Simplifying PostgreSQL Upgrades with pgdump-each
 Alex Havok
Alex HavokUpgrading PostgreSQL to a new major version can be a daunting task, especially when ensuring data integrity and minimizing downtime. Traditional methods often involve complex procedures and significant manual intervention. Enter pgdump-each, a command-line tool designed to streamline and secure the backup and restoration process during PostgreSQL major version upgrades.
What is pgdump-each?
pgdump-each is a CLI utility that facilitates concurrent logical backups and restores of all databases within a PostgreSQL cluster. It's particularly tailored for major version upgrades, providing a safer and more efficient alternative than writing bash scripts for this purpose (that are not allow concurrent processing).
🎬 Demo: dump cluster (version 16, port 5432) and restore on cluster (version 17, port 5433).
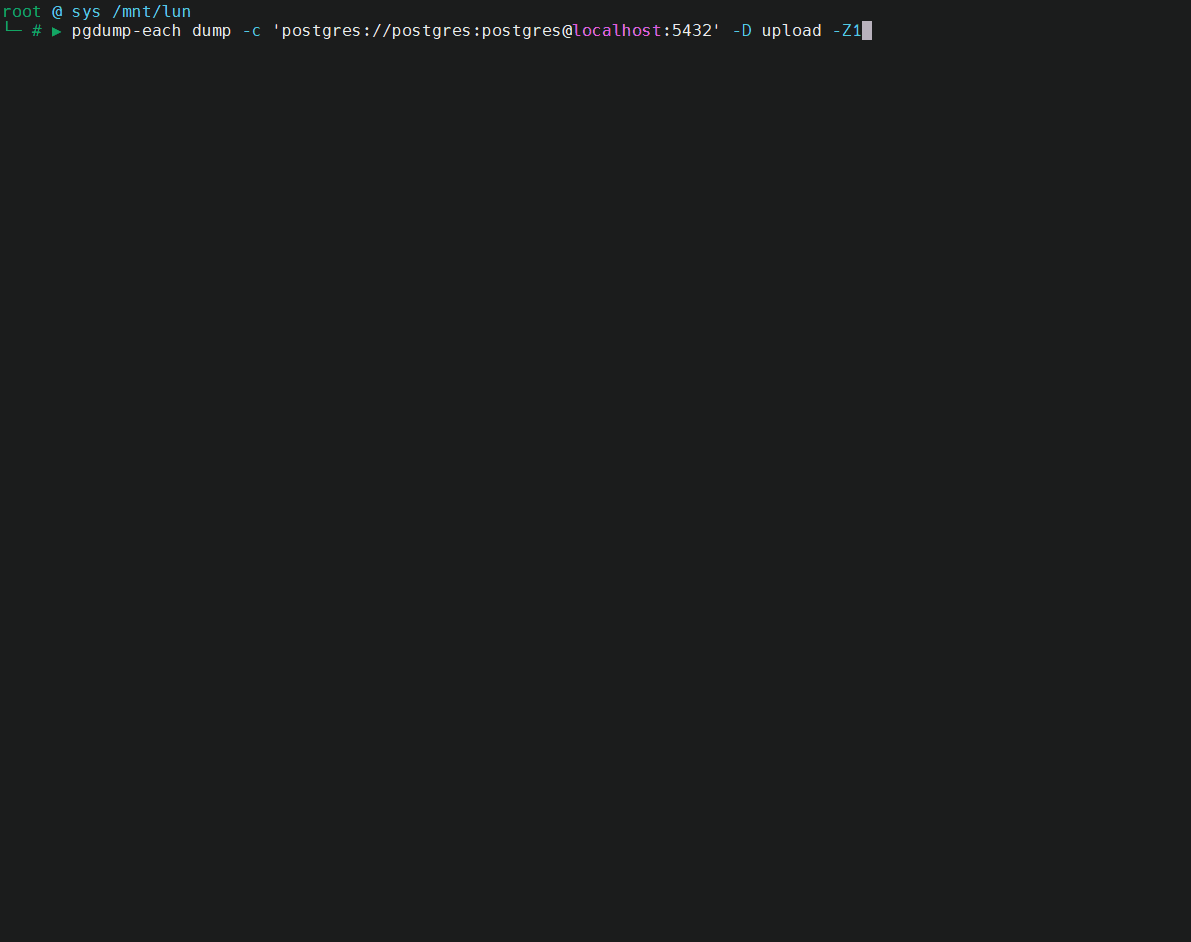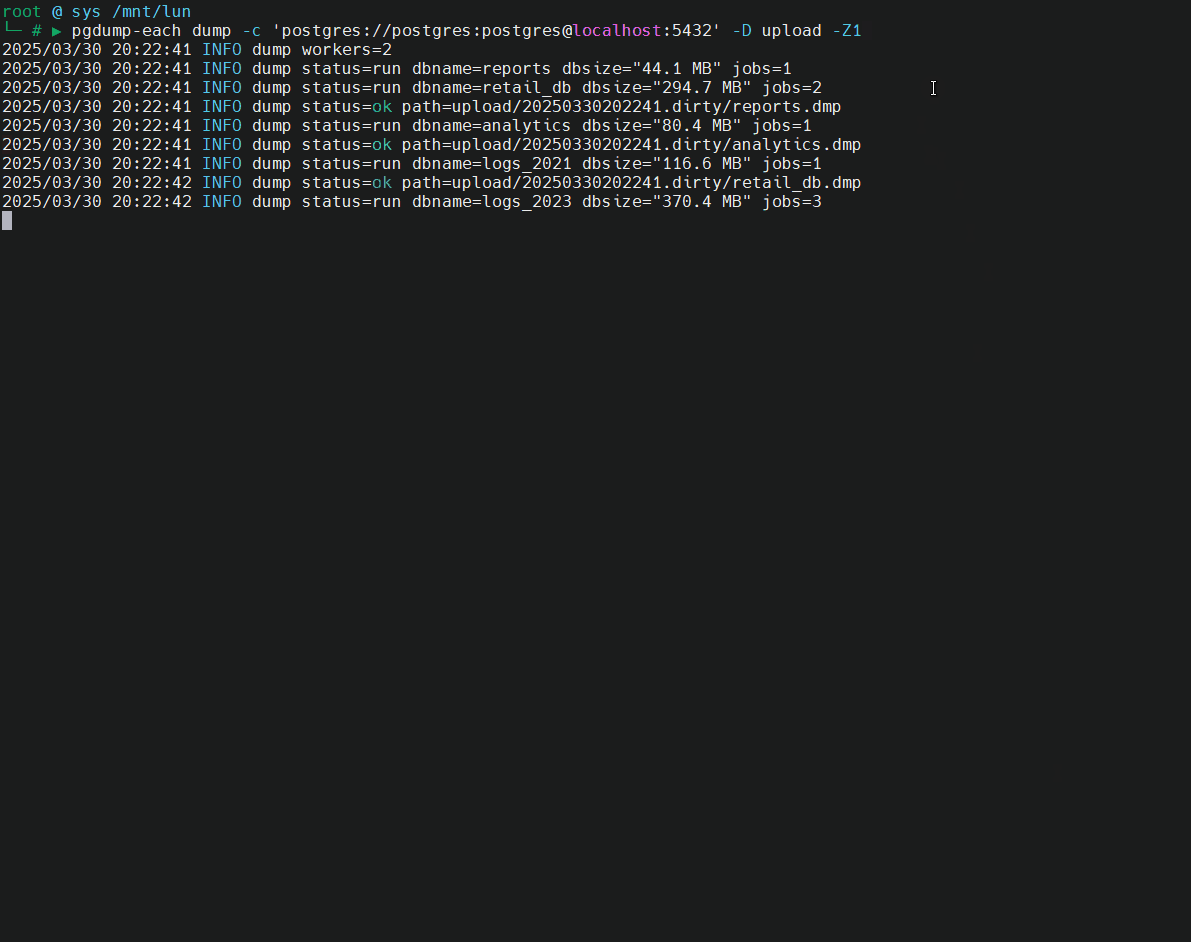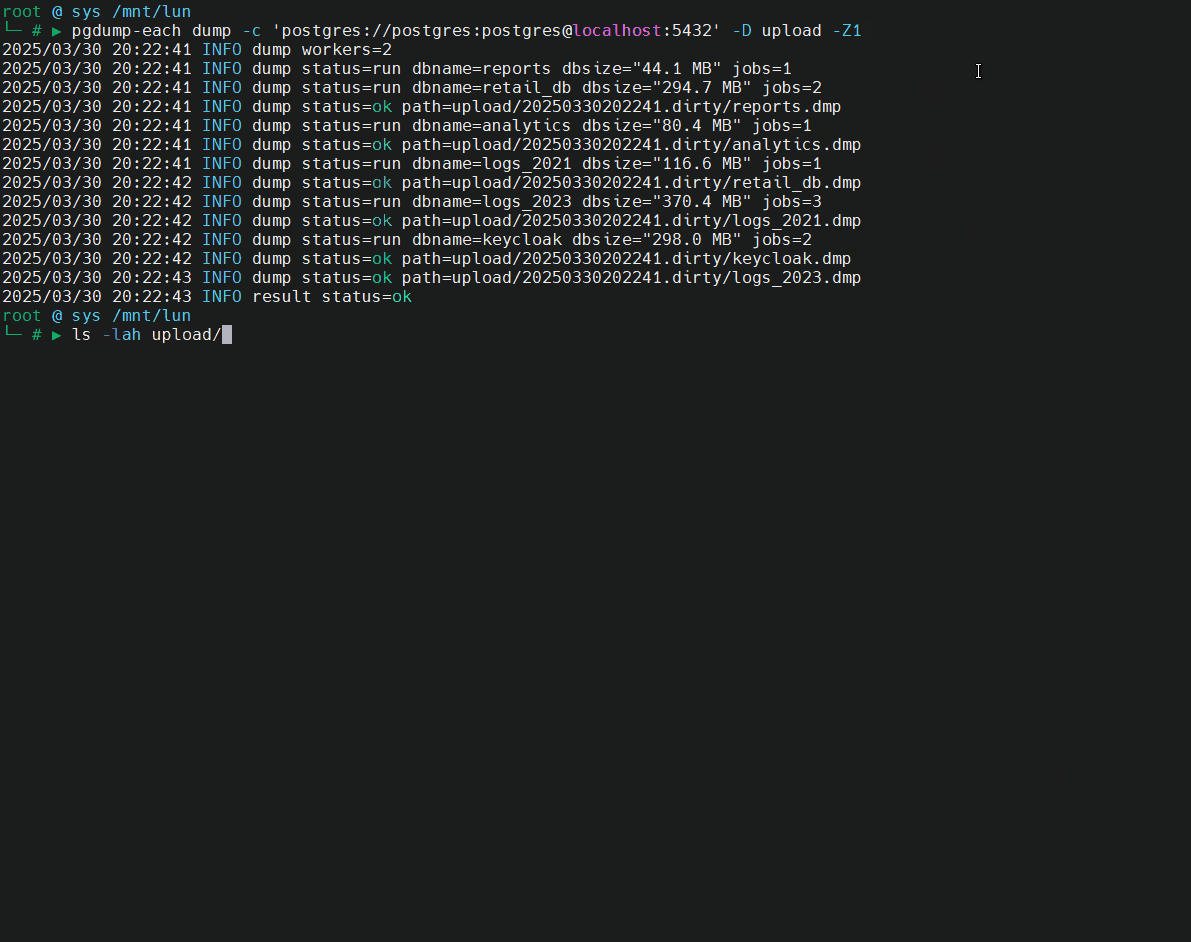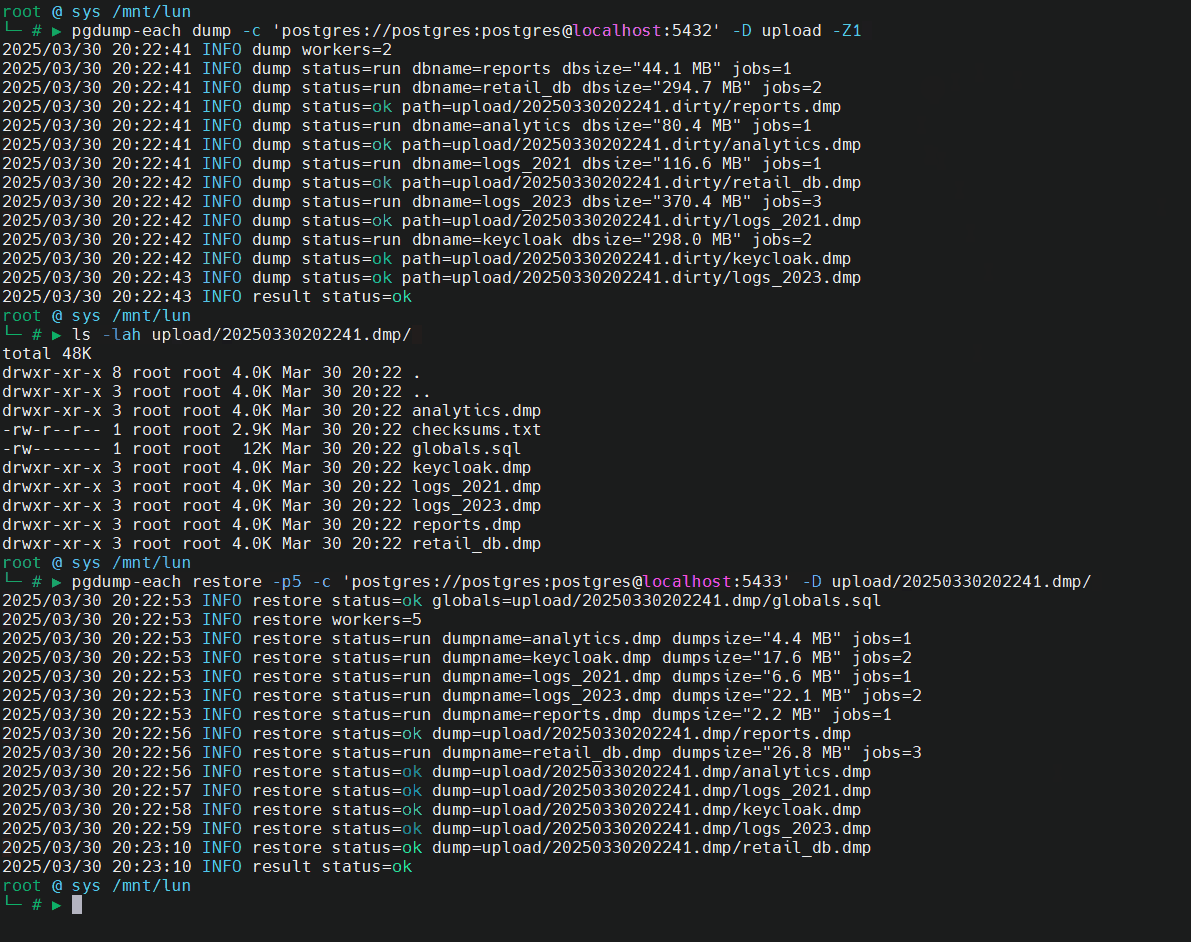
