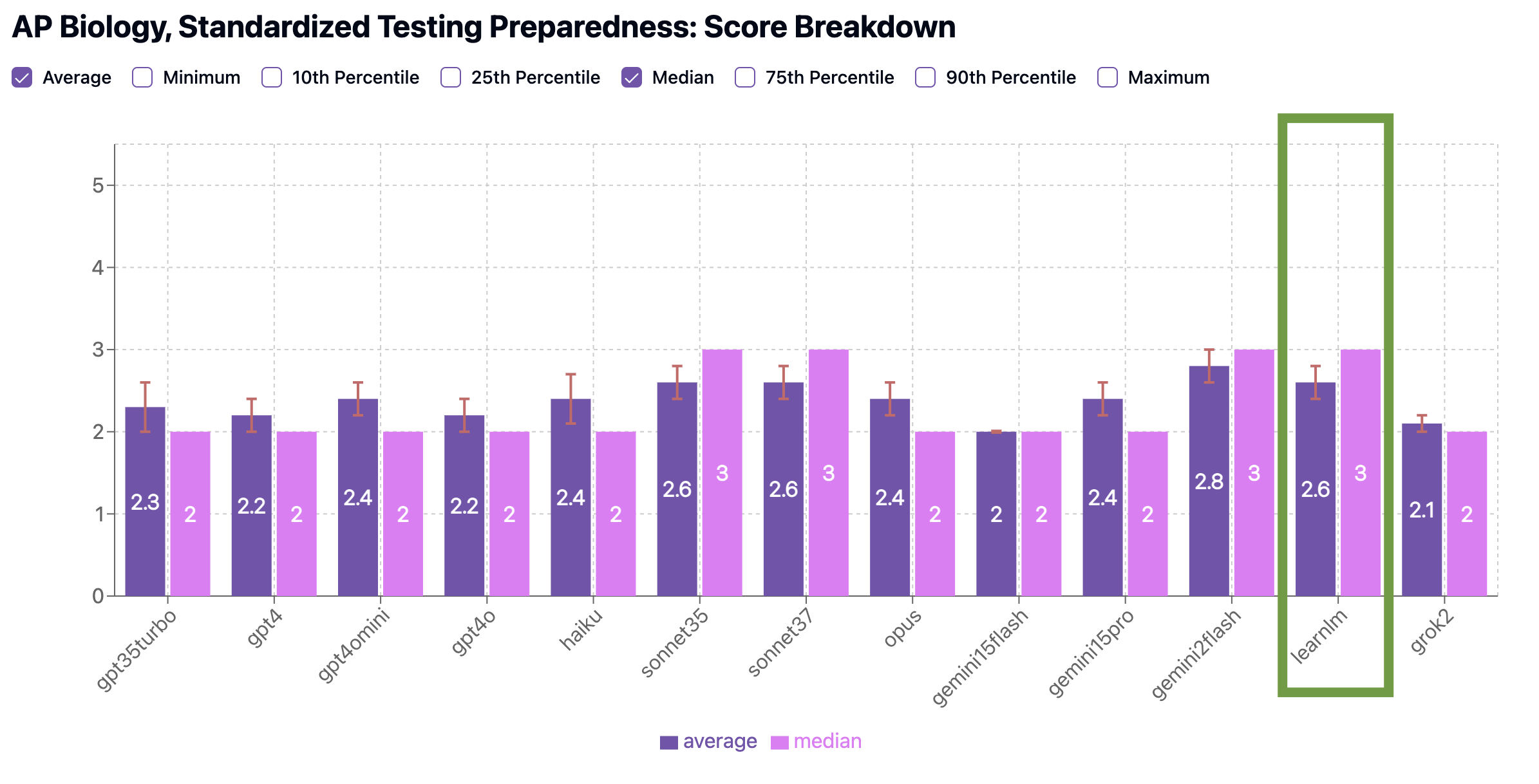
In our benchmarks, LearnLM scored the highest in Concept Coverage (1.8 average, tied with Claude Haiku 3.5), meaning its quizzes included broadest, most representative range of key topics—everything from cell structure to gene expression to natural selection.
LearnLM also performed second-best (2.6 average, behind Gemini 2.0 Flash’s 2.8 average) in Standardized Testing Preparedness, generating questions that closely resemble those you’ll see on the AP exam in both style and difficulty. It’s worth noting however that more of Gemini 2.0 Flash’s quizzes scored a 3 (70%) or 4 (5%) than LearnLM’s quizzes (60% 3, 0% 4).
Nonetheless, taken together, LearnLM gets a slight edge over runner-up Gemini 2.0 Flash, especially if you use Google’s prompt recommendations for even better, personalized results.
Benchmark Scores: AP Biology
We scored each model on two criteria: how well it covers key concepts (Concept Coverage), and how closely its quizzes resemble real AP exams (Standardized Testing Preparedness).
Concept Coverage Benchmark
Standardized Testing Preparedness Benchmark
Example: LearnLM AP Biology Quiz
Here’s a sample quiz generated by LearnLM on Population Genetics, Topic 7.4 in the AP Biology curriculum:
AP Biology Quiz: Population Genetics (Topic 7.4)
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each multiple-choice question.
1. Which of the following best describes a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
(A) A population undergoing natural selection.
(B) A small population with significant gene flow.
(C) A large population with random mating and no mutations.
(D) A population experiencing a bottleneck event.
Answer: (C)2. The Hardy-Weinberg equation, p² + 2pq + q² = 1, is used to:
(A) Predict the rate of mutations in a population.
(B) Calculate allele and genotype frequencies in a population.
(C) Determine the rate of gene flow between populations.
(D) Measure the fitness of individuals in a population.
Answer: (B)3. Which factor is MOST likely to disrupt Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and cause evolution to occur?
(A) Random mating
(B) Large population size
(C) Natural selection
(D) Lack of mutations
Answer: (C)4. In a population of 1000 individuals, 490 are homozygous dominant (AA), 420 are heterozygous (Aa), and 90 are homozygous recessive (aa). What is the frequency of the dominant allele (A)?
(A) 0.3
(B) 0.49
(C) 0.7
(D) 0.98
Answer: (C)5. Genetic drift is most likely to affect which type of population?
(A) Large populations
(B) Populations with high gene flow
(C) Small populations
(D) Populations in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Answer: (C)6. The founder effect is a specific example of:
(A) Gene flow
(B) Genetic drift
(C) Natural selection
(D) Mutation
Answer: (B)7. Gene flow tends to:
(A) Increase genetic variation within a population.
(B) Decrease genetic variation within a population.
(C) Increase genetic differences between populations.
(D) Decrease genetic differences between populations.
Answer: (D)8. Which of the following mechanisms of evolution consistently leads to adaptive evolution?
