How to Build a Dockerfile, Push to Docker Hub, and Run a Container with the image.
 Nweke Henry
Nweke Henry
Docker is a powerful tool for packaging applications into portable containers that can run consistently across different environments. In this guide, I'll walk you through the process of creating a Dockerfile, pushing the image to Docker Hub, and running a container from the image.
NOTE
Before we begin, make sure you have the following installed:
Docker: Install Docker from the official website.
Docker Hub Account: Sign up for a free account at Docker Hub.
Basic Knowledge of Terminal/Command Line.
Repository
Step 1: Write Dockerfile
The Dockerfile is a blueprint for building your Docker image. It contains instructions on how to set up the environment and run your application.
first create a directory using the command code mkdir and enter the directory using the command code cd name of directory
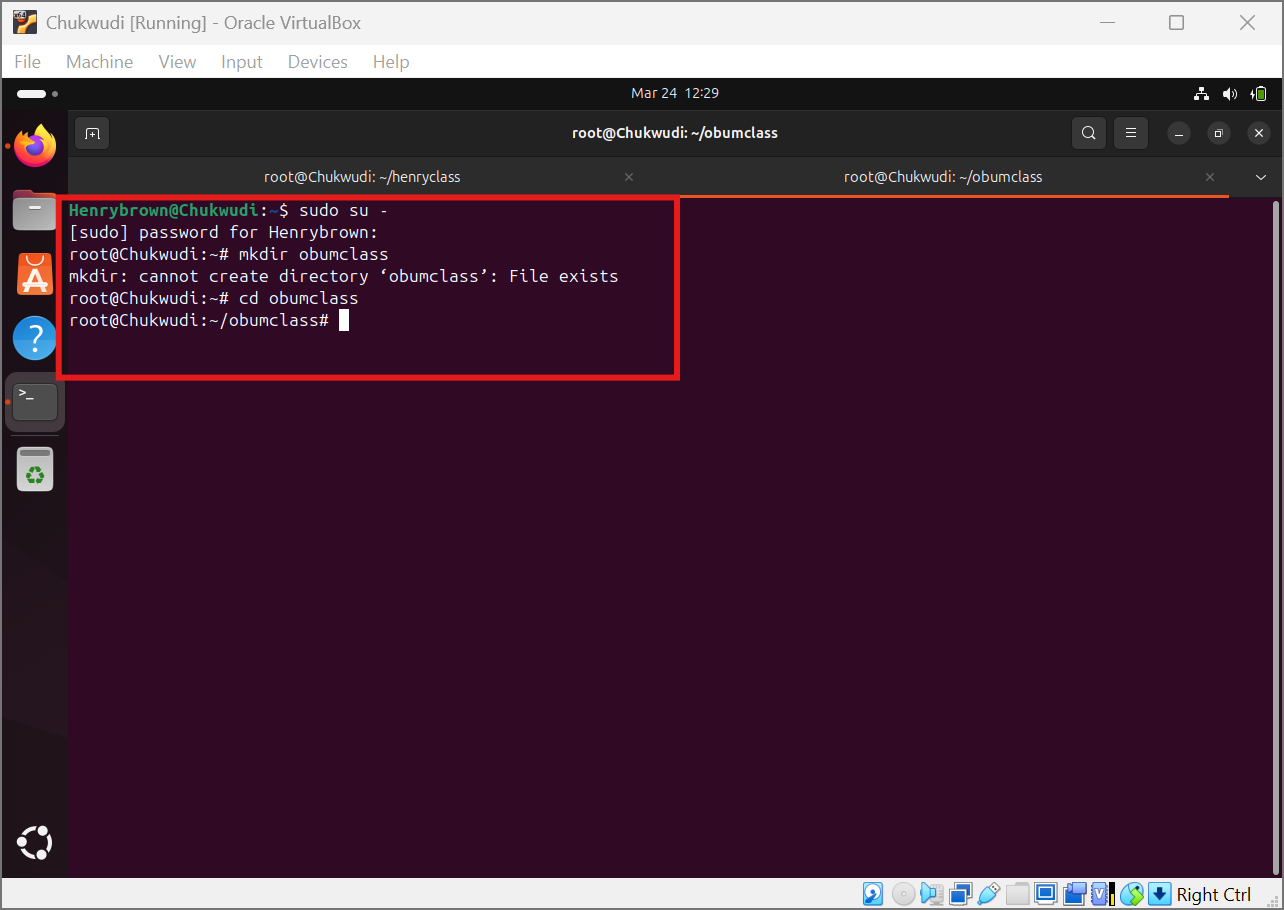
.
Next step is to create a dockerfile and note you must name it or use the name dockerfile, using the command code vim dockerfile.
