Phishing: How Not to Become a Victim of Cybercriminals
 Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn
Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn
Introduction: What is Phishing?
Phishing is one of the most common methods of cybercrime, where fraudsters attempt to gain access to your personal information (passwords, credit card numbers, bank details) through deception. They use fake emails, messages, websites, or calls that masquerade as official requests from banks, social networks, or government organizations. The goal is to force you to voluntarily provide confidential data. Phishing is a major threat to internet security. According to statistics, 90% of all cyberattacks start with phishing messages.
It has become especially dangerous in Ukraine after the start of the russian aggression. Scammers exploit people's trust and emotions, creating fake fundraisers to help the army or victims.
A Real-Life Phishing Attack Scenario
Imagine: you receive an email from a "bank" with a message about suspicious activity on your account. In a panic, you click on the link, enter your data... and a few hours later, a large sum disappears from your card. Could this have been avoided? Yes! Let's understand how scammers operate and how not to fall into their trap.
The Psychology of Phishing: How Scammers Manipulate People
Phishing is not just a technical trick, but also a psychological attack. Scammers use our emotions and psychological weaknesses to make us act thoughtlessly.
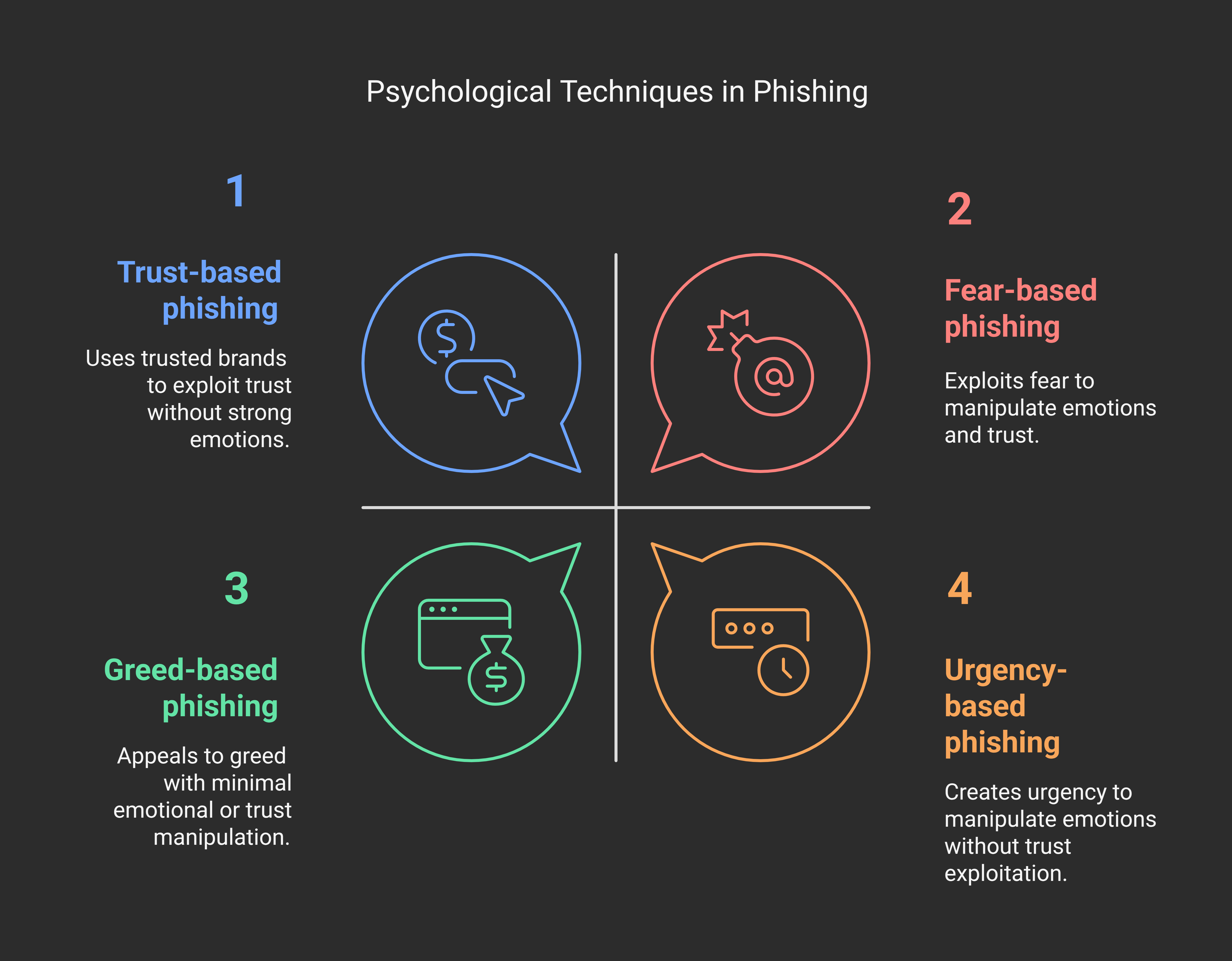
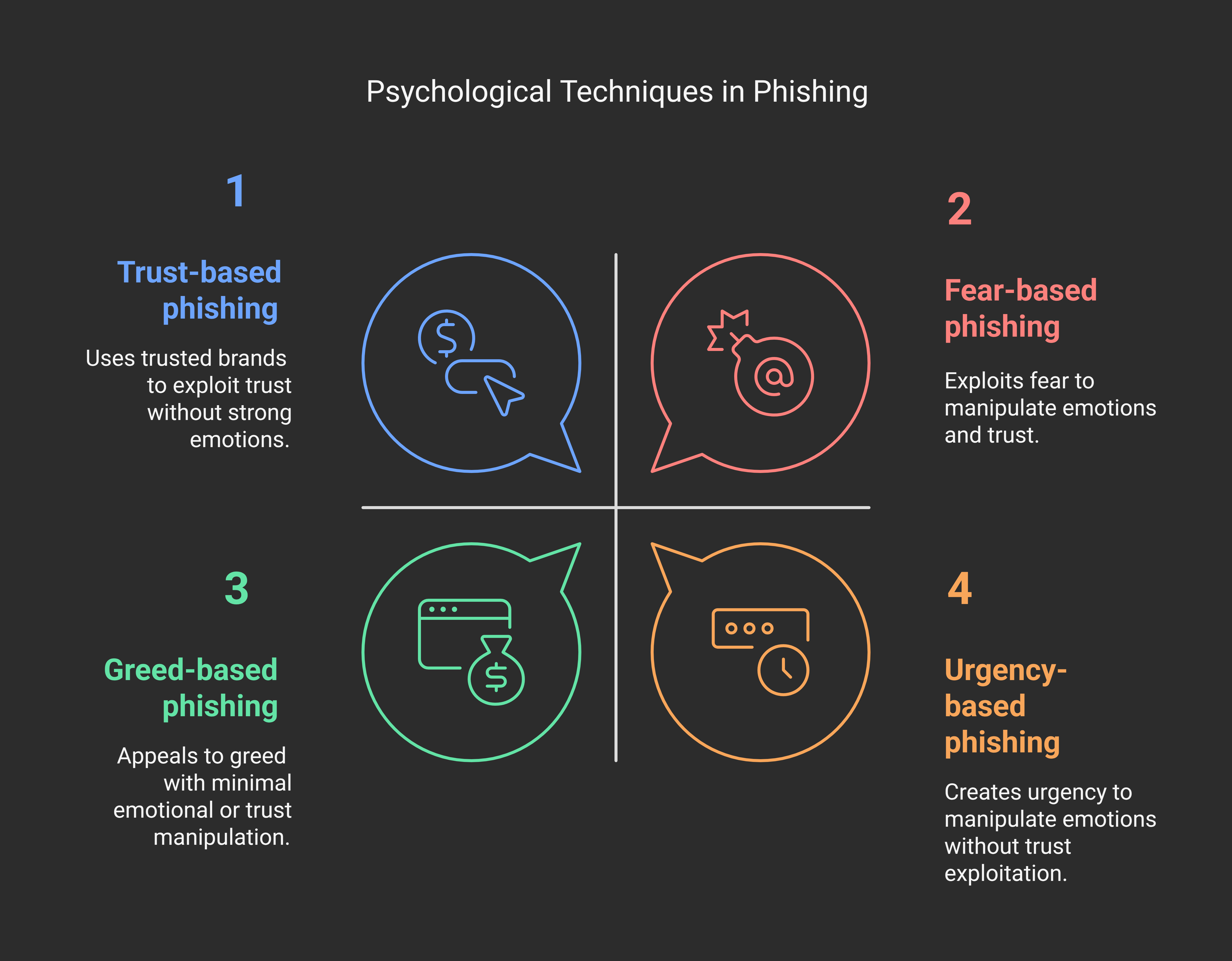
Key Psychological Techniques Used by Phishers
Phishing is more than a technical attack; it's a clever psychological manipulation. Scammers leverage your fears, greed, trust, and sense of urgency to provoke impulsive actions.
Example of a Real Attack
You receive a message: "Your card will be blocked! Urgently follow the link and confirm your data." You panic, follow the link, enter your data... Money disappears from your account.
How Not to Get Caught?
- Never enter passwords or financial data through links in emails or SMS messages.