(A) Gene flow
(B) Genetic drift
(C) Mutation
(D) Natural selection
Answer: (D)9. A population bottleneck can lead to:
(A) Increased genetic diversity.
(B) Reduced genetic diversity.
(C) No change in genetic diversity.
(D) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Answer: (B)10. Sexual selection can result in:
(A) Traits that increase survival but decrease reproductive success.
(B) Traits that decrease survival but increase reproductive success.
(C) Traits that increase both survival and reproductive success.
(D) No change in allele frequencies.
Answer: (B)
This quiz received a score of 3 for both Concept Coverage and Standardized Testing Preparedness, with the following explanations:
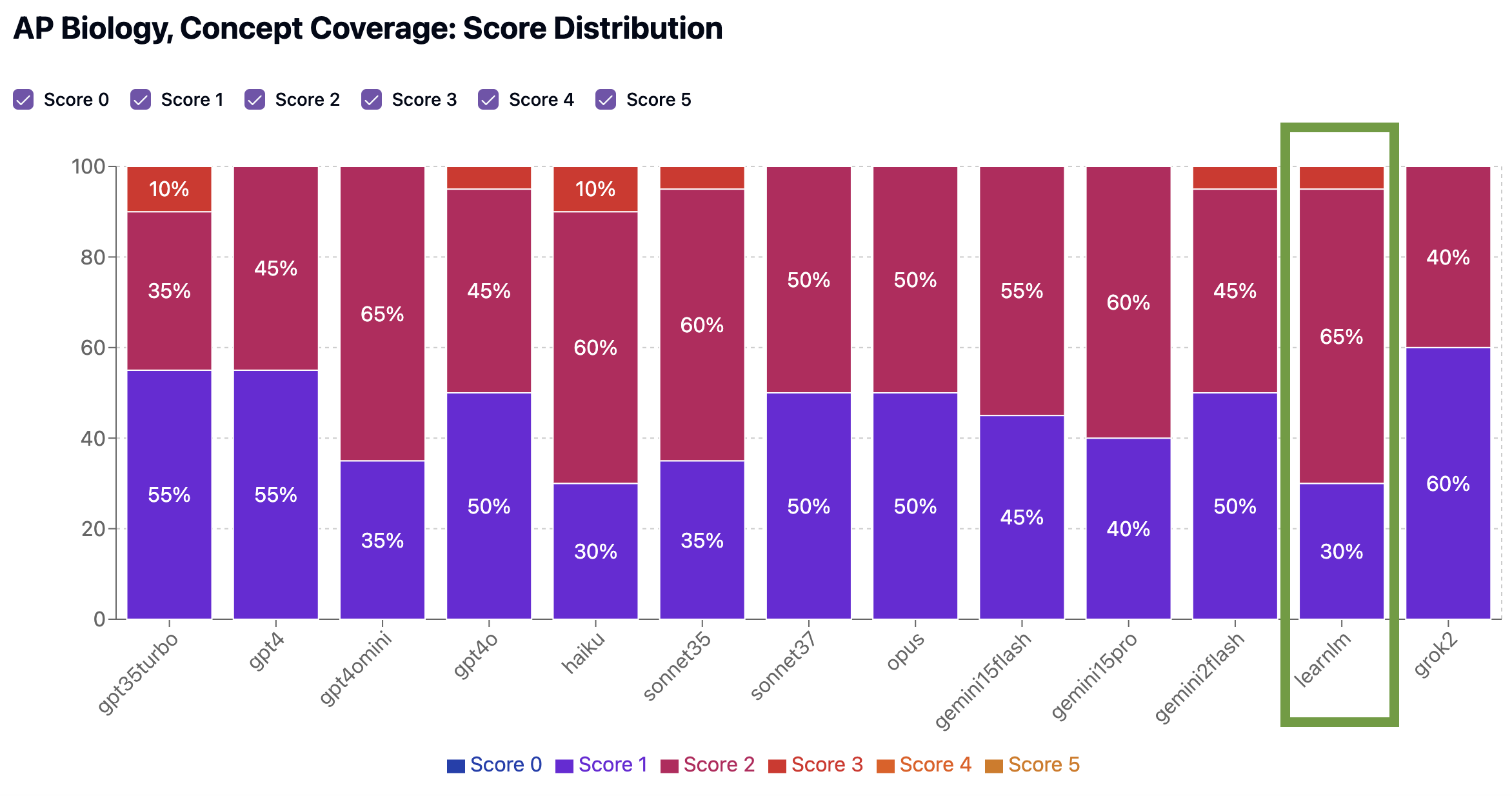
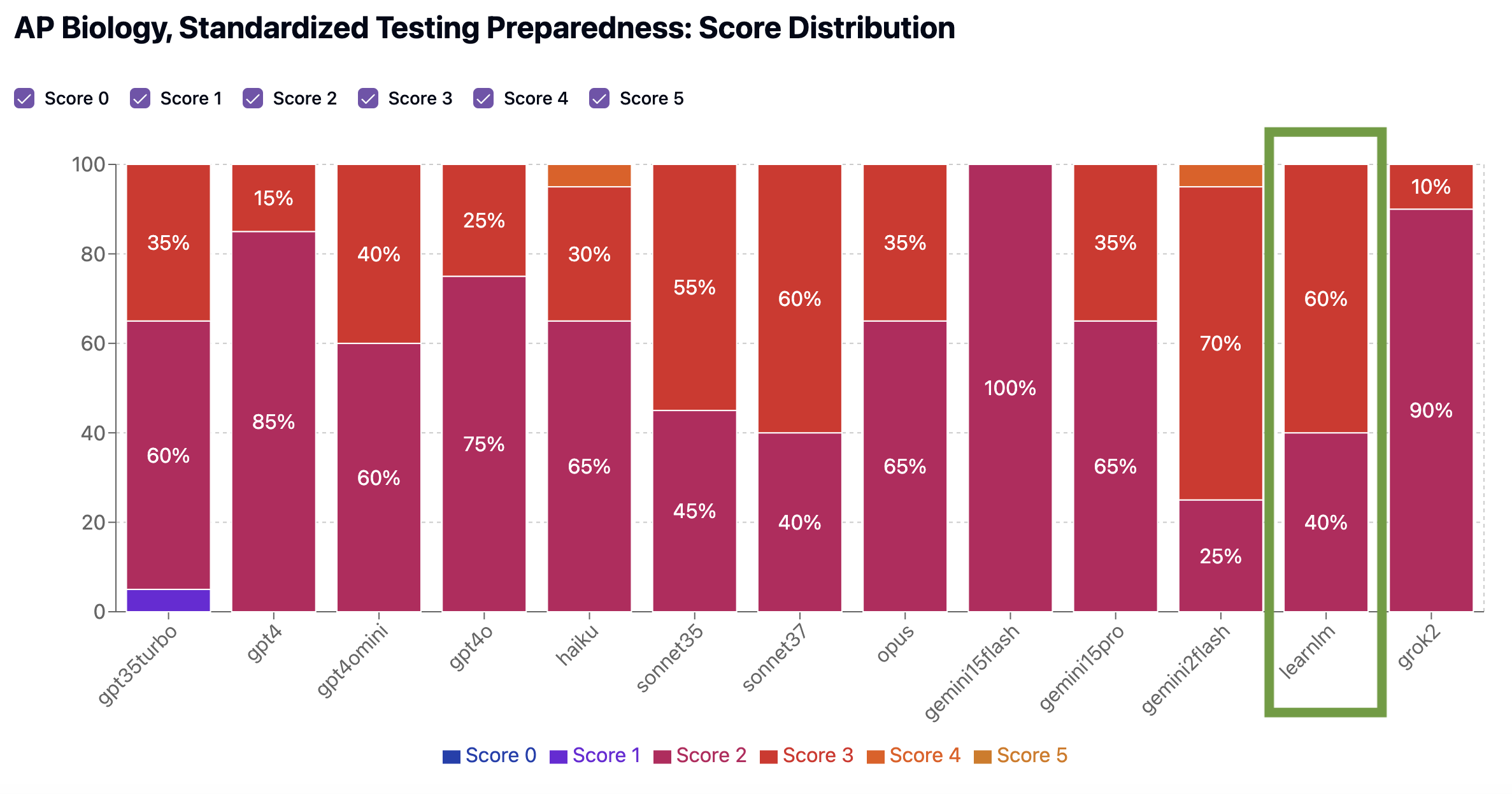
Concept Coverage: 3. The quiz covers some key concepts, such as genetic drift, gene flow, and the effects of bottlenecks and founder effects. However, it lacks coverage of mutation as a random process contributing to genetic diversity and the role of mutations in generating phenotypic changes. The quiz also does not address the reduction of genetic variation and its impact on population differences. While genetic drift and gene flow are well-represented, the quiz is imbalanced, with multiple questions focusing on Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which is not directly aligned with the provided standards. Overall, the quiz assesses only about half of the key concepts, with significant gaps in mutation-related topics.
Standardized Testing Preparedness: 3. The quiz partially aligns with the expected standardized test composition for AP Biology, focusing on population genetics. It includes questions on Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, genetic drift, gene flow, and bottleneck effects, which are relevant to the standards. However, the quiz primarily consists of multiple-choice questions that emphasize recall and basic application, lacking deeper analysis or synthesis questions that are typical in standardized tests. There is also a lack of questions that require constructing or interpreting data representations, which are important for assessing understanding of genetic drift and migration effects. These deviations impact the quiz's resemblance to standardized assessments.
Not perfect by any means, but when it comes to using commonly available AI for AP Biology test prep, this is as good as it gets.
AP U.S. History: AI Model Recommendation
Best Model: LearnLM (Runner-Up: Claude Sonnet 3.7)
Why LearnLM wins: Stronger alignment with tested topics while maintaining good AP-style exam structure
When it comes to prepping for AP U.S. History, two models rise to the top—but LearnLM edges out the win once more.
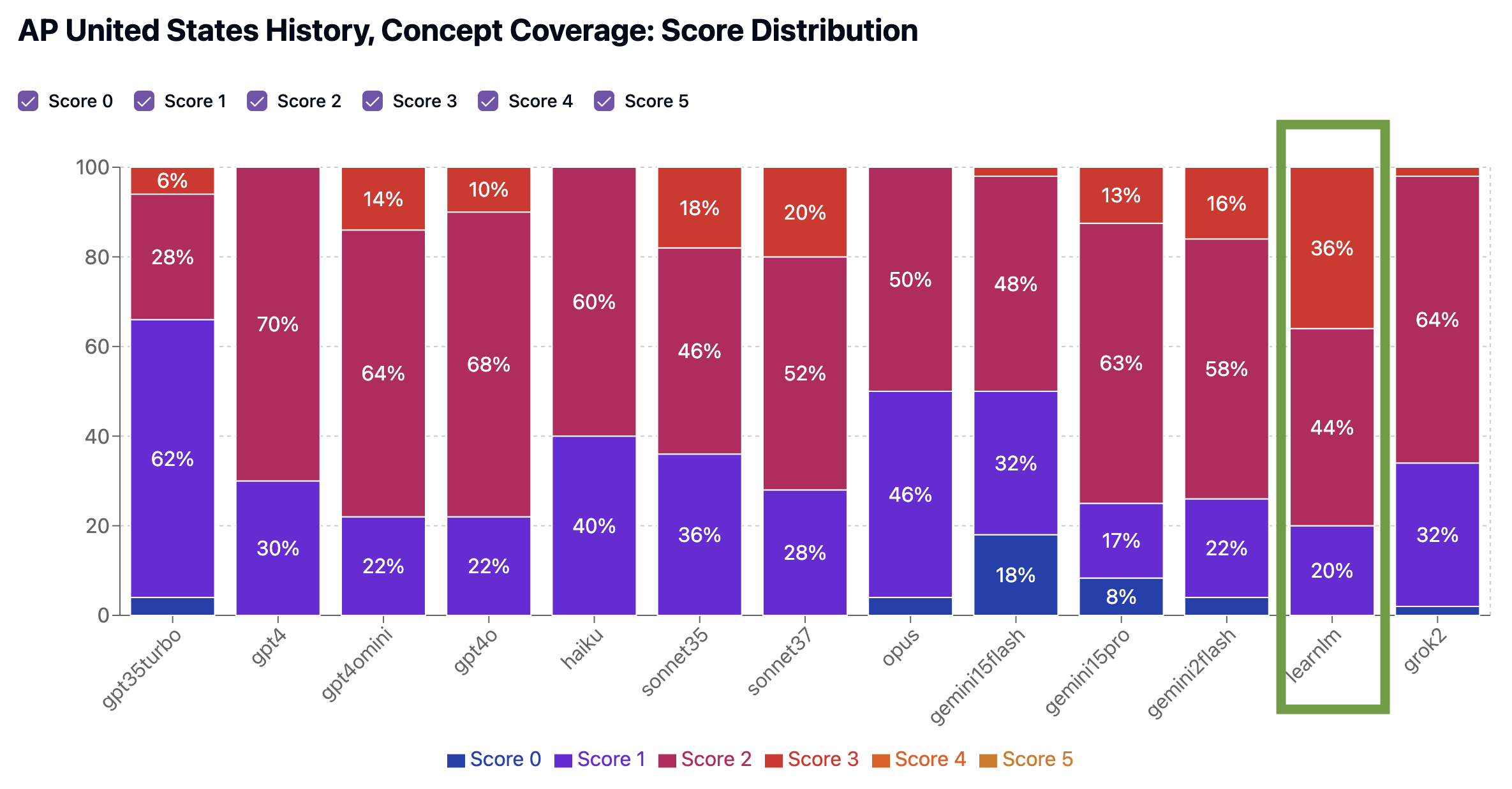
Both LearnLM and Claude Sonnet 3.7 performed well in our benchmarks. On Concept Coverage, LearnLM (2.2 average) edged out Claude Sonnet 3.7 (1.9 average), meaning both models touched on a wide range of important historical events, figures, and themes across the APUSH curriculum.