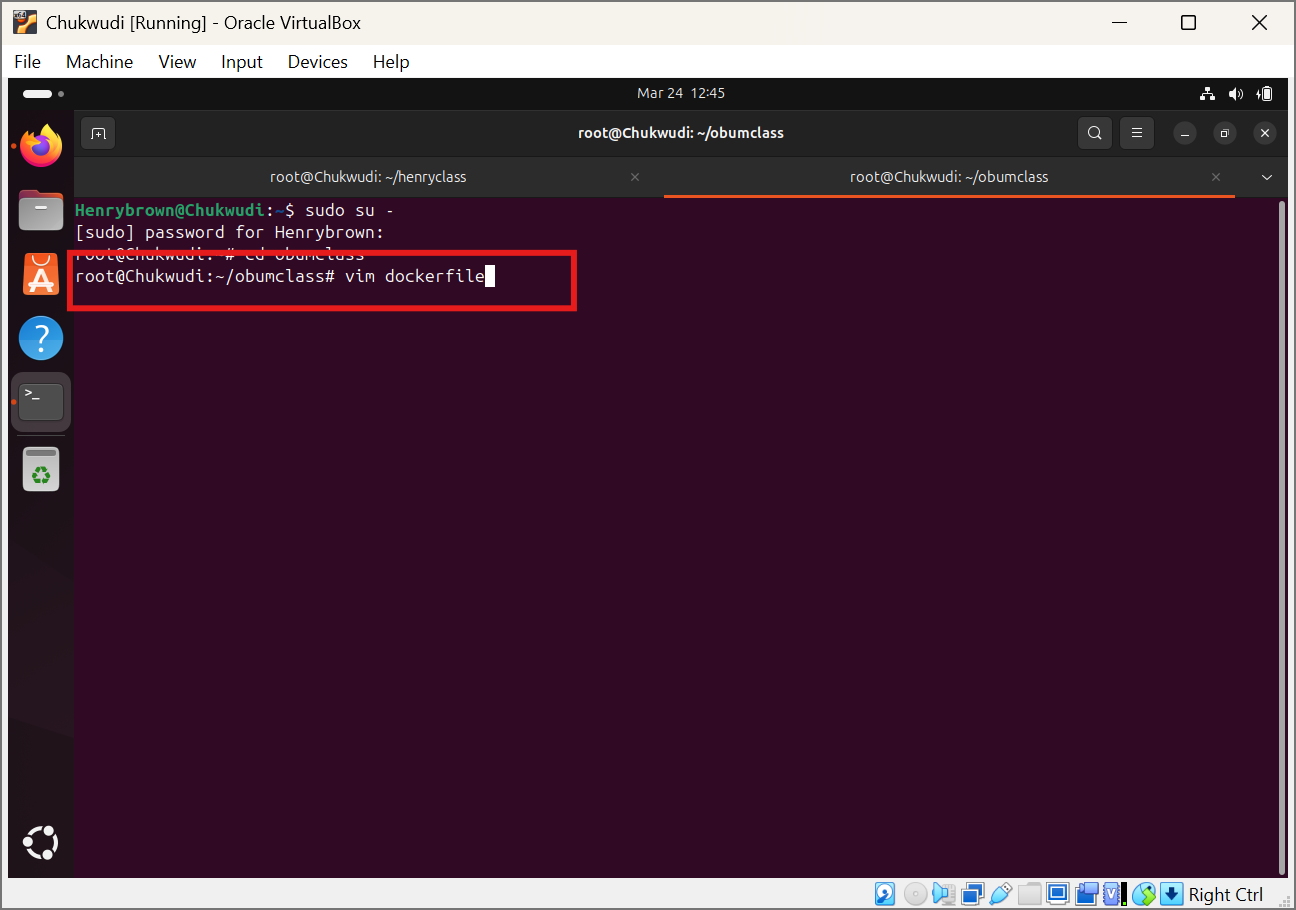
Input your docker instructions: To save and exit from dockerfile press the esc button and column then wq and enter
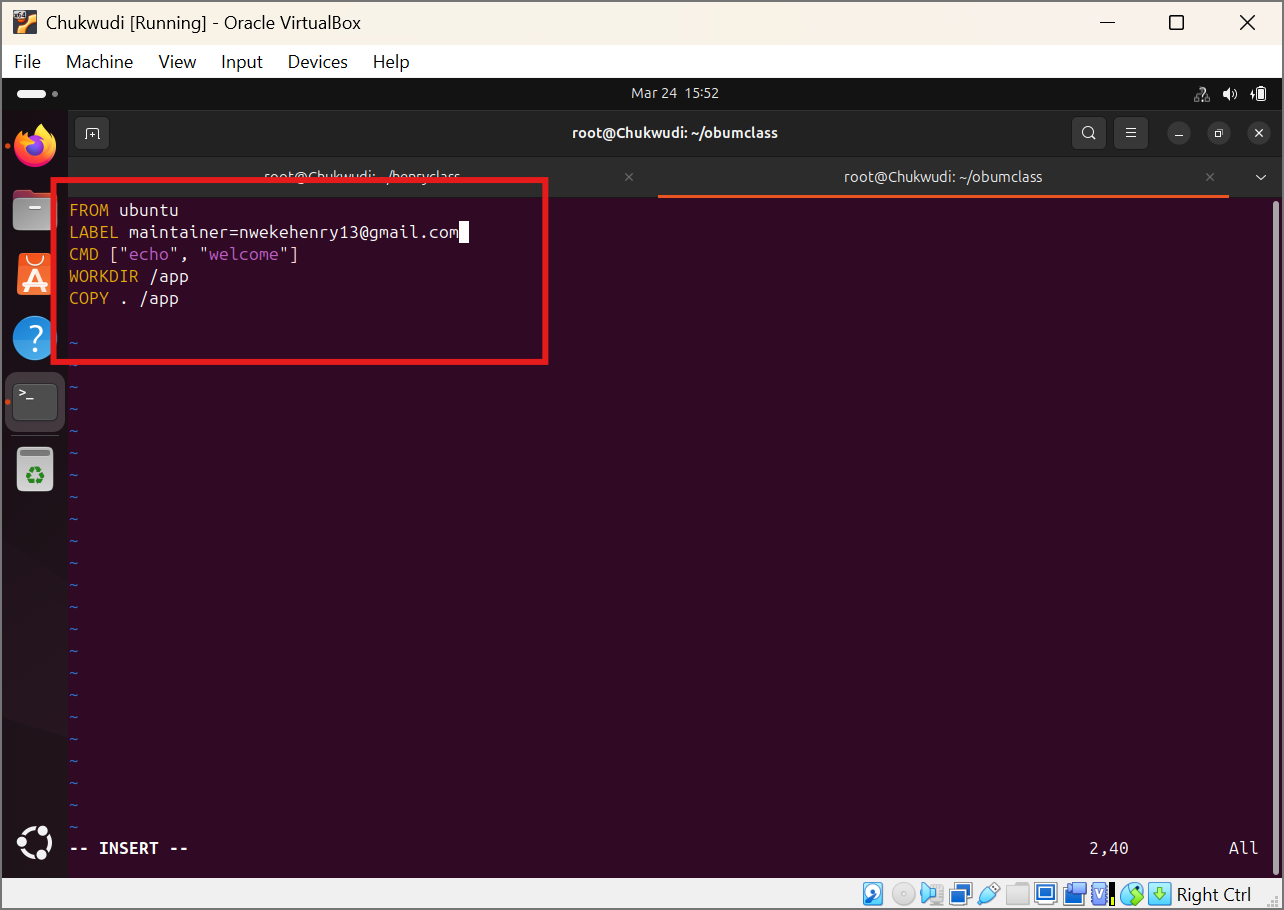
Step 2: Build the Docker Image
Now that we have a Dockerfile, let's build the Docker image.
