Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Disrupting Traditional Banking System
 Someshwar Mashetty
Someshwar Mashetty
Abstract Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is revolutionizing the financial landscape by offering open, permissionless financial services that operate without traditional intermediaries. Built primarily on blockchain technology, DeFi leverages smart contracts to facilitate lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management. This paper explores DeFi's key principles, its impact on traditional banking, advantages, risks, and future trends.
Introduction DeFi refers to a financial ecosystem that utilizes blockchain technology to provide decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services. Unlike conventional financial institutions, DeFi platforms operate on transparent protocols where users maintain direct control over their assets. DeFi's rise has gained momentum due to its promise of greater financial inclusivity, enhanced security, and reduced reliance on centralized authorities.
Core Principles of DeFi DeFi is built on several foundational concepts:
Decentralization: DeFi applications operate on blockchain networks, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks or brokers.
Smart Contracts: Automated self-executing contracts encoded on blockchain networks that enable secure and transparent financial transactions.
Interoperability: DeFi platforms often integrate across multiple blockchain networks to facilitate asset transfers and liquidity.
Transparency: Blockchain's immutable ledger ensures transaction data is publicly accessible and verifiable.
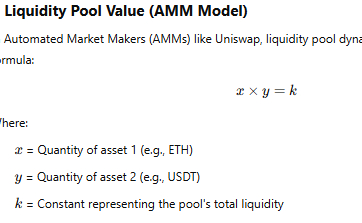
Key DeFi Applications DeFi platforms offer a wide range of services that mimic traditional financial systems:
Lending and Borrowing: Platforms such as Aave and Compound enable users to lend or borrow assets without intermediaries, earning interest or gaining liquidity.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Uniswap and SushiSwap allow users to trade digital assets directly without centralized control.
Yield Farming and Staking: DeFi users earn rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized protocols.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies such as DAI are pegged to fiat currencies, offering price stability in volatile crypto markets.
Insurance Protocols: Platforms like Nexus Mutual provide decentralized insurance services to mitigate risks in DeFi investments.

Impact on Traditional Banking Systems DeFi's rapid growth is disrupting traditional banking systems in several key areas:
Disintermediation: By eliminating middlemen, DeFi platforms reduce transaction fees and enable faster settlements.
Enhanced Financial Inclusion: DeFi platforms provide financial services to unbanked populations worldwide by allowing anyone with internet access to participate.
Improved Transparency: Traditional banking systems rely on opaque processes, whereas DeFi offers open-source protocols visible to all participants.
Innovation in Financial Products: DeFi platforms introduce novel financial instruments such as flash loans and decentralized derivatives.
Advantages of DeFi
Accessibility: Anyone with a digital wallet can access DeFi services without credit checks or lengthy verification processes.
Security: Blockchain's cryptographic security minimizes risks of manipulation and fraud.
Control and Ownership: DeFi users maintain complete control of their private keys and assets.
Innovation and Flexibility: DeFi promotes rapid innovation, offering customizable financial products for diverse needs.
Risks and Challenges Despite its potential, DeFi presents several risks and challenges:
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Coding flaws can lead to exploits and financial losses.
Regulatory Uncertainty: DeFi platforms operate outside conventional financial regulations, posing compliance challenges.
Market Volatility: DeFi assets are often subject to extreme price fluctuations, increasing investor risk.
Scalability and Performance: Blockchain networks face scalability issues that can hinder transaction speeds and increase costs.
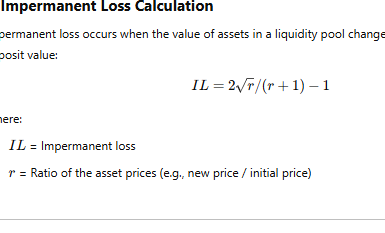
Future Trends in DeFi The DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups improve blockchain scalability and transaction speeds.
Cross-Chain Compatibility: Enhanced interoperability will allow seamless asset transfers across multiple blockchain networks.
Institutional Adoption: Traditional financial institutions are increasingly exploring DeFi integration for enhanced services.
Enhanced Security Solutions: Advances in auditing tools and smart contract security are improving DeFi's resilience against cyber threats.
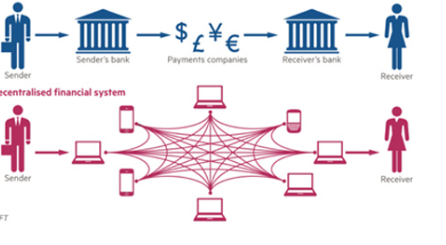

Conclusion Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a transformative shift in the financial landscape, challenging traditional banking models with innovative, open-source financial solutions. By offering greater accessibility, transparency, and efficiency, DeFi has the potential to redefine global finance. However, addressing risks related to security, regulation, and volatility remains crucial for sustainable growth. As DeFi continues to mature, its integration with traditional finance could lead to a more inclusive and secure financial ecosystem.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Someshwar Mashetty directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