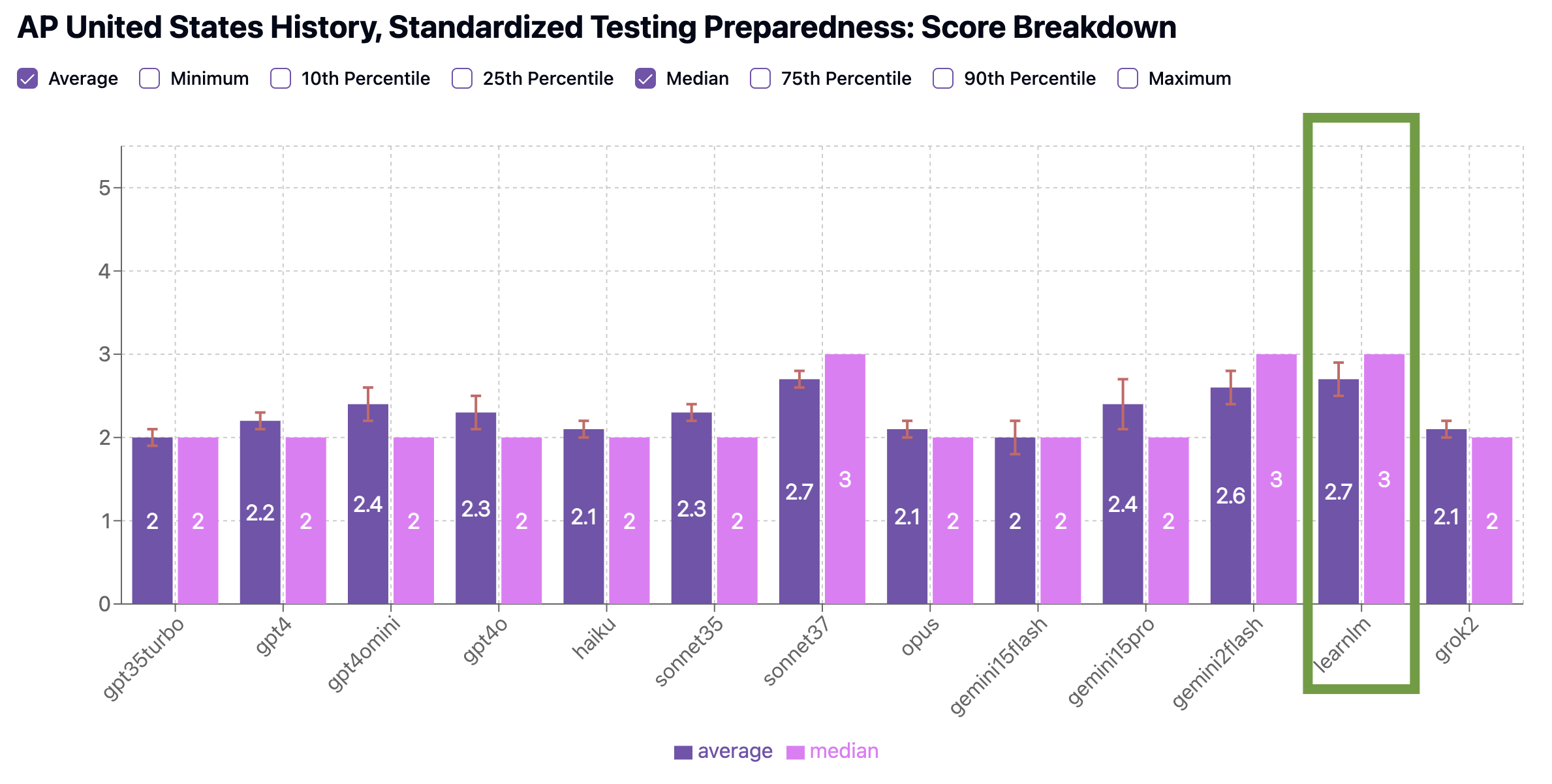
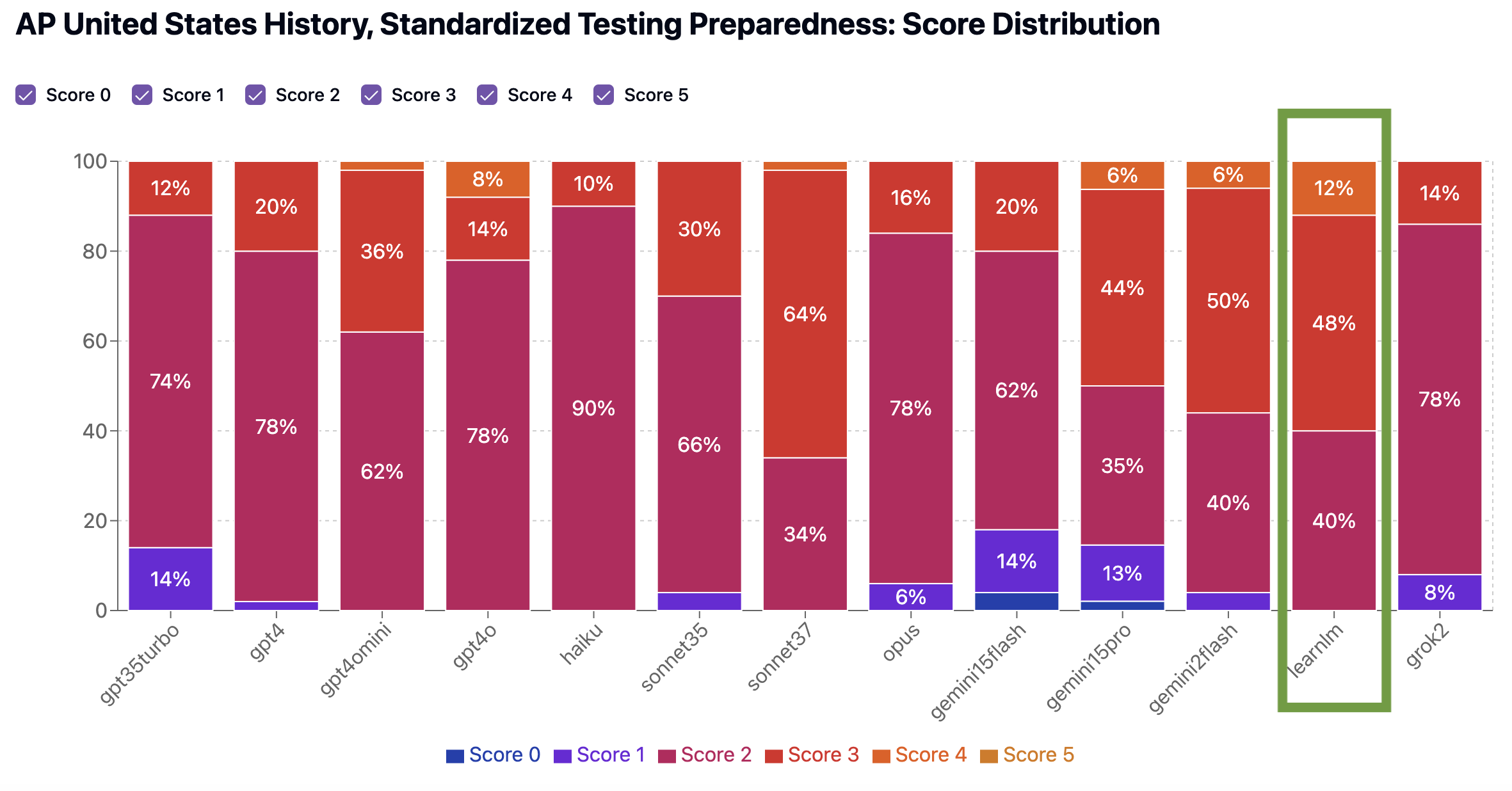
Both LearnLM and Claude Sonnet 3.7 had similar performance on the Standardized Testing Preparedness benchmark (2.7 average), but LearnLM’s quizzes had a significantly higher proportion (12% vs. 2%) of strong quizzes scoring a 4, better reflecting the tone, structure, and difficulty of actual AP exam items. Even a 10% improvement in high-scoring quizzes can mean the difference between a 3 and a 4 on test day!
All together, these results give LearnLM the edge for AP US History (don’t forget Google’s prompt recommendations!), though Claude Sonnet 3.7 is also a reasonable choice.
Benchmark Scores: AP U.S. History
We scored each model on two criteria: how well it covers key concepts (Concept Coverage), and how closely its quizzes resemble real AP exams (Standardized Testing Preparedness).
Concept Coverage Benchmark
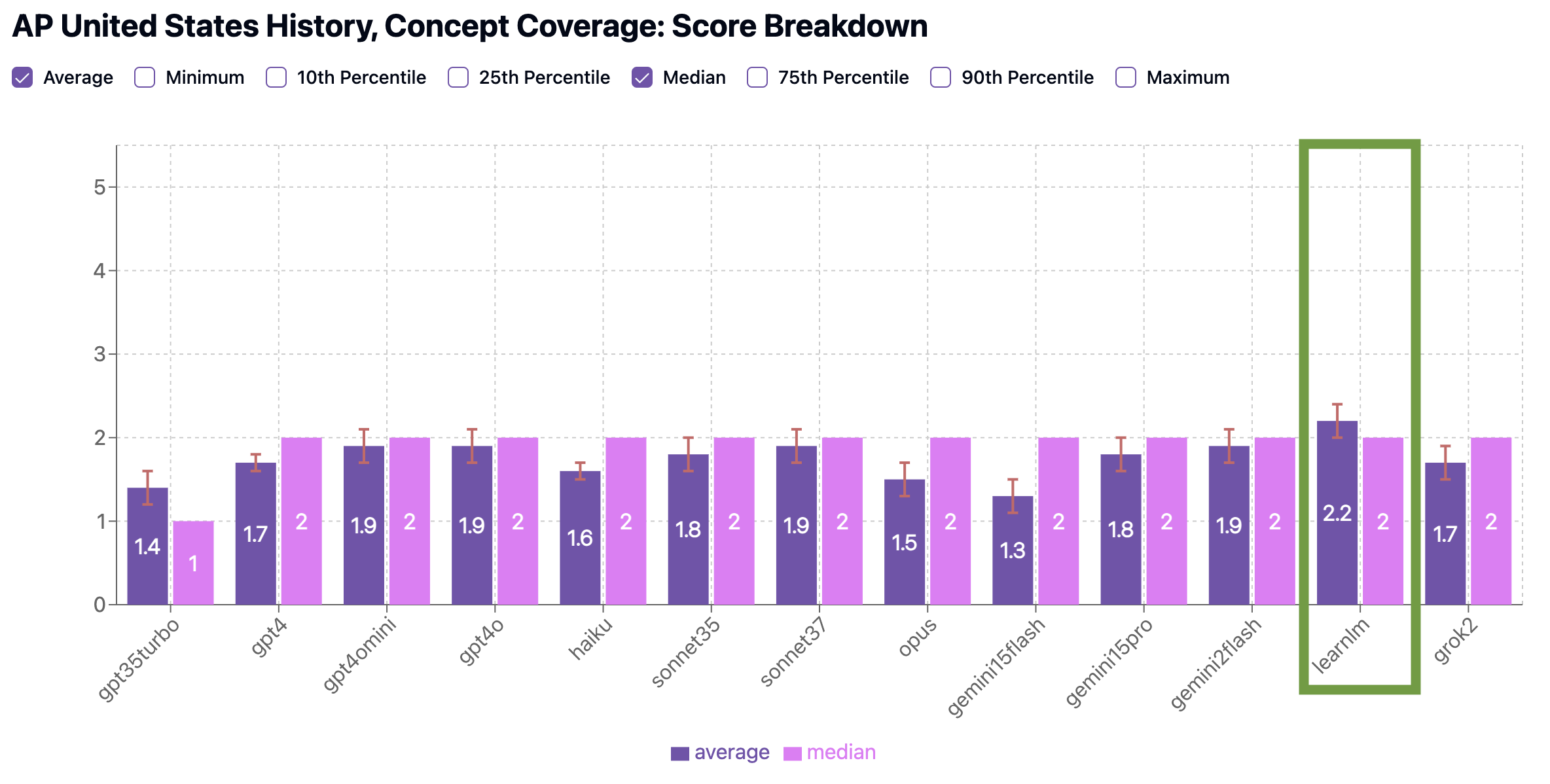
Standardized Testing Preparedness Benchmark
Example: Claude Sonnet 3.7 AP U.S. History Quiz
Since we already dove into the details of an example LearnLM quiz, let’s look at one of Claude Sonnet 3.7’s quizzes to see how it compares. This quiz covers Topic 5.8 of the AP United States History curriculum, Military Conflict in the Civil War.