Types of Phishing Attacks
There are many different types of phishing, so it is important to be aware of them all. Be careful with emails, text messages, and phone calls from strangers.
Why are Smartphones Vulnerable?
Owners are less likely to check URLs.
Mobile browsers do not show the full website address.
People are used to scanning QR codes without checking their source.
Main Threats
Fake Mobile Apps: Look like official apps, but steal passwords.
QR Phishing: Scammers place fake QR codes in public places.
Phishing Websites for Smartphones: Look like real ones, but collect data.
Tip: Download apps only from official stores (Google Play, App Store).
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Phishing
Scammers use artificial intelligence (AI) to:
Create realistic fraudulent messages that are difficult to distinguish from real ones.
Automate attacks by sending millions of emails at once.
Bypass security systems by analyzing victim behavior.
How Not to Become a Victim of Phishing: Security Tips
✅ Check the sender's address. If a bank writes to you, check the official website.
✅ Do not follow suspicious links in emails, SMS messages, or messengers.
✅ Use two-factor authentication (2FA) for important accounts.
✅ Update your antivirus and operating system.
✅ Do not share passwords or bank details by phone or message.
Phishing During the russian aggression against Ukraine
Scammers pose as volunteer organizations.
Use fake fundraising.
Forge government services (e.g., "IDP Assistance").
Verify information and do not transfer money to dubious accounts.
Conclusion: How to Be Prepared for Phishing Attacks in the Future
Phishing is evolving – scammers are becoming more sophisticated, their messages more realistic. Be vigilant, check any information before entering personal data. Educate others – the more people know about phishing, the harder it is for scammers to deceive.
❗ Remember: the best defense is your caution and common sense.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Volodymyr "anumag" Voloshyn directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