Run the following command to build the image:
docker build -t [name your image] .-t [name your image]: Tags the image with the name.
.: Specifies the build context (current directory)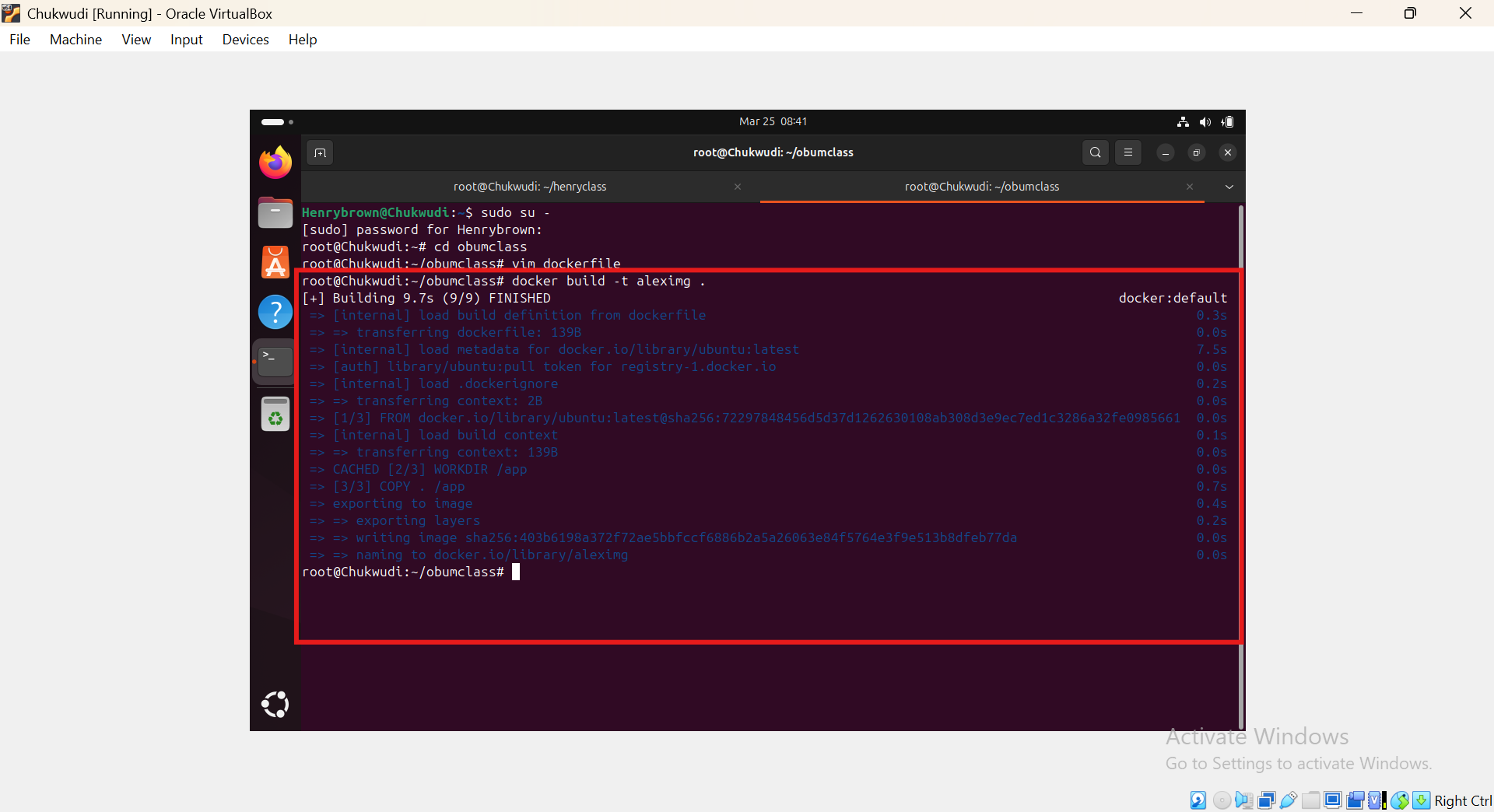