AP United States History Quiz
Topic 5.8: Military Conflict in the Civil War1. Which Union military strategy aimed to divide and weaken the Confederacy by controlling the Mississippi River?
A. Peninsula Campaign
B. Anaconda Plan
C. March to the Sea
D. Overland Campaign
Correct Answer: B2. The Battle of Antietam was significant because:
A. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history
B. It gave Lincoln the opportunity to issue the Emancipation Proclamation
C. It ended General Lee's first invasion of the North
D. All of the above
Correct Answer: D3. Which Civil War innovation significantly changed naval warfare?
A. Submarine warfare
B. Ironclad ships
C. Steam-powered vessels
D. Naval mines
Correct Answer: B4. What was General William Tecumseh Sherman's primary objective in his "March to the Sea"?
A. To capture Confederate President Jefferson Davis
B. To destroy Southern infrastructure and civilian morale
C. To liberate enslaved people across Georgia
D. To establish a Union presence along the Atlantic coast
Correct Answer: B5. The Battle of Gettysburg was a turning point in the Civil War because:
A. It effectively ended the war in the Western Theater
B. It halted Lee's second invasion of the North
C. It coincided with the fall of Vicksburg, giving the Union control of the Mississippi
D. Both B and C
Correct Answer: D6. Which of the following was NOT an advantage the North held during the Civil War?
A. Superior industrial capacity
B. Larger population
C. More extensive railroad network
D. More experienced military leadership
Correct Answer: D7. What strategy did the Confederacy initially hope would bring European nations into the war on their side?
A. "Cotton diplomacy" - restricting cotton exports to create economic pressure
B. Naval blockade of Northern ports
C. Demonstrating military superiority through early victories
D. Promising to abolish slavery if recognized
Correct Answer: A8. Which development most significantly improved medical care during the Civil War?
A. The establishment of the U.S. Sanitary Commission
B. The development of anesthesia
C. The widespread use of antibiotics
D. The introduction of the ambulance corps
Correct Answer: A9. The Pickett's Charge at the Battle of Gettysburg is best described as:
A. A surprise flanking maneuver that nearly succeeded
B. A failed frontal assault ordered by General Lee against the Union center
C. A successful cavalry charge led by General Pickett
D. The final Union offensive that broke Confederate lines
Correct Answer: B10. How did technological developments affect the nature of combat during the Civil War?
A. They decreased the number of casualties
B. They made defensive positions nearly impregnable
C. They led to higher casualty rates as tactics failed to adapt to new weapons
D. They eliminated the advantage of defensive positions
Correct Answer: C
This quiz scored a 3 on both Concept Coverage and Standardized Testing Preparedness. Here’s the explanations:
Concept Coverage: 3. The quiz covers several key concepts, such as Union strategies (Anaconda Plan), key battles (Gettysburg, Antietam), and the impact of technological and strategic innovations (ironclad ships, Sherman's March). However, it lacks comprehensive coverage of economic mobilization efforts, societal mobilization, and the role of leadership in Union victories. The quiz is skewed towards military strategies and battles, with insufficient focus on economic and societal factors, as well as the destruction of Southern infrastructure. This results in a partial but not comprehensive assessment of the standards.
Standardized Testing Preparedness: 3. The quiz partially aligns with the expected standardized test composition for AP United States History, focusing on military conflict in the Civil War. It includes questions on key battles, strategies, and technological advancements, which are relevant to the standards. However, it lacks depth in assessing economic and societal mobilization, leadership strategies, and resource advantages, which are crucial elements of the standards. The quiz primarily consists of recall questions with limited analysis or application, deviating from the expected cognitive demand balance.
Another imperfect quiz, but once again, just about as good as it gets for using standard AI models for AP US History test prep. LearnLM was slightly better, but not by much (check it out yourself on EduBench).
AP World History Modern: AI Model Recommendation
Best Model: Gemini 2.0 Flash (Runner-Up: Claude Sonnet 3.7)
Why Gemini 2.0 Flash wins: Superior performance covering topics and consistent AP-style formatting
For AP World History: Modern, the top performer isn’t LearnLM—it’s Gemini 2.0 Flash.
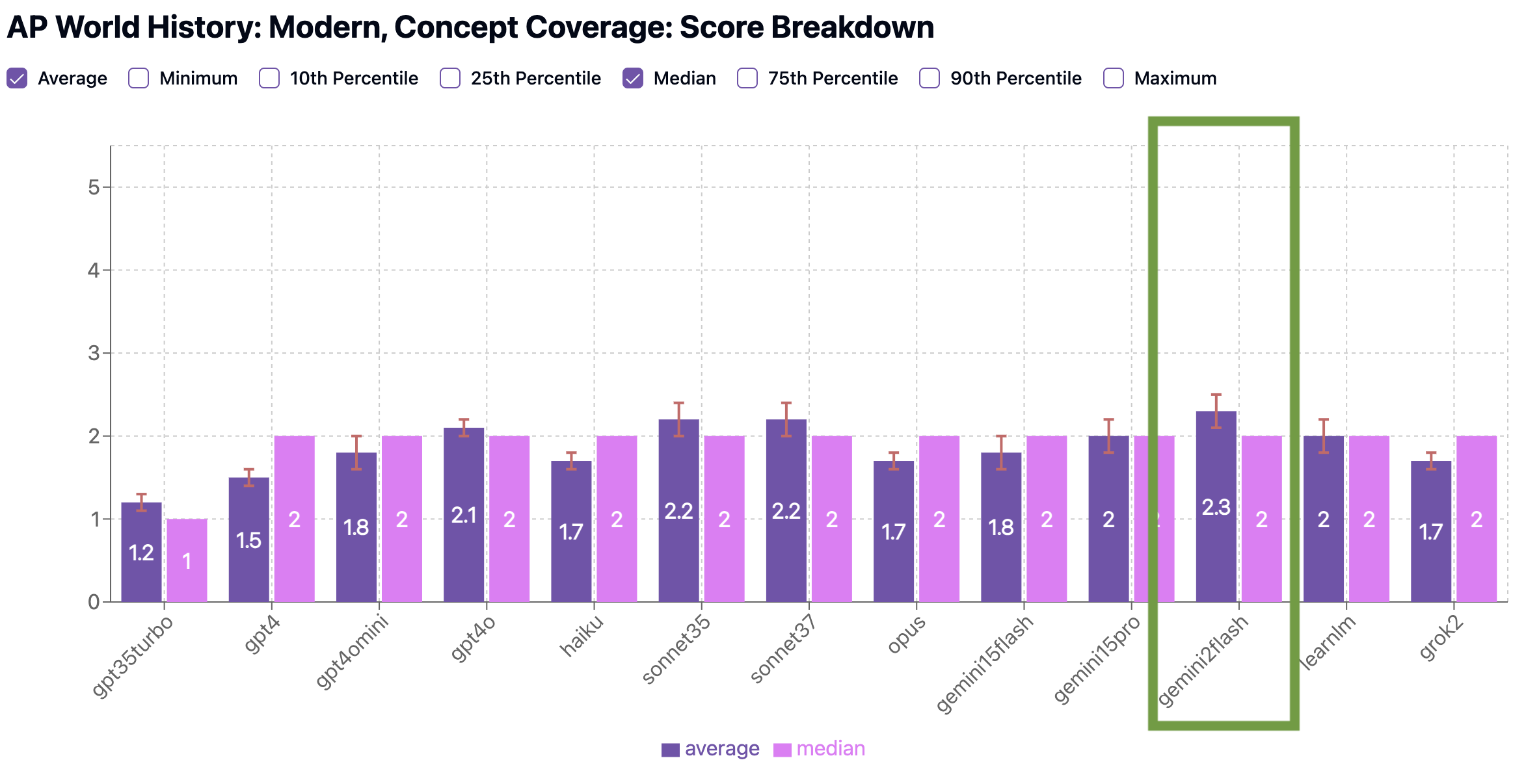
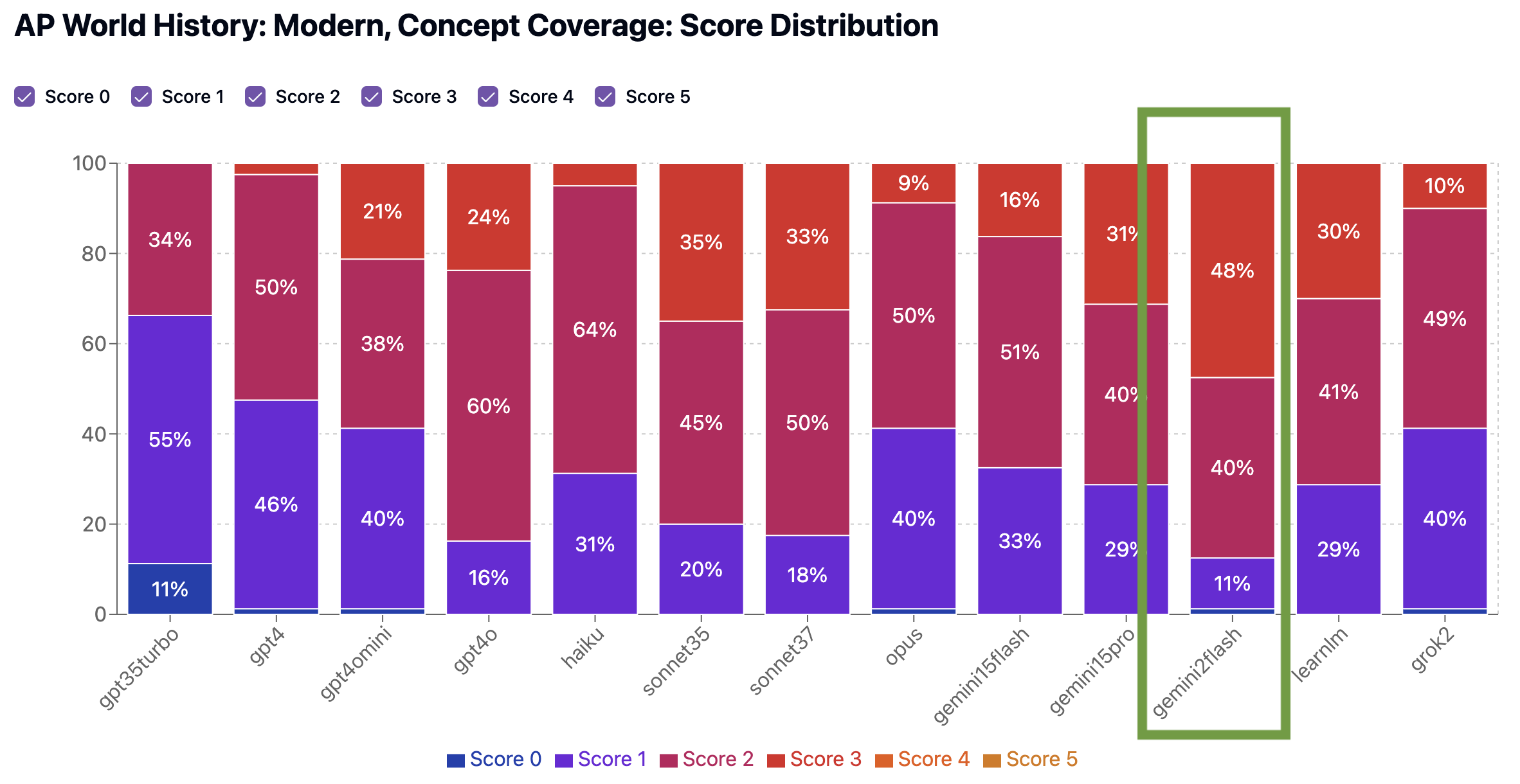
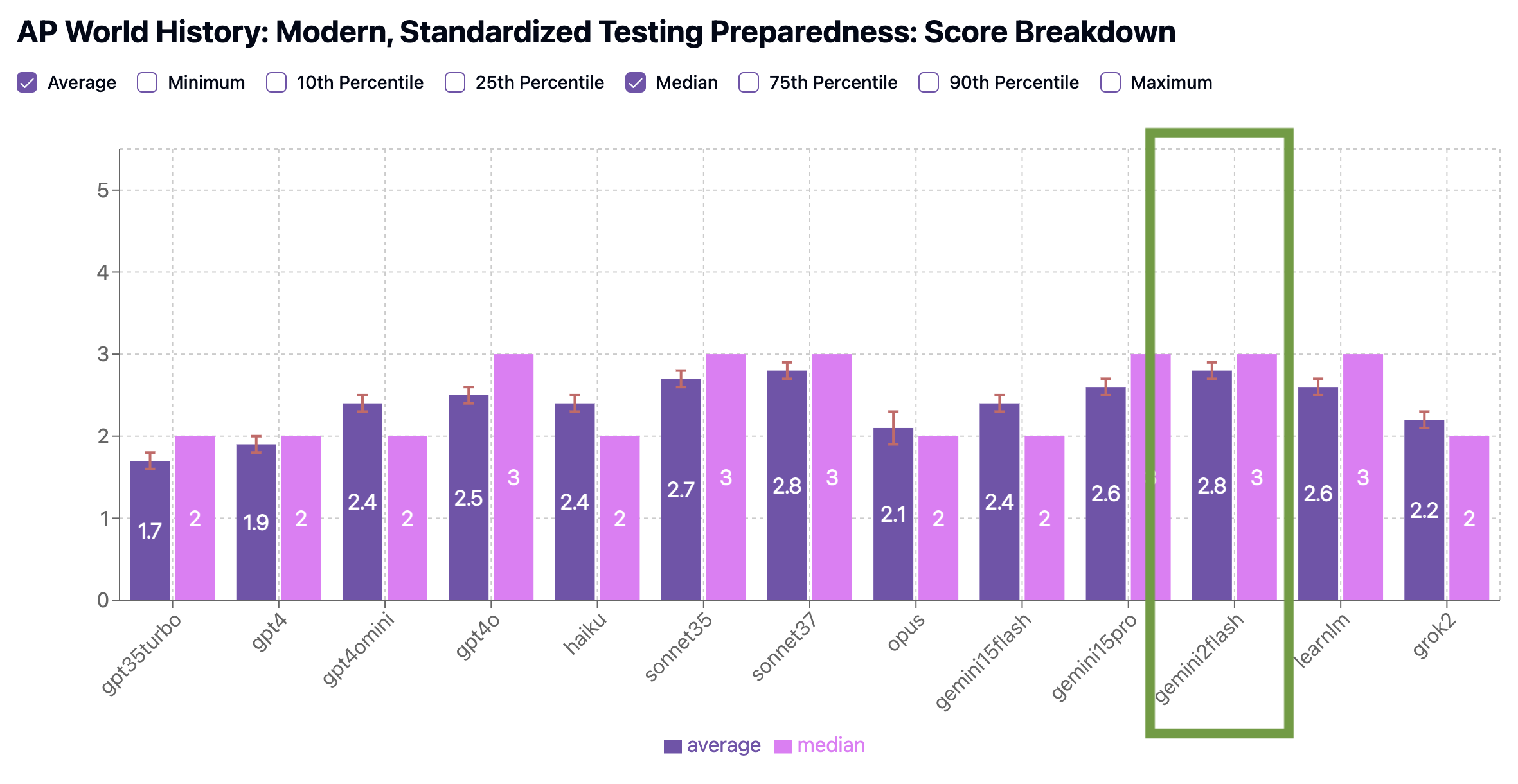
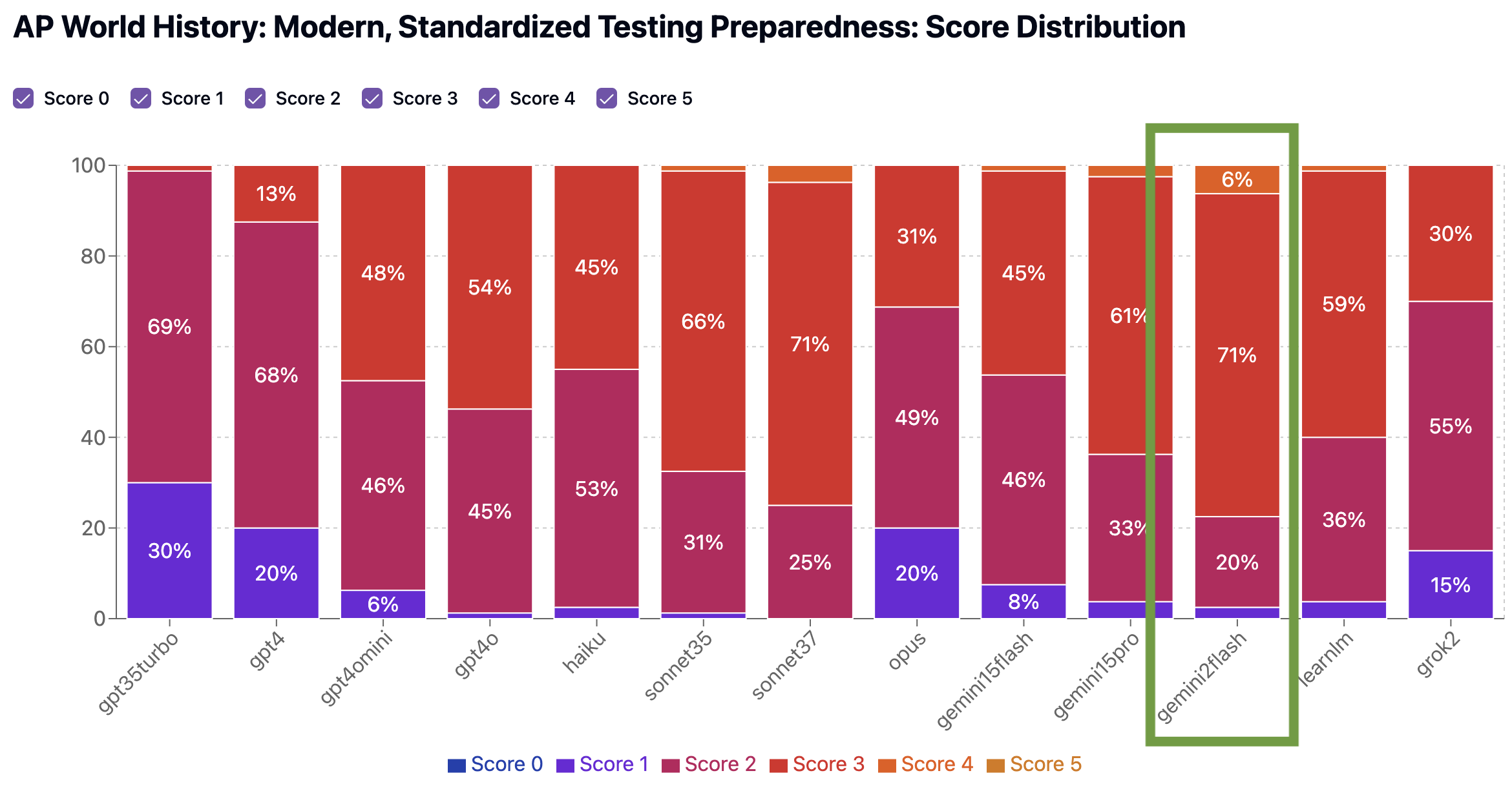
In our benchmarks, Gemini outscored other models in both Concept Coverage (average 2.3, edging out Claude Sonnet 3.7 at 2.2 average) and Standardized Testing Preparedness (average 2.8, tying Claude Sonnet 3.7). Its quizzes reflected the best understanding of the global themes, time periods, and cause-and-effect relationships emphasized in the AP World curriculum. Gemini was also more consistent than other models in structuring questions that match the tone, format, and pacing of the actual exam, with a significantly better proportion of its quizzes getting a 3 (71%) or 4 (6%) for Standardized Testing Preparedness than other models.
All-up, this places Gemini 2.0 Flash at the front of the pack for standard AI models in AP World History: Modern test prep.
Benchmark Scores: AP World History
We scored each model on two criteria: how well it covers key concepts (Concept Coverage), and how closely its quizzes resemble real AP exams (Standardized Testing Preparedness).
Concept Coverage Benchmark
Standardized Testing Preparedness Benchmark
Example: Gemini 2.0 Flash AP World History: Modern Quiz
The example quiz below was generated by Gemini 2.0 Flash, and covers AP World Topic 4.6: Internal and External Challenges to State Power from 1450 to 1750.
