Eco-Friendly Automotive Manufacturing: The Shift Towards Carbon-Neutral Factories
 Anil Lokesh Gadi
Anil Lokesh Gadi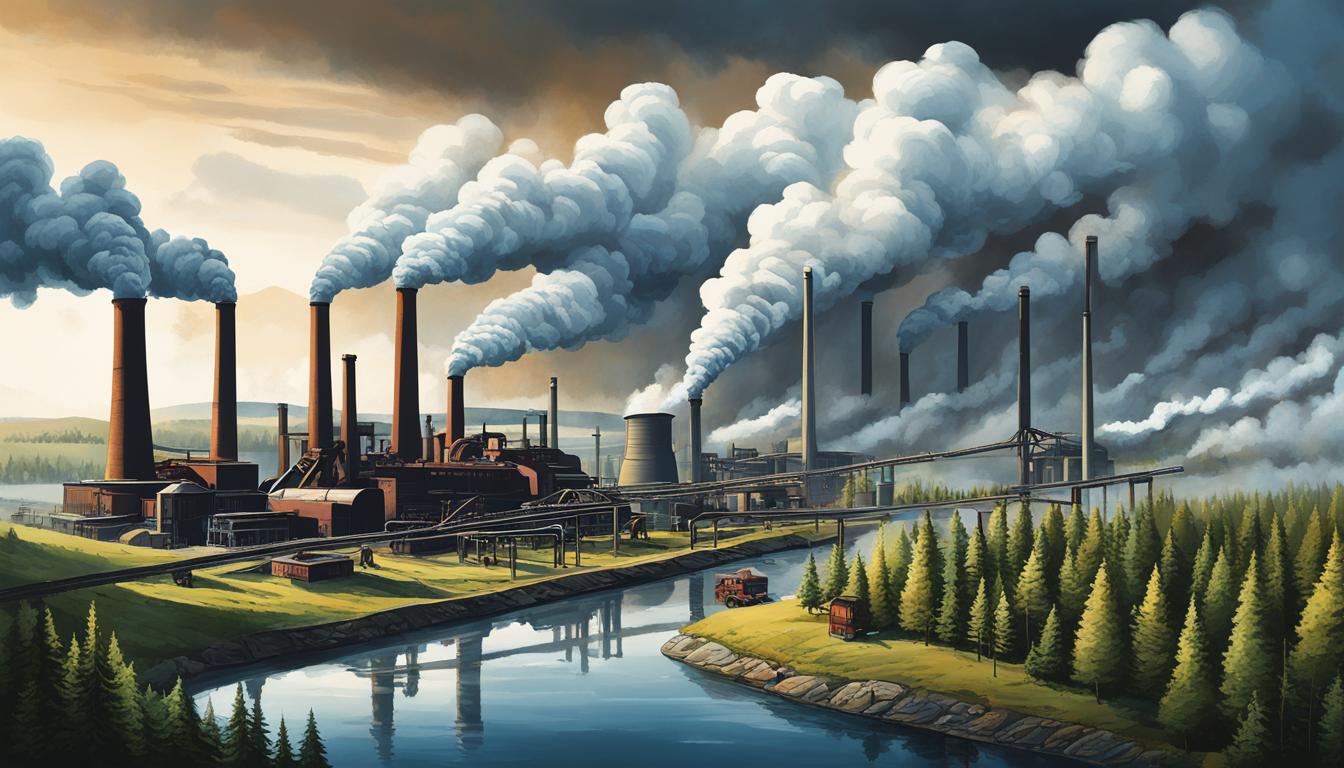
Introduction
The automotive industry has long been associated with environmental concerns due to its significant carbon footprint, from raw material extraction to vehicle production and disposal. However, as climate change intensifies, there is a growing push toward sustainability. Leading automakers are increasingly focusing on eco-friendly manufacturing practices, particularly aiming for carbon-neutral factories. This transition is driven by regulatory pressures, corporate sustainability goals, and consumer demand for greener products.
The Need for Carbon-Neutral Manufacturing
The transportation sector accounts for nearly 20% of global CO₂ emissions, and a significant portion of this comes from vehicle production. Traditional manufacturing processes rely heavily on fossil fuels, generate large amounts of waste, and consume vast amounts of water and energy. To mitigate these environmental impacts, companies are adopting carbon-neutral strategies that emphasize renewable energy, resource efficiency, and waste reduction.
Regulatory and Market Drivers
Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter environmental policies, such as the European Union’s Green Deal, the Paris Agreement targets, and China’s carbon neutrality commitment by 2060. Additionally, consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, prompting automakers to rethink their manufacturing strategies. Companies that fail to adapt risk falling behind in a competitive market where eco-consciousness is becoming a key purchasing factor.