Verify the image was created:
docker images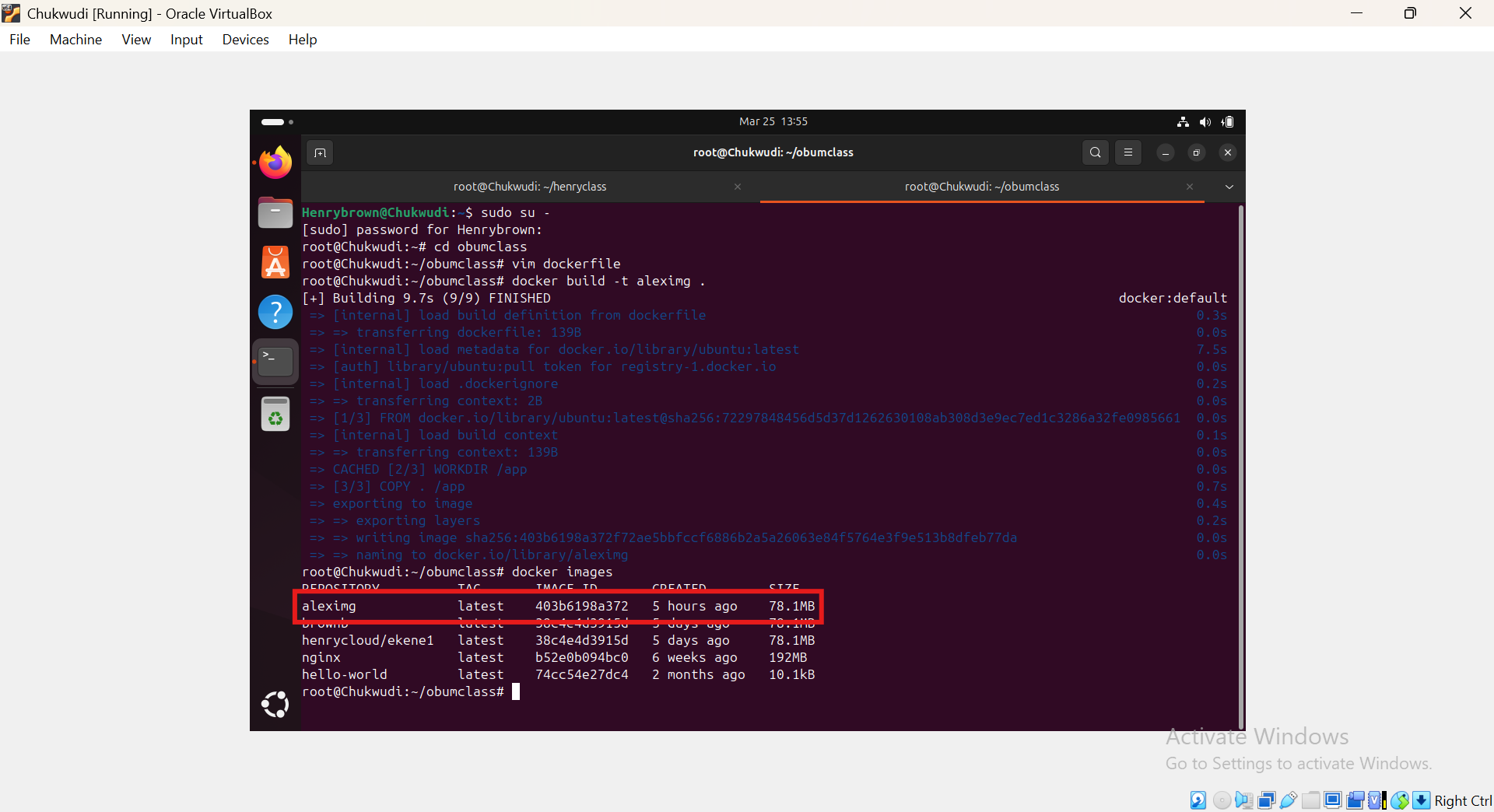
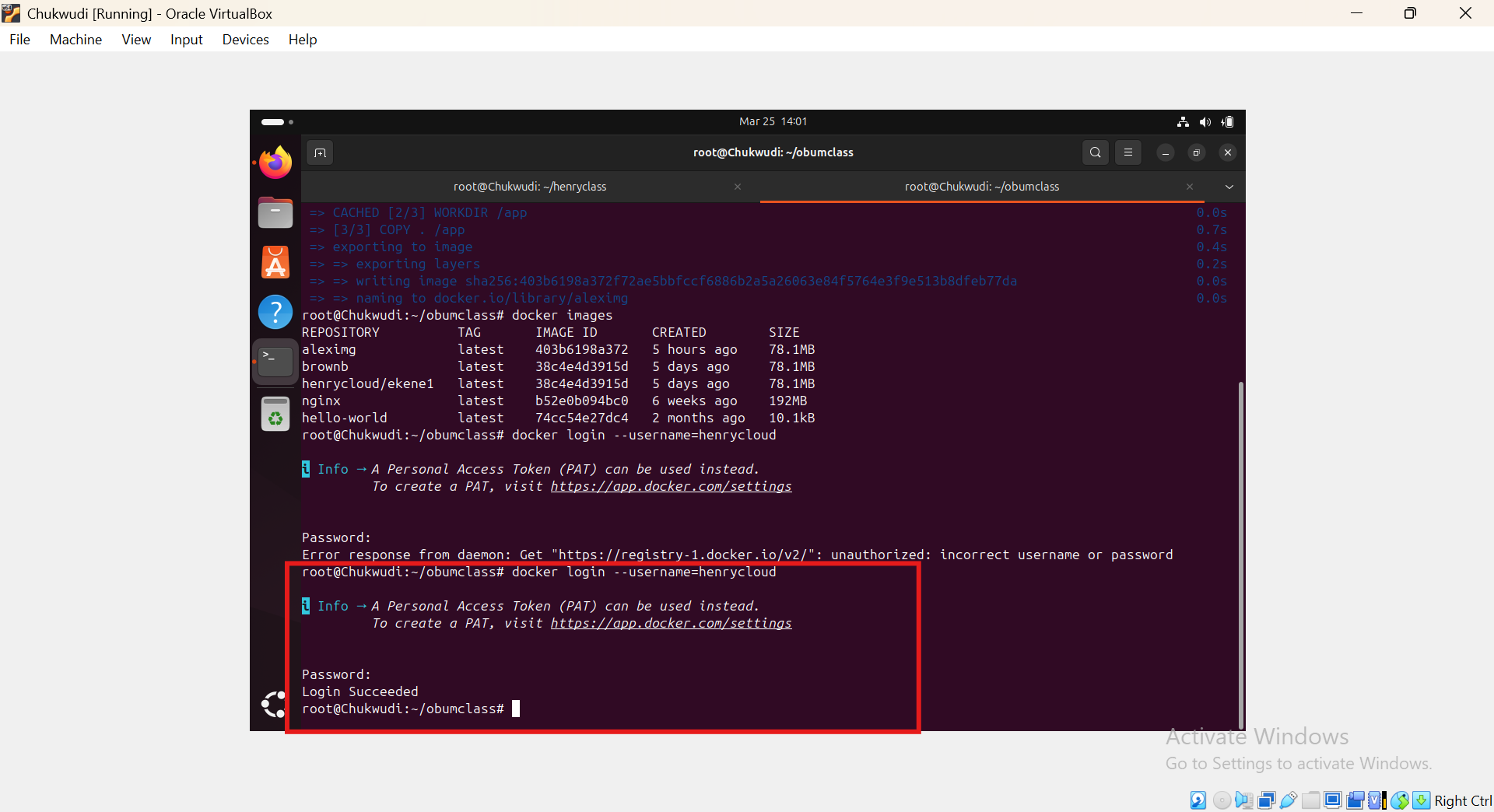
3, NEXT We have to login our docker hub from the terminal using the command docker login --username=docker hub user