1. Which of the following BEST describes a common factor contributing to peasant revolts during the period 1450-1750?
(A) Religious unification imposed by state authorities
(B) Increased political participation and representation for commoners
(C) Growing economic inequality and oppressive labor systems
(D) Decline in agricultural productivity due to climate change
Correct Answer: (C)2. The Fronde, a series of revolts in France during the mid-17th century, was primarily a challenge to the power of:
(A) The Catholic Church
(B) The Estates-General
(C) The nobility
(D) The monarchy
Correct Answer: (D)3. Which of the following was a significant cause of the Pueblo Revolt in 1680?
(A) Forced conversion to Christianity by Spanish colonizers
(B) Economic competition between Pueblo farmers and Spanish ranchers
(C) Pueblo demands for greater political autonomy within the Spanish Empire
(D) All of the above
Correct Answer: (D)4. The Ottoman Empire faced internal challenges during the period 1450-1750, including:
(A) Successful secession movements by various ethnic and religious groups
(B) Revolts by the Janissaries due to perceived weakening of their power
(C) Widespread adoption of European democratic ideals
(D) Complete disintegration of the empire into smaller independent states
Correct Answer: (B)5. Which of the following best describes the impact of the Stono Rebellion (1739) in colonial South Carolina?
(A) It led to the immediate abolition of slavery in the colony.
(B) It resulted in the loosening of slave codes and greater autonomy for enslaved Africans.
(C) It prompted stricter slave codes and greater fear among the white population.
(D) It encouraged further large-scale slave revolts throughout the colonies.
Correct Answer: (C)6. The Cossack rebellions in Russia, such as the Pugachev Rebellion, were primarily driven by:
(A) Religious persecution by the Orthodox Church
(B) Economic grievances and the desire for greater autonomy from the central government
(C) Demands for the abolition of serfdom and land redistribution
(D) Influence from Enlightenment thinkers advocating for democratic reforms
Correct Answer: (B)7. Which of the following states experienced significant slave revolts in the period 1450-1750?
(A) England
(B) The Mughal Empire
(C) Brazil
(D) The Holy Roman Empire
Correct Answer: (C)8. Which of the following BEST exemplifies a challenge to state power based on religious differences?
(A) The English Civil War
(B) The Boston Tea Party
(C) The French Revolution
(D) The Taiping Rebellion
Correct Answer: (A)9. What was a common long-term consequence of many internal rebellions and revolts during the period 1450-1750?
(A) The immediate overthrow of existing governments and the establishment of democracies
(B) Strengthening of state power and increased efforts to maintain control
(C) A significant decrease in social stratification and economic inequality
(D) Widespread adoption of secular values and the decline of religious institutions
Correct Answer: (B)10. Which of the following is NOT a primary reason for challenges to state consolidation or expansion during this period?
(A) Competition over resources
(B) Local resistance
(C) Ethnic and religious divisions
(D) Widespread state-sponsored healthcare initiatives
Correct Answer: (D)
This quiz scored a 3 for Concept Coverage, but got a 4 on Standardized Testing Prep, showing signs of genuinely helpful prep for the AP exam.
Concept Coverage: 3. The quiz covers several key concepts related to resistance against state expansion and centralization, such as economic grievances, political challenges, and specific historical examples like the Fronde and the Stono Rebellion. However, it underrepresents the motivations and strategies of enslaved persons' resistance in the Americas, as well as the broader social and political impacts of these movements. While the quiz addresses some aspects of local resistance and state challenges, it lacks a balanced representation of all standards, particularly in exploring the diverse motivations and forms of resistance across different regions and groups.
Standardized Test Prep: 4. The quiz aligns well with the expected standardized test composition for AP World History: Modern, focusing on internal and external challenges to state power from 1450 to 1750. It includes a variety of question types that assess understanding of social, political, and economic resistance, as well as specific historical examples like the Fronde and the Stono Rebellion. The cognitive demands are appropriate, requiring students to recall, analyze, and apply knowledge. However, the quiz could benefit from more stimulus-based questions to better reflect the evaluation of primary or secondary sources, which is a key aspect of the standards. Overall, the quiz is a strong match but has slight deviations in its lack of source-based questions.
This quiz has some shortcomings, but overall serves as a relatively useful bit of test prep for AP World History: Modern.
So is Any AI Model OK to Use for AP Test Prep?
All of the recommended models and runner-ups did fairly similarly on quiz benchmarks, so does that mean they are all more or less the same? Can you just choose any model and get the same middling level of performance?
No! Let’s look at an AP Biology quiz question generated by Grok 2, a well-known model that scored poorly in both of our key benchmarks. (Note: while Grok 3 is xAI’s latest model, it’s not yet available via API, which is required for EduBench.)
Grok2 Quiz Example: AP Biology
This quiz, created by Grok 2, focuses on the same topic, Topic 7.4: Population Genetics, in the AP Biology curriculum as the previous example:
Question 1:
Which of the following best describes the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A. A population in which allele frequencies do not change over generations
B. A population with high mutation rates
C. A population undergoing rapid evolution
D. A population with high gene flow
Correct Answer: AQuestion 2:
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is represented as p² + 2pq + q² = 1. What does p represent in this equation?
A. The frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype
B. The frequency of the dominant allele
C. The frequency of the heterozygous genotype
D. The frequency of the recessive allele
Correct Answer: BQuestion 3:
Which of the following is NOT a condition required for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A. No natural selection
B. No gene flow
C. Random mating
D. Small population size
Correct Answer: DQuestion 4:
If the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in a population is 0.3, what is the frequency of the dominant allele (p)?
A. 0.3
B. 0.7
C. 0.9
D. 0.6
Correct Answer: BQuestion 5:
In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, if the frequency of individuals with the homozygous recessive genotype (q²) is 0.04, what is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (2pq)?
A. 0.16
B. 0.24
C. 0.32
D. 0.48
Correct Answer: CQuestion 6:
Which of the following evolutionary forces can cause a deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A. Random mating
B. Large population size
C. Genetic drift
D. No mutation
Correct Answer: CQuestion 7:
The bottleneck effect is an example of which evolutionary force?
A. Gene flow
B. Mutation
C. Genetic drift
D. Natural selection
Correct Answer: CQuestion 8:
Which of the following best describes gene flow?
A. The movement of alleles between populations
B. The change in allele frequencies due to random events
C. The process by which advantageous traits become more common
D. The introduction of new alleles into a population through mutation
Correct Answer: AQuestion 9:
Which of the following conditions would most likely lead to a decrease in genetic variation within a population?
A. High rates of gene flow
B. Large population size
C. Genetic drift in a small population
D. Random mating
Correct Answer: CQuestion 10:
If a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which of the following is a possible explanation?
A. The population is undergoing random mating
B. The population is very large
C. The population is experiencing natural selection
D. There is no gene flow
Correct Answer: C
This quiz scored a 2 for Standardized Testing Preparedness and an astonishingly low 1 for Concept Coverage. Here’s why:
Concept Coverage: 1. The quiz primarily focuses on Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which is not directly related to the key concepts outlined in the standards for Population Genetics. Key concepts such as mutation as a random process, genetic drift, gene flow, and the reduction of genetic variation are barely addressed. Only one question (Question 7) touches on genetic drift, and one question (Question 8) touches on gene flow, but these are insufficient to cover the breadth of the standards. The quiz lacks questions on the impact of mutations, the role of genetic drift in small populations, and the effects of migration on genetic diversity. Overall, the quiz fails to comprehensively assess the key concepts from the standards, focusing instead on a narrow aspect of population genetics.
Standardized Testing Preparedness: 2. The quiz significantly deviates from the expected standardized test composition for AP Biology, particularly in the Population Genetics cluster. The questions focus heavily on Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which is only a part of the broader standards. There is a lack of diversity in question types and cognitive demands, with most questions being recall-based and not addressing the full range of learning objectives such as mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow. The quiz does not adequately cover the analysis, application, or interpretation of statistical data, which are crucial for standardized assessments in this subject area.
Pretty bad! It’s clear to see you can’t just grab any model you like for AP test prep, even models like Grok that have a good deal of hype and perform well on other tasks and benchmarks.
This isn’t about dunking on a model though. It’s about showing why evidence-based, data-driven benchmarks like EduBench matter. Without a structured evaluation like EduBench, you’re flying blind. A quiz that feels okay might actually waste your study time—or worse, leave you underprepared. We benchmark models so you don’t have to guess. And as you’ve seen in this post, some models are significantly better at test prep than others.
Sneak Peek: Incept Outperforms Every Other Model
It’s Not Public Yet—But It’s Already Setting a New Benchmark for AP Prep
We didn’t include it in our official recommendations because it’s not publicly available (yet!), but we’d be remiss if we didn’t show you what’s coming next from us over at LearnWith.AI.