Key Features
Concurrent Backups: Utilizes
pg_dumpto perform simultaneous backups of each non-template database, leveraging the directory format with compression and parallelism for efficiency.Global Objects Backup: Captures global entities such as roles and tablespaces using
pg_dumpall --globals-only.Concurrent Restores: Plans for concurrent restoration using
pg_restore, significantly reducing downtime during upgrades.Safety Mechanisms: Implements checks to prevent restoration into non-empty clusters, safeguarding against accidental data overwrites.
KISS: It's not reinventing the wheel - just a handy wrapper around PostgreSQL tools. Think of it like familiar shell scripts, but cleaner and managed with Go.
How to Use pgdump-each
Prerequisites
Ensure that PostgreSQL client binaries (pg_dump, pg_dumpall, pg_restore, psql) are available in your system's PATH. Additionally, connection parameters like PGHOST, PGPORT, PGUSER, and PGPASSWORD can be inferred from the provided connection string.
Installation
Manual Installation
Download the latest binary for your platform from the Releases page.
Place the binary in a directory included in your system's
PATH(e.g.,/usr/local/bin).
Homebrew Installation
For macOS users, pgdump-each can be installed via Homebrew:
brew tap hashmap-kz/pgdump-each
brew install pgdump-each
Performing dumps
To initiate a backup of all databases in your current PostgreSQL cluster:
pgdump-each dump \
--connstr "postgres://postgres:secret@old-cluster:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable" \
--output ./backups
This command will:
Create a timestamped directory within
./backups.Concurrently dump each user database using
pg_dump.Dump global objects with
pg_dumpall --globals-only.Log the output for each database, facilitating troubleshooting if necessary.
Restoring to a New Cluster
After setting up a new PostgreSQL cluster, restore the backups using:
pgdump-each restore \
--connstr "postgres://postgres:newpass@new-cluster:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable" \
--input ./backups/20250328154501.dmp
This process involves:
Validating that the target cluster is empty to prevent data conflicts.
Restoring global objects and all database dumps concurrently using
pg_restore.Logging progress and errors for each database, ensuring transparency and ease of monitoring.
Conclusion
Upgrading PostgreSQL major versions doesn't have to be a complex and error-prone process. With pgdump-each, database administrators can perform efficient, concurrent backups and restores, ensuring data integrity and reducing downtime. By automating critical aspects of the upgrade process, pgdump-each empowers teams to focus on what matters most—delivering reliable and performant applications.
For more details and to contribute to the project, visit the GitHub repository.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Alex Havok directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
