Automated Incident Response Systems: How AI is Reducing Cyber Threat Impact
 Phanish Lakkarasu
Phanish Lakkarasu
Introduction
The growing complexity and frequency of cyber threats have made traditional incident response (IR) approaches inadequate for modern cybersecurity challenges. Cyberattacks such as ransomware, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and zero-day exploits require rapid detection and response to minimize damage. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in incident response by enabling automated systems that detect, analyze, and mitigate threats in real time. Automated Incident Response Systems (AIRS) leverage AI-driven analytics, machine learning (ML), and orchestration technologies to improve response efficiency, reduce human intervention, and minimize cyber threat impact. This research note explores the role of AI in automated incident response, key components of AIRS, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
The Role of AI in Automated Incident Response
AI enhances automated incident response by enabling real-time threat detection, intelligent decision-making, and swift mitigation. Its role in cybersecurity includes:
Threat Intelligence and Anomaly Detection – AI-driven systems continuously analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify deviations from normal activity, flagging potential threats before they escalate.
Automated Threat Containment – AI-powered Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms can isolate infected endpoints, block malicious IPs, and revoke compromised credentials without human intervention.
Predictive Incident Management – AI-based risk assessment models analyze past attack patterns and security logs to predict and preemptively mitigate potential threats.
Forensic Analysis and Learning – AI accelerates post-incident investigations by identifying attack vectors, root causes, and affected assets, allowing for continuous improvement of security protocols.
Eq.1.Threat Probability Estimation
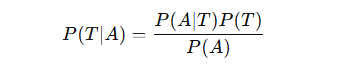
Key Components of AI-Driven Automated Incident Response Systems
A comprehensive AIRS framework consists of the following core components:
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Classification – Machine learning algorithms analyze security data to detect and classify threats based on severity and risk level. Behavioral analytics further enhance detection accuracy.
Security Event Correlation and Analysis – AI-driven Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems aggregate and analyze logs from multiple sources, providing real-time insights into potential security incidents.
Automated Response and Mitigation – AI-based response engines execute predefined actions such as quarantining malware, enforcing security patches, or adjusting firewall rules based on threat intelligence.
Incident Prioritization and Risk Scoring – AI assigns risk scores to incidents, enabling security teams to focus on the most critical threats while automating routine responses.
Continuous Learning and Adaptive Defense – AI models continuously learn from past incidents, improving response strategies and adapting to evolving cyber threats.

Benefits of AI-Driven Automated Incident Response
The integration of AI into incident response delivers several key benefits:
Faster Threat Containment – AI-powered automation significantly reduces the time taken to detect and neutralize cyber threats, minimizing the potential damage of attacks.
Improved Accuracy and Reduced False Positives – AI models refine threat detection by analyzing vast datasets, reducing errors and ensuring that security teams focus on genuine threats.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings – Automating repetitive tasks such as log analysis, alert triaging, and incident resolution allows security teams to allocate resources more effectively.
Scalability and Adaptability – AI-driven response systems can handle large-scale security incidents and adapt to new attack techniques without requiring constant manual updates.
Eq.2.Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR)
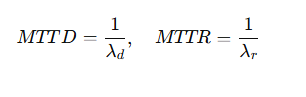
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, AI-driven automated incident response faces several challenges:
Adversarial AI and Evasion Techniques – Cybercriminals use AI to generate sophisticated attacks that evade automated detection systems.
Data Privacy and Compliance Concerns – AI-based IR systems require extensive access to security logs and network data, raising concerns about regulatory compliance and privacy protection.
Implementation Complexity and Costs – Deploying and maintaining AI-driven response systems requires significant investment in infrastructure, talent, and continuous model training.
False Positives and Overreliance on Automation – While AI reduces false positives, misclassification of benign activities as threats can lead to unnecessary disruptions. Over-reliance on automation without human oversight can also pose risks.

Future Trends in AI-Driven Incident Response
As AI continues to evolve, future advancements in automated incident response are expected to include:
Autonomous Cyber Defense Systems – AI-driven systems with autonomous decision-making capabilities will respond to cyber threats in real time with minimal human intervention.
AI-Powered Deception Technologies – Honeypots and deception-based AI systems will mislead attackers, providing cybersecurity teams with early warning signals.
Quantum-Safe AI Security – AI models will be developed to counter quantum computing threats, ensuring long-term cybersecurity resilience.
Federated Learning for Threat Intelligence – Decentralized AI models will enable secure sharing of threat intelligence across organizations without exposing sensitive data.

Conclusion
AI-driven Automated Incident Response Systems represent a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, enabling organizations to detect, analyze, and mitigate cyber threats in real time. By leveraging AI for threat detection, risk assessment, and automated mitigation, AIRS reduces response time, enhances accuracy, and improves overall security posture. However, challenges such as adversarial AI, compliance issues, and implementation costs must be addressed to maximize its effectiveness. As AI technology advances, the future of automated incident response will see greater autonomy, improved threat intelligence, and more resilient cyber defense mechanisms.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Phanish Lakkarasu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