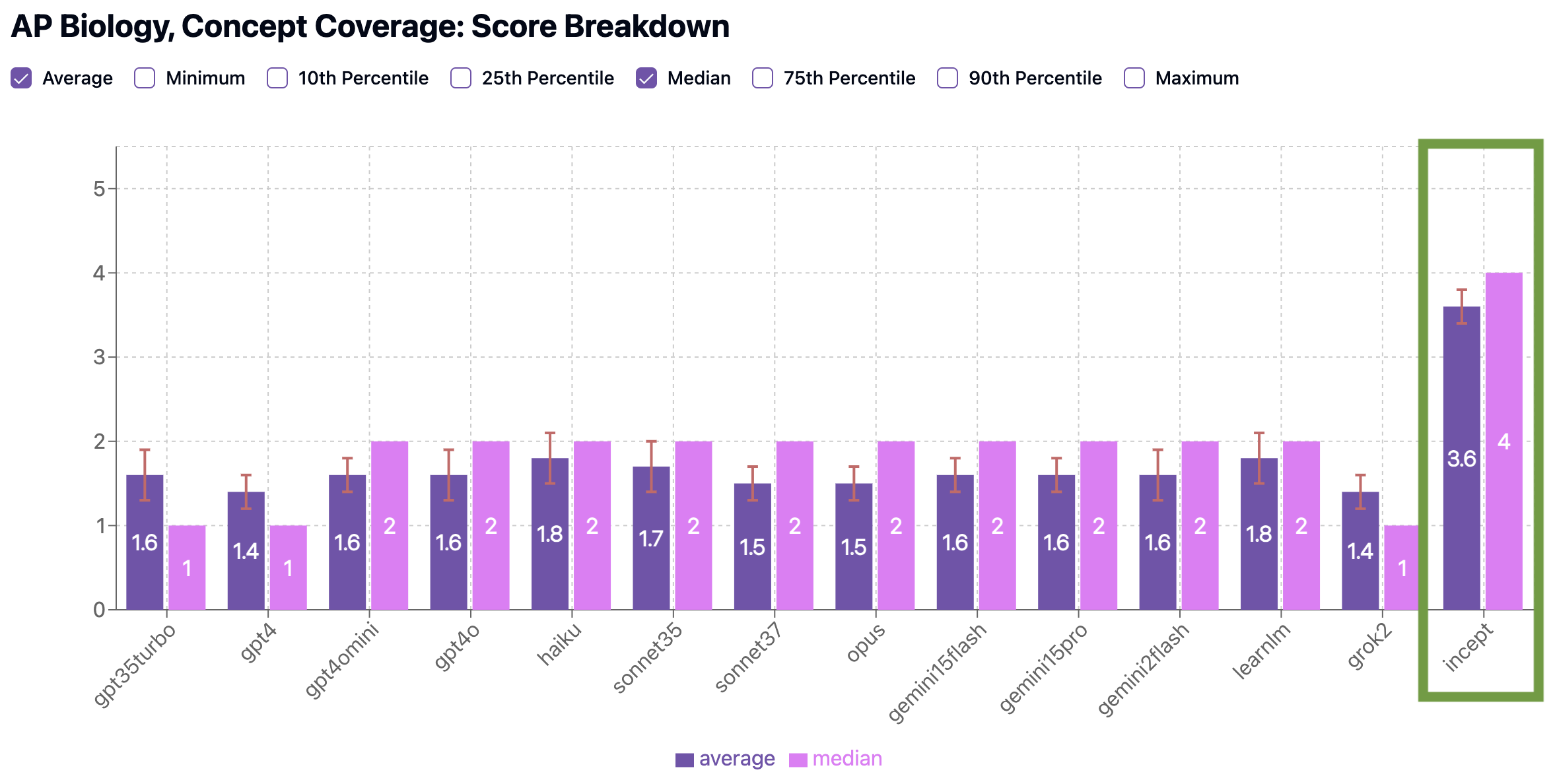
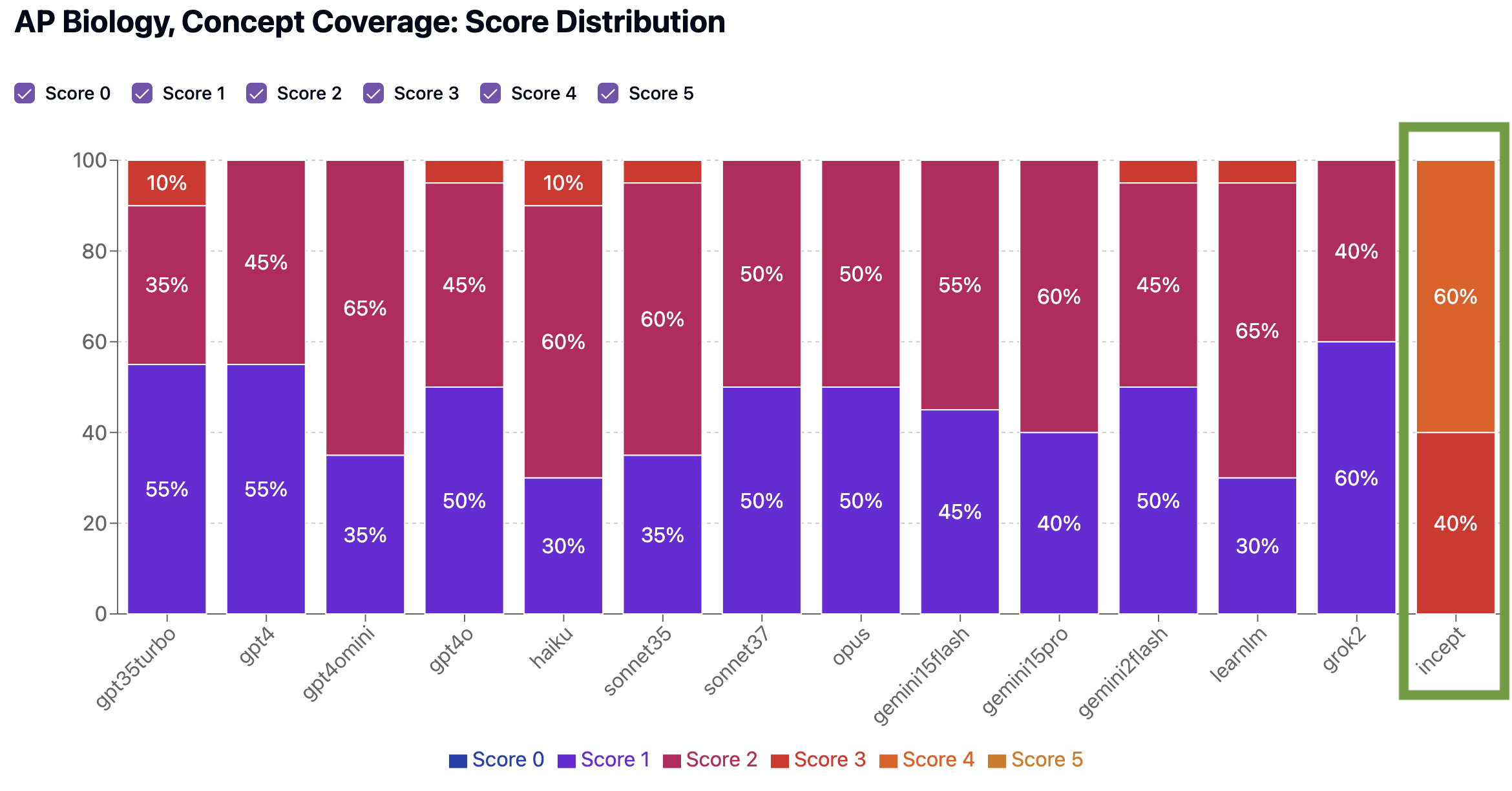
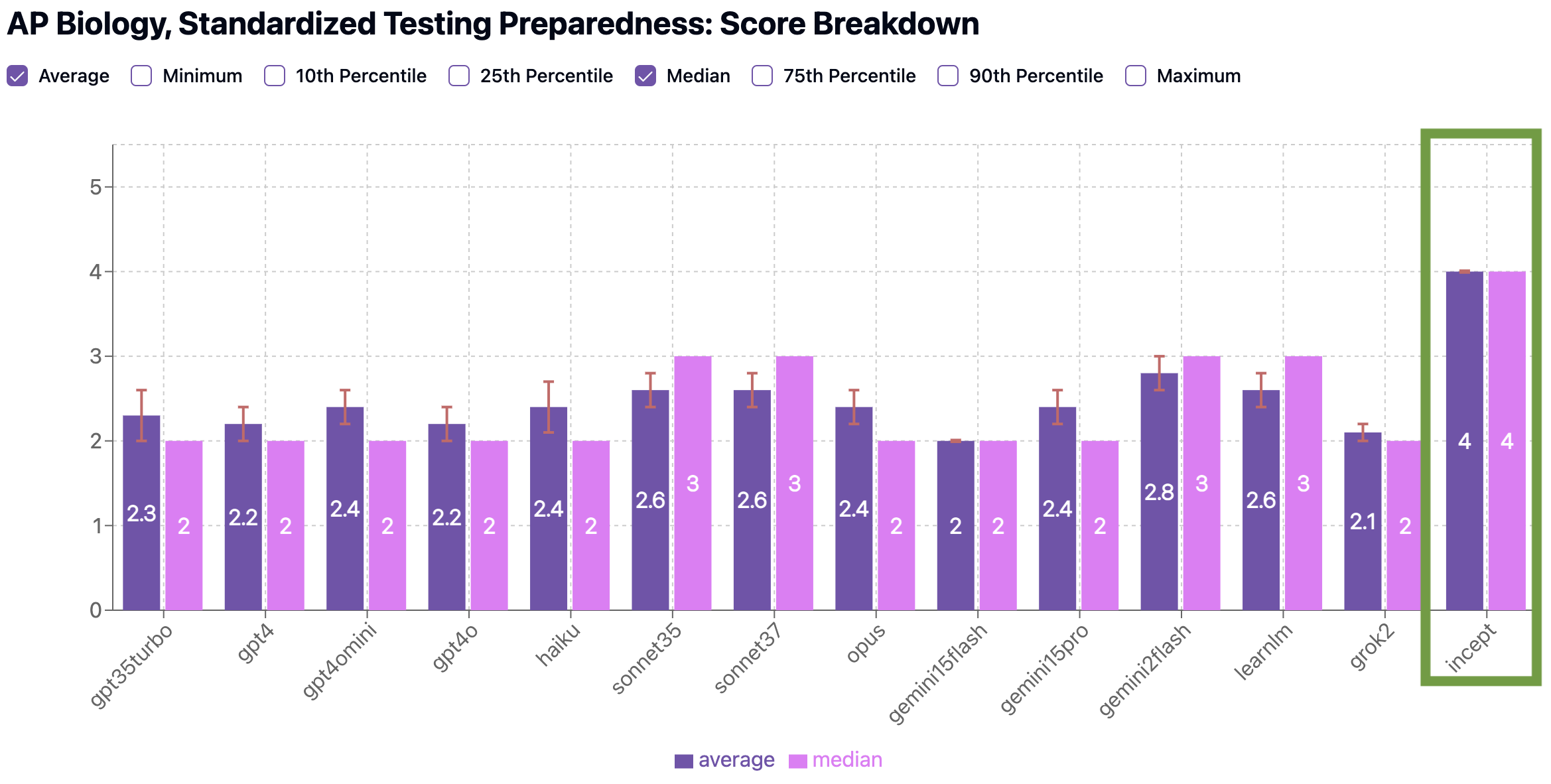
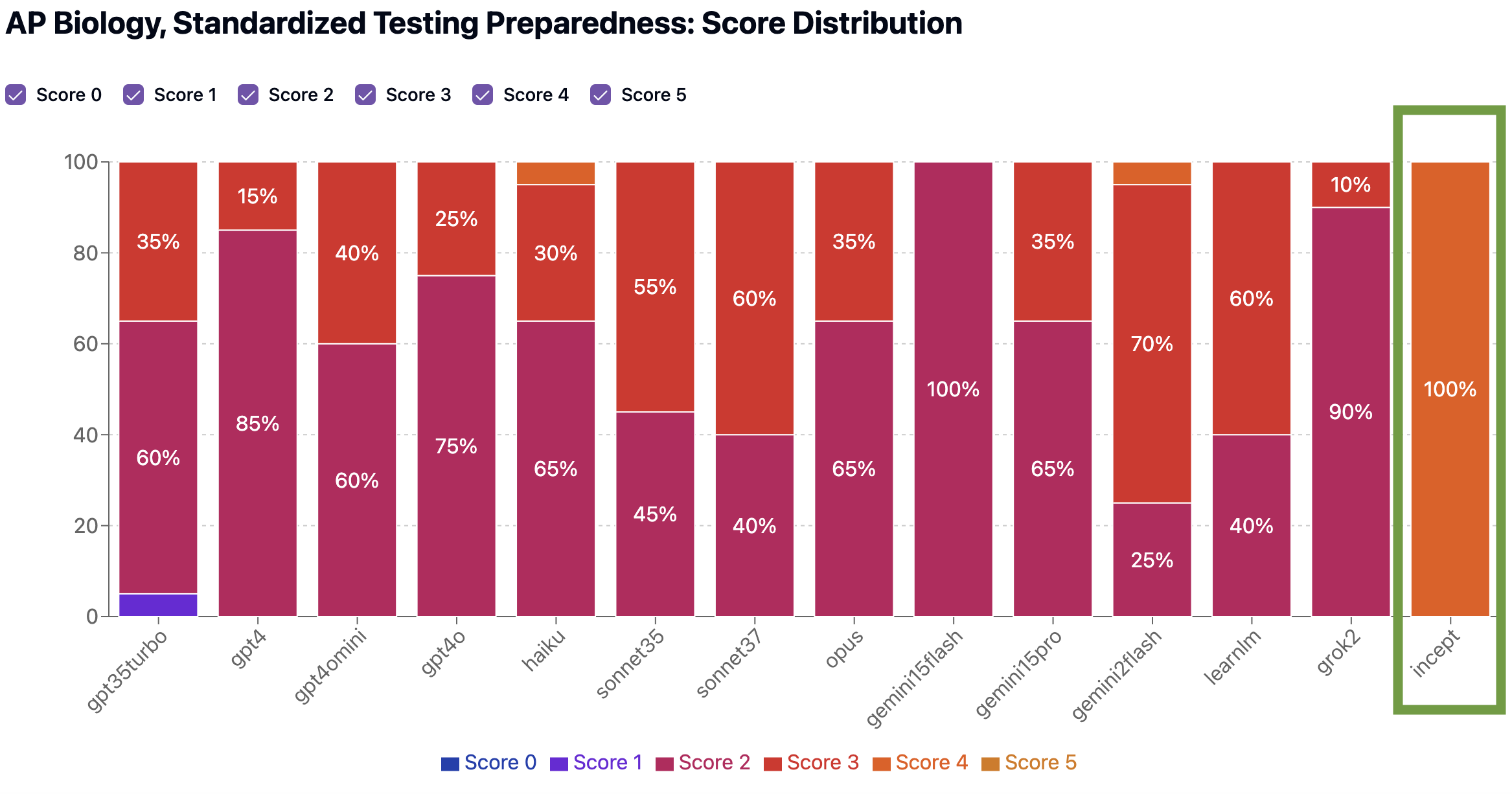
Our team has been developing a new model called Incept—and in initial benchmarks, it outperformed every other model across all three AP subjects we tested. Let’s look at how it scores in AP Biology as an example.