account enter. you will be asked for password, once you are in you will get login succeeded.
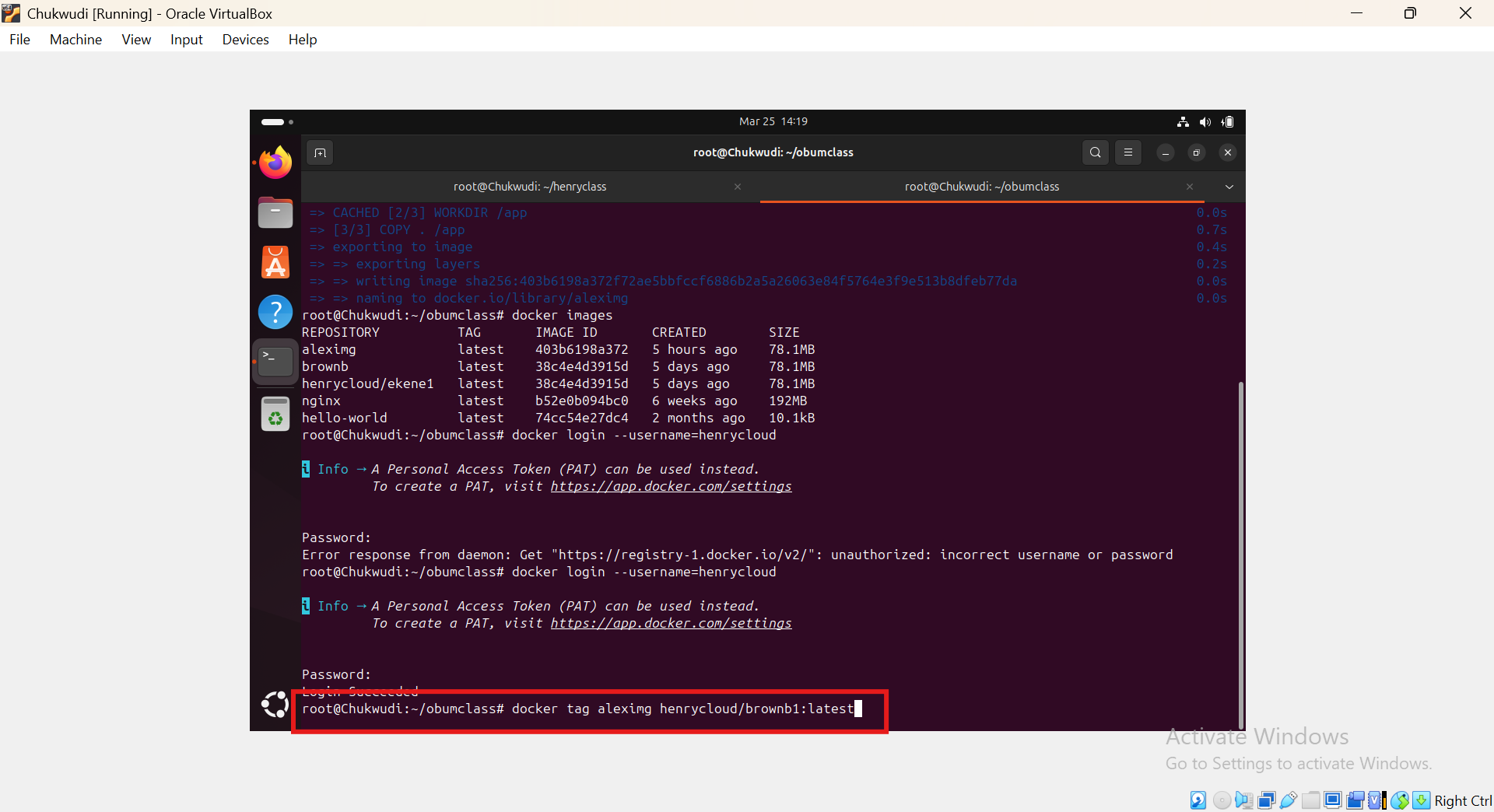
4, Tag the image with your Docker Hub username: we do this so so docker can recognize the image.