Strategies for Carbon-Neutral Automotive Factories
1. Renewable Energy Integration
One of the most effective ways to achieve carbon neutrality in automotive manufacturing is through the adoption of renewable energy sources. Many automakers are investing in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power to run their facilities.
Tesla’s Gigafactories are designed to operate on 100% renewable energy, leveraging solar panels and energy storage systems.
Volkswagen’s Zwickau Plant in Germany, which produces electric vehicles (EVs), is powered entirely by green energy.
BMW’s Leipzig Plant uses wind power to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
By shifting to renewable energy, manufacturers significantly cut their carbon emissions while also reducing operational costs in the long run.
Eq.1.Carbon Footprint Calculation
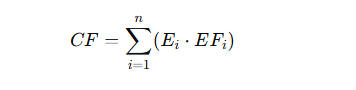
2. Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Automakers are implementing innovative technologies to enhance energy efficiency in their production lines. These include:
Smart Manufacturing & Industry 4.0: The use of AI, IoT, and data analytics helps optimize energy usage by predicting equipment maintenance needs and reducing downtime.
Lightweight Materials: Replacing traditional steel with aluminum, carbon fiber, or recycled materials reduces energy consumption in manufacturing while making vehicles more fuel-efficient.
Advanced Robotics: Automated processes minimize material waste and improve precision, leading to lower energy use per unit produced.
For instance, Toyota’s "lean manufacturing" approach minimizes waste and energy consumption by streamlining production processes and reducing inefficiencies.
3. Circular Economy & Recycling
Sustainable automotive manufacturing is also moving towards a circular economy, where waste is minimized and materials are continuously reused. This includes:
Closed-loop recycling: Companies are reclaiming and reusing materials like aluminum, steel, and plastics in vehicle production.
Battery Recycling: As EV adoption grows, recycling lithium-ion batteries is crucial. Automakers like Tesla, Nissan, and Volkswagen are developing programs to repurpose used batteries for energy storage.
Biodegradable and Recyclable Materials: Some manufacturers are incorporating sustainable materials, such as plant-based plastics and natural fibers, into their vehicles.
4. Water Conservation and Waste Reduction
Water scarcity is a growing global issue, and the automotive sector is responding by reducing water consumption in production.
Ford’s "Zero Water Waste" initiative has reduced water use by millions of gallons annually through closed-loop water recycling systems.
BMW’s Sustainable Paint Shop in Leipzig uses 50% less energy and 70% less water compared to conventional systems.
Additionally, automakers are cutting down landfill waste by reusing and repurposing industrial by-products.
5. Carbon Offsetting and Sustainable Supply Chains
Even with significant improvements, some emissions are unavoidable. To counterbalance this, many companies engage in carbon offset programs, such as reforestation projects and carbon capture technologies.
Furthermore, the push for carbon neutrality extends beyond factory walls. Automakers are working with suppliers to ensure sustainable material sourcing. For example, Mercedes-Benz requires its battery suppliers to use only renewable energy in the production of EV batteries.

Eq.2.Renewable Energy Contribution
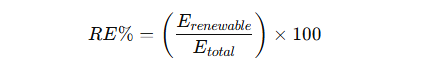
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite progress, achieving full carbon neutrality in automotive manufacturing remains challenging due to:
High Initial Costs: Investing in renewable energy, new technologies, and process overhauls requires substantial capital.
Supply Chain Complexity: Ensuring sustainability across a global supply chain is difficult due to varying regulations and standards.
Energy Storage Limitations: While renewable energy is promising, the intermittency of sources like solar and wind presents storage challenges.
However, advancements in battery technology, energy-efficient innovations, and stricter environmental policies are expected to accelerate the shift toward carbon-neutral factories.

Conclusion
Eco-friendly automotive manufacturing is no longer an option but a necessity. With increasing regulatory pressure, consumer demand, and environmental concerns, automakers are making significant strides toward carbon-neutral factories. Through renewable energy, energy-efficient processes, recycling, and sustainable supply chains, the industry is paving the way for a cleaner future. While challenges remain, continued innovation and investment in sustainability will drive the next era of green automotive production.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Anil Lokesh Gadi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
