Sustainable Railway Manufacturing: Reducing Carbon Footprints in Production
 Rama Chandra Rao Nampalli
Rama Chandra Rao Nampalli
Introduction
Railway transportation is widely regarded as one of the most sustainable modes of transport due to its energy efficiency and lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions compared to road and air transport. However, the sustainability of railway systems extends beyond their operation to the manufacturing phase, where significant carbon emissions occur. Sustainable railway manufacturing aims to minimize environmental impacts by adopting green technologies, optimizing material use, and reducing energy consumption during production. This paper explores the challenges and strategies associated with reducing carbon footprints in railway manufacturing.

Carbon Footprint in Railway Manufacturing
The carbon footprint of railway manufacturing primarily arises from the extraction and processing of raw materials, energy-intensive production processes, and transportation logistics. The key contributors include:
Steel and Aluminum Production – The production of steel and aluminum, essential materials for rail tracks and train bodies, generates substantial carbon emissions. Steel manufacturing alone contributes around 7-9% of global CO₂ emissions.
Energy Use in Factories – Railway manufacturing plants consume vast amounts of energy in welding, casting, and machining, often relying on fossil fuels.
Supply Chain Emissions – Transporting raw materials and components adds to the overall carbon footprint due to reliance on diesel-powered trucks and ships.
Waste Generation – Material wastage and inefficient use of resources during manufacturing contribute to environmental degradation.
Strategies for Sustainable Railway Manufacturing
To reduce the carbon footprint of railway production, manufacturers are adopting various sustainable practices, including the use of green materials, energy-efficient processes, and circular economy principles.
EQ.1.Energy Consumption in Manufacturing
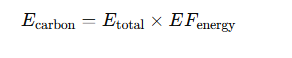
1. Green Materials and Recycling
Using sustainable materials can significantly reduce emissions:
High-Strength, Low-Carbon Steel – Modern steel-making techniques, such as electric arc furnaces (EAF) and hydrogen-based reduction, lower CO₂ emissions compared to traditional blast furnaces.
Recycled Aluminum and Steel – Utilizing recycled metals instead of virgin materials reduces energy consumption by up to 95%.
Biodegradable and Composite Materials – Advanced composite materials and bio-based polymers can replace certain components, reducing reliance on fossil fuel-derived plastics.
2. Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Reducing energy consumption in production is a key strategy for sustainability:
Renewable Energy Integration – Manufacturing plants are increasingly adopting solar, wind, and hydroelectric power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Energy-Efficient Machinery – Advanced automation, AI-driven optimization, and smart manufacturing technologies minimize energy waste.
Heat Recovery Systems – Utilizing waste heat from industrial processes for internal energy needs improves overall efficiency.
3. Sustainable Supply Chains
Minimizing transportation emissions and optimizing logistics enhances sustainability:
Local Sourcing of Materials – Reducing transportation distances for raw materials lowers emissions associated with long-haul shipping.
Green Logistics and Electric Transport – Utilizing electric or hydrogen-powered trucks for material transport can significantly cut emissions.
Eco-Friendly Packaging – Reducing packaging waste and using biodegradable materials contribute to lower environmental impact.
4. Circular Economy and Waste Reduction
The adoption of circular economy principles ensures long-term sustainability:
Remanufacturing and Refurbishment – Extending the life of railway components through repair and repurposing reduces the demand for new materials.
Waste Recycling and Upcycling – Scrap metal, plastics, and other waste materials are reintroduced into production cycles rather than being discarded.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing – These techniques minimize material waste by using only the necessary amount of raw materials for component fabrication.

Case Studies in Sustainable Railway Manufacturing
Several railway manufacturers have successfully implemented sustainable practices:
Alstom’s Green Rail Solutions – Alstom has integrated eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production, and hydrogen-powered trains to reduce carbon emissions.
Siemens Mobility – Siemens has invested in sustainable manufacturing by utilizing 3D printing, renewable energy, and lightweight train designs to lower emissions.
Japan’s Shinkansen Rail – Japan’s high-speed rail system has incorporated recycled materials and energy-efficient processes to minimize its carbon footprint.
Eq.2.Carbon Savings from Recycling
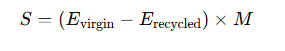
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in achieving fully sustainable railway manufacturing:
High Initial Investment – Transitioning to sustainable practices requires substantial capital investment in new technologies and infrastructure.
Supply Chain Disruptions – Securing sustainable raw materials and ensuring consistency in supply chains can be complex.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers – Inconsistent environmental regulations across different countries create challenges for global manufacturers.
Future advancements in green hydrogen, carbon capture, and AI-driven production optimization offer promising pathways for further reducing emissions in railway manufacturing. Governments and industries must collaborate to establish policies, incentives, and research initiatives that support sustainable practices.

Conclusion
Sustainable railway manufacturing is essential for minimizing the environmental impact of rail transport. By adopting green materials, energy-efficient production processes, sustainable supply chains, and circular economy principles, manufacturers can significantly reduce carbon emissions. While challenges remain, ongoing technological advancements and policy support will drive the industry toward a greener future. Investing in sustainability not only benefits the environment but also enhances economic efficiency and corporate responsibility in the railway sector.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rama Chandra Rao Nampalli directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