docker tag your imagename <your-dockerhub-username>/repositoryname:latest
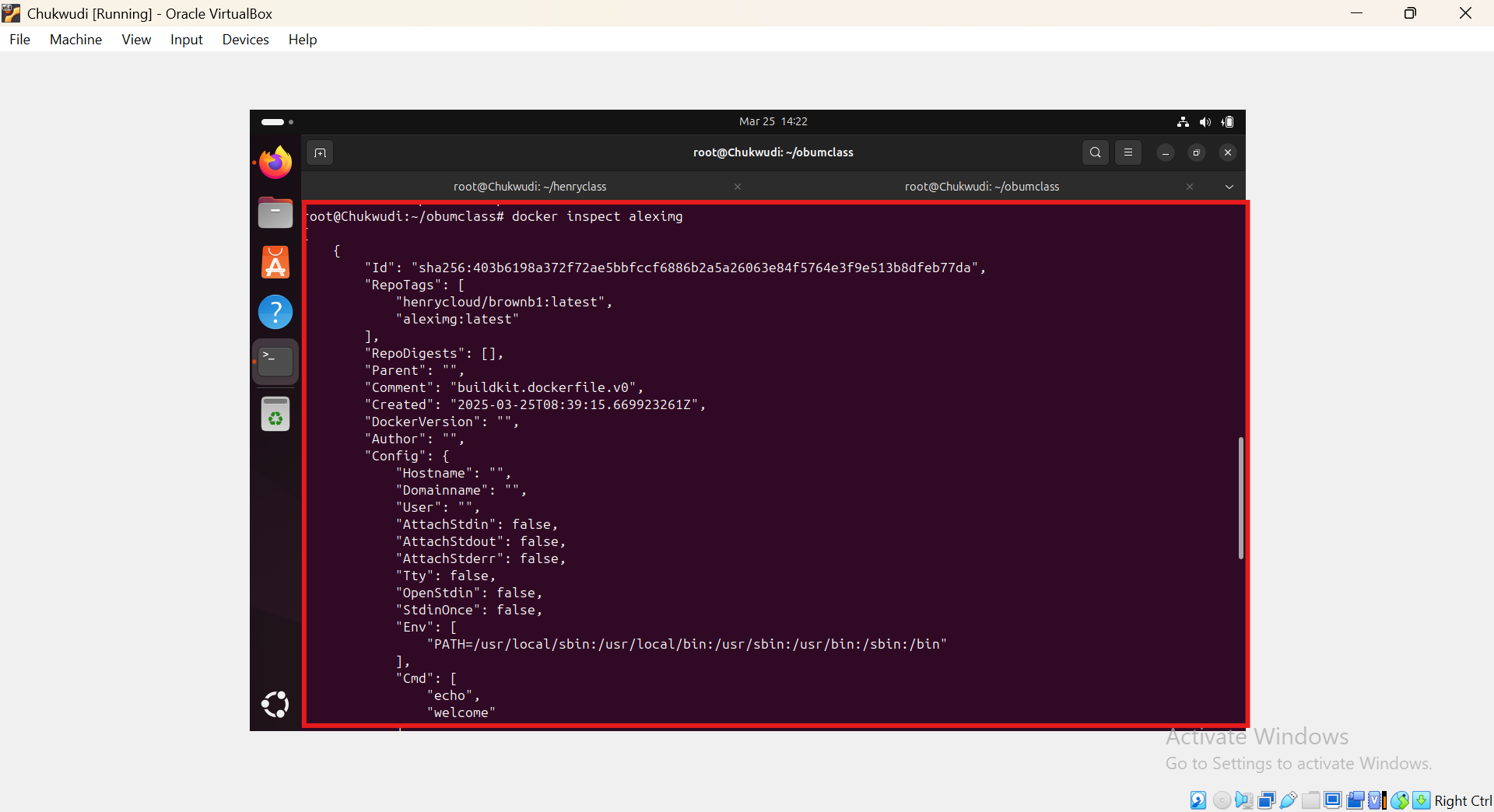
5, At this point we need to inspect the image using the command code docker inspect enter
6, Push the image to Docker Hub:
docker push <your-dockerhub-username>/repositoryname:latest
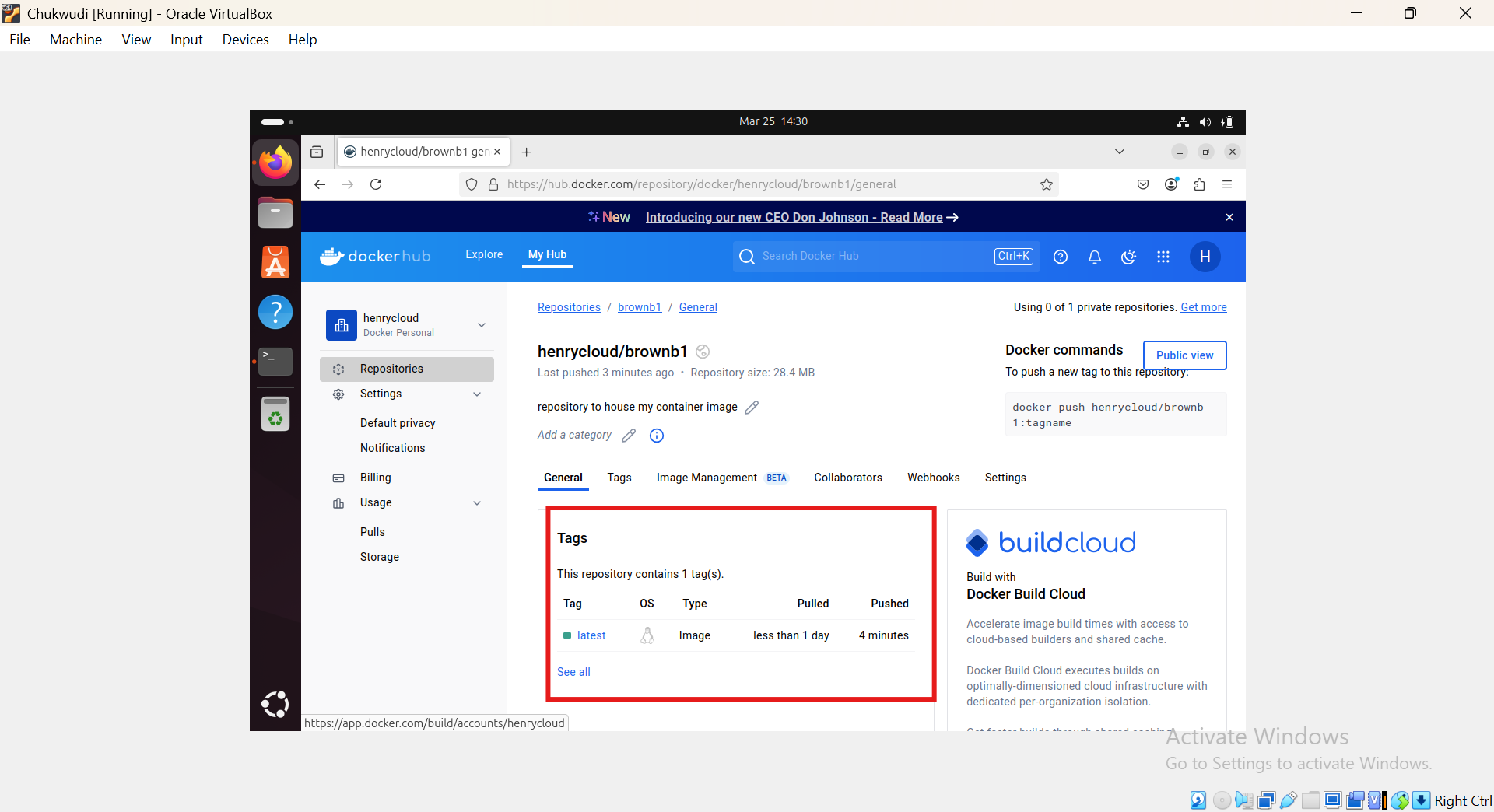