Benchmark Scores: AP Biology
We scored Incept on the exact same two criteria as other models: how well it covers key concepts (Concept Coverage), and how closely its quizzes resemble real AP exams (Standardized Testing Preparedness).
Concept Coverage Benchmark
Standardized Testing Preparedness Benchmark
Example: Incept AP Biology Quiz
If you’re wondering what makes Incept’s quizzes so different, here’s an example of an AP Biology quiz it generated (again on Topic 7.4, Population Genetics). Compare it to the earlier LearnLM and Grok 2 AP Biology quizzes to see for yourself.
Quiz on Population Genetics
1. Question: Which of the following statements correctly describes mutations?
A) Mutations are directed by environmental pressures.
B) Mutations always result in negative phenotypic changes.
C) Mutations are random events that contribute to genetic diversity.
D) All mutations are hereditary and passed to offspring.
Correct Answer: C) Mutations are random events that contribute to genetic diversity.2. Question: What is the primary effect of genetic drift in small populations?
A) It increases genetic variation by introducing new alleles.
B) It maintains allele frequencies through selective pressures.
C) It alters allele frequencies through a nonselective process.
D) It prevents the occurrence of bottlenecks and founder effects.
Correct Answer: C) It alters allele frequencies through a nonselective process.3. Question: Which process can lead to the homogenization of allele frequencies between populations?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Gene flow
D) Bottleneck effect
Correct Answer: C) Gene flow4. Question: How do bottleneck effects influence genetic variation in a population?
A) They increase genetic diversity by introducing new mutations.
B) They reduce genetic variation, leading to increased differences between populations.
C) They maintain the original genetic makeup of the population.
D) They prevent populations from diverging genetically.
Correct Answer: B) They reduce genetic variation, leading to increased differences between populations.5. Question: What is a common misconception about mutations and natural selection?
A) Mutations occur randomly and provide genetic variation.
B) Natural selection acts on existing genetic variation.
C) Mutations occur in response to an organism's needs.
D) Natural selection causes new mutations to arise.
Correct Answer: C) Mutations occur in response to an organism's needs.6. Question: In the context of population genetics, what role does migration play?
A) It prevents genetic drift from occurring.
B) It introduces genetic material, altering allele frequencies.
C) It decreases population diversity by removing alleles.
D) It always results in beneficial traits entering a population.
Correct Answer: B) It introduces genetic material, altering allele frequencies.7. Question: What can be an outcome of genetic drift in a small population over time?
A) Stabilization of allele frequencies
B) Fixation or loss of alleles
C) Introduction of new alleles
D) Increase in genetic diversity
Correct Answer: B) Fixation or loss of alleles8. Question: Why might populations with high mutation rates under varying environmental pressures have different evolutionary outcomes?
A) Mutations are always harmful, leading to population decline.
B) Environmental pressures have no impact on mutation rates.
C) High mutation rates provide diverse phenotypes for natural selection to act upon.
D) Mutation rates are irrelevant to evolutionary processes.
Correct Answer: C) High mutation rates provide diverse phenotypes for natural selection to act upon.9. Question: How do the founder effect and bottleneck effect differ in their impact on populations?
A) Both effects increase genetic diversity by adding new alleles.
B) Both effects reduce genetic variation, but the founder effect occurs when a new population is established.
C) The bottleneck effect increases genetic variation, while the founder effect decreases it.
D) They have no significant impact on the genetic structure of populations.
Correct Answer: B) Both effects reduce genetic variation, but the founder effect occurs when a new population is established.10. Question: How does the reduction of genetic variation within a population affect its evolutionary potential?
A) It enhances the population's ability to adapt to environmental changes.
B) It decreases the likelihood of population divergence.
C) It increases the genetic differences between populations of the same species.
D) It stabilizes the genetic makeup, preventing evolutionary change.
Correct Answer: C) It increases the genetic differences between populations of the same species.
This quiz received a 4 for both Concept Coverage and Standardized Testing Preparedness, indicating it’s approaching the usefulness of an expert human tutor. Here’s why it got those scores:
Concept Coverage: 4. The quiz covers most key concepts from the standards, with questions addressing mutation as a random process, genetic drift, gene flow, bottleneck effects, and the role of mutations in natural selection. However, the quiz slightly underrepresents the interplay between migration and other evolutionary forces, as well as the construction and interpretation of statistical data representations related to genetic drift. Overall, the distribution of coverage is strong but could be slightly more balanced to ensure all learning objectives are equally assessed.
Standardized Testing Preparedness: 4. The quiz aligns well with the expected standardized test composition for AP Biology, focusing on population genetics. It covers key concepts such as mutations, genetic drift, gene flow, and bottleneck effects, which are central to the standards. The questions address common misconceptions and require understanding of processes rather than rote memorization, reflecting the cognitive demands expected in standardized tests. However, the quiz primarily consists of multiple-choice questions without incorporating diverse question types like data interpretation or model construction, which are also part of the expected composition. This slight deviation prevents a perfect score.
Still room for improvement (we’re working on it!), but much closer to being able to provide ideal practice MCQ quizzes. Also of note, 100% of the quizzes Incept generated received 4’s on both benchmarks, indicating it is much more reliably consistent generating effective quizzes than other models.
What Makes Incept Different?
Incept’s scores make it clear it’s doing something different from other AI models - even Google’s LearnLM model that was built for educational scenarios. What is it doing that’s so special?
Incept was designed from the ground up for educational performance, not just conversational fluency. It draws on our years of experience using AI to educate children, including running a real AI-powered school. We’ve been doing this for many years, before the current AI hype wave started.
We’re using everything we know about education to build an AI that embeds learning science, instructional techniques, test prep, assessment, curriculum alignment, mastery learning, and more directly into the model’s performance. That means:
Deeper concept alignment with AP curriculum frameworks
More realistic question structure based on actual AP exams
Instructional clarity that helps reinforce key ideas while challenging you
Incept doesn’t just sound smart—it helps you get smarter.
Stay Tuned
We’re still putting the final touches on Incept and preparing it for public release. If you want to be the first to try it (and help shape what it becomes), follow us for updates—we’ll be opening early access to students and educators soon.
Want More Than a Model? Try Athena
Everything we’ve shown so far is based on raw model performance—which is great if you're just experimenting or trying to quiz yourself quickly using basic AI models. But just using a ChatBot for AP test prep is like asking a brain surgeon to coach your soccer team. Smart? Yes. Helpful? Not unless it’s designed for the job.
If you're serious about earning a 4 or 5 on the AP exam, you’ll want more than a chatbot playing at AP test prep. You’ll want structure. Feedback. Progress tracking. And tools that actually help you master the material.
That’s why we built Athena. Athena uses the best-performing models (including Incept) as part of a complete AP prep system that includes:
✅ Personalized study paths based on your strengths and gaps
📈 Progress tracking and review loops
🧠 Instructionally sound quizzes, not just model outputs
🗂️ Coverage of real AP frameworks, not random facts
✍️ Written practice with AI-powered feedback (actual FRQs - not just MCQs!)
In short: Athena is built to help you actually improve, not just “play school.” If you’d like to try Athena for AP test prep, join the beta!
Final Takeaways
Recommended Models for AP Test Prep
There are dozens of AI models out there. Some are great at chatting. Some are built for reasoning. But only a few are actually good at helping you study for a high-stakes test like the AP exam.
Here’s the bottom line from our benchmarks:
AP Biology → Use LearnLM for the best concept coverage and realistic practice questions. Second choice: Gemini 2.0 Flash
AP U.S. History → Use LearnLM, with Claude Sonnet 3.7 as a solid backup
AP World History: Modern → Use Gemini 2.0 Flash for the most globally balanced, exam-aligned quizzes, with Claude Sonnet 3.7 as your next choice
Other AP Subjects → While other subjects weren’t explicitly benchmarked, based on our observations, we recommend trying LearnLM, Claude Sonnet 3.7, and Gemini 2.0 Flash to see which works best for you
Want to know what not to do? Don’t just use whatever model. They might give you shallow questions, off-topic content, or prep that doesn’t align with the AP exam. Stick with recommended models.
Stay in the Loop
We’re just getting started! Follow us for future benchmark reports on a wide variety of topics. Want to see how your favorite model performs, or want to see something benchmarked? @ us and let us know what you want to see!
And good luck on your AP exams!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shawn Sullivan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