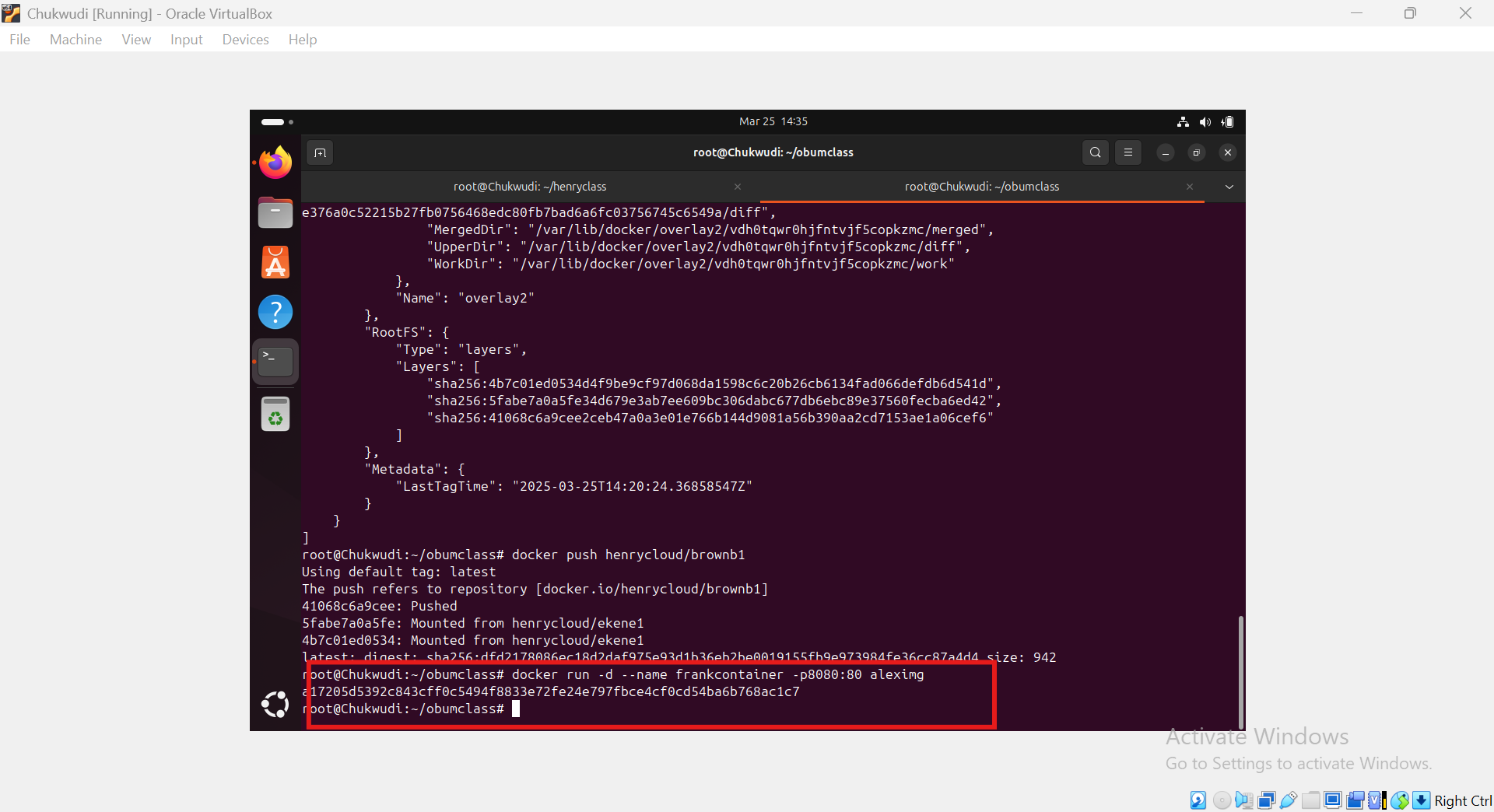
After Pushing: we will use the image to create a container by running the command code docker run -d --name give the container a name -p8080:80 name of image enter
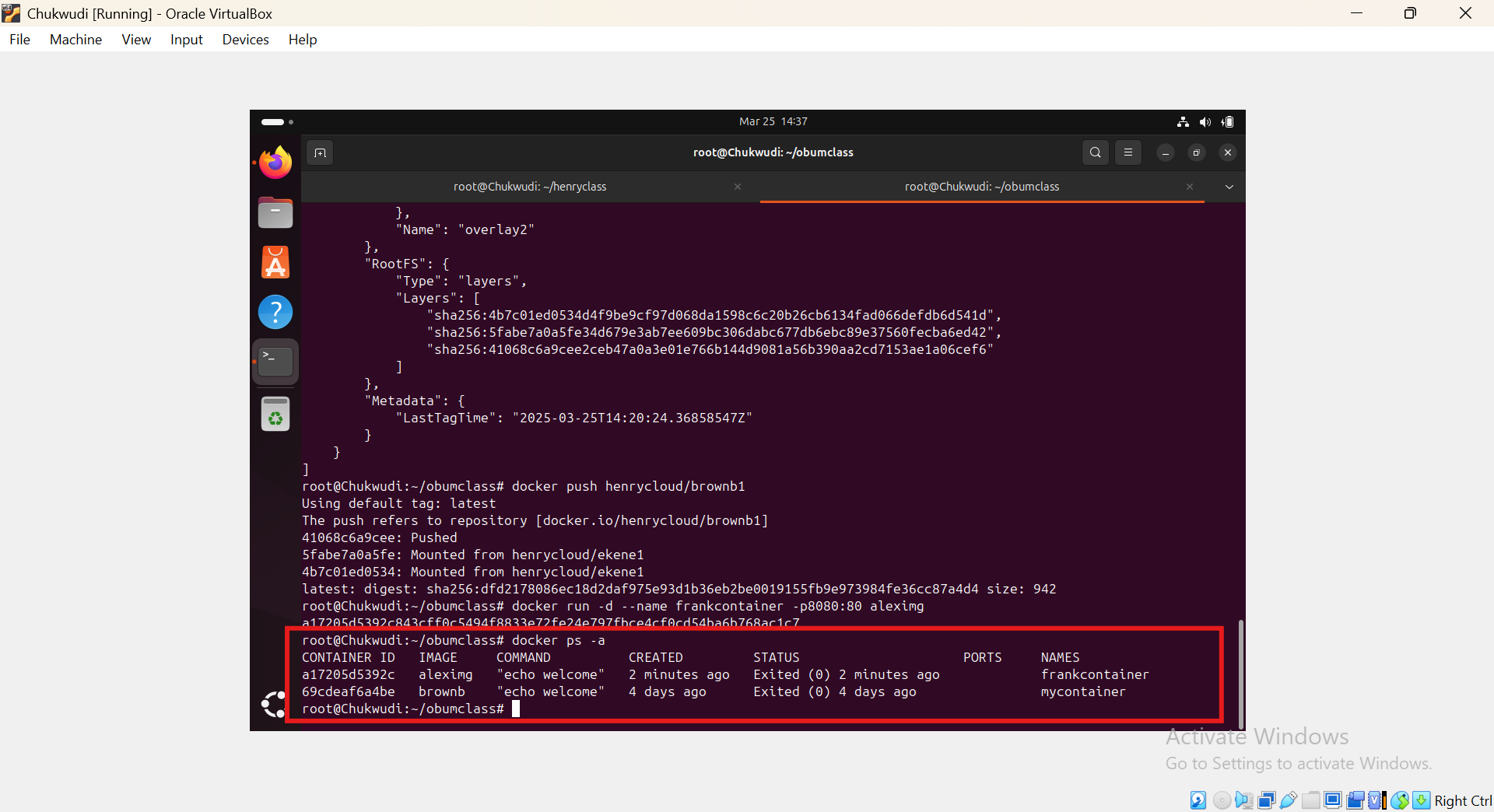
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've successfully built a Dockerfile, pushed the image to Docker Hub, and run a container. Docker is a powerful tool that simplifies application deployment and ensures consistency across environments. With this knowledge, you can start containerizing your own applications and sharing them with the world.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nweke Henry directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
