Behind the Internet : Understanding Computer Networks 🌍💡
 Tambadkar Rohit Yashwant
Tambadkar Rohit Yashwant
Definition of a Network
Network : A network is a set of devices that are connected with a physical media link. In a network, two or more nodes are connected by a physical link or two or more networks are connected by one or more nodes. A network is a collection of devices connected to each other to allow the sharing of data.
Types of Networks
Personal Area Network (PAN) 📱
A small network for personal use.
Includes Bluetooth connections, smartwatches, and phone hotspots.
Advantage : Transmission speed is very high, easy maintenance and low cost .
Local Area Network (LAN) 🏠
A small network covering a limited area (e.g., home, office, school).
Uses Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi for connectivity.
Example: A Wi-Fi network in your house.
Advantage : Transmission speed is very high, easy maintenance and low cost .
Campus Area Network (CAN )🏫
Larger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN.
Covers a limited geographical area (e.g., school, collages ).
Advantage : Transmission speed is very high, moderated maintenance cost.
Range : 1 km to 5 km.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) 🏙️
Larger than a CAN but smaller than a WAN.
Covers a city or a large campus.
Example: City-wide Wi-Fi network.t
Disadvantage : speed is average, difficult to maintain, high cost.
Range : 5 km to 50 km .
Wide Area Network (WAN) 🌍
Covers a large geographical area.
The Internet is the largest example of a WAN.
Uses cables, satellites, and fiber optics.
Range : above 50 km.
Topology
Network Topology : Network topology specifies the layout of a computer network. It shows how devices and cables are connected to each other.
Types of Network Topology :
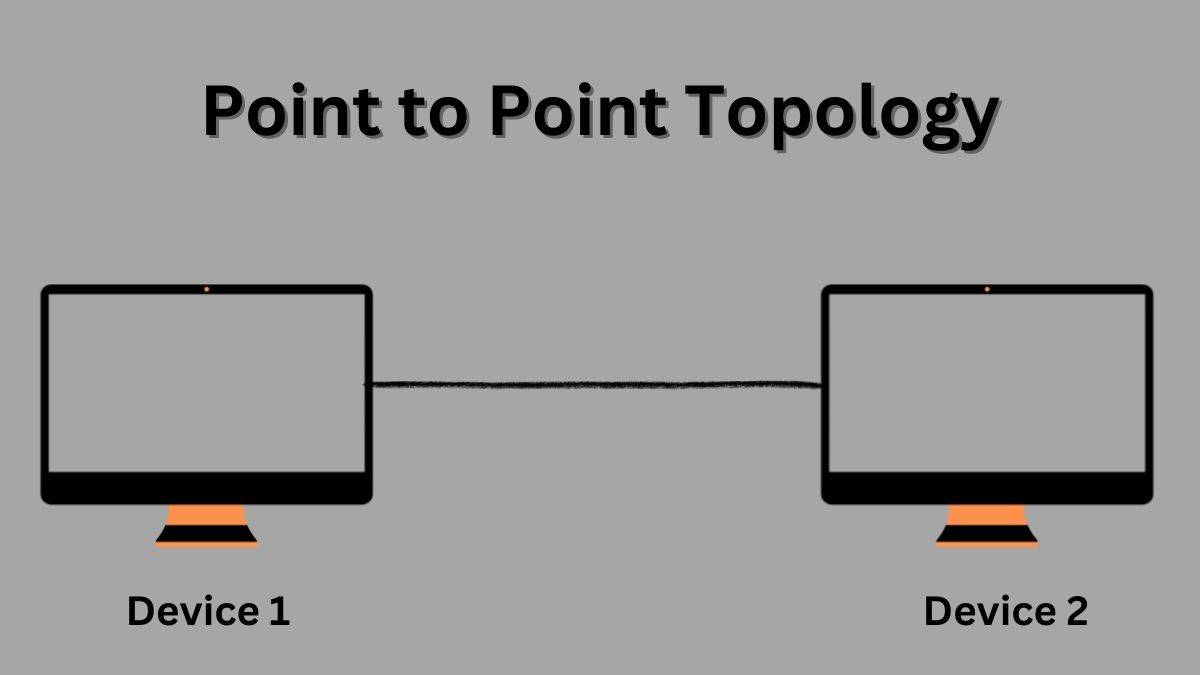
Point-to-point Topology :
Points-to-points topology is type of topology that works on the functionality of the sender and receiver.
It is the simplest communication between two nodes in which one is the sender and the other is receiver.
Provide high bandwidth.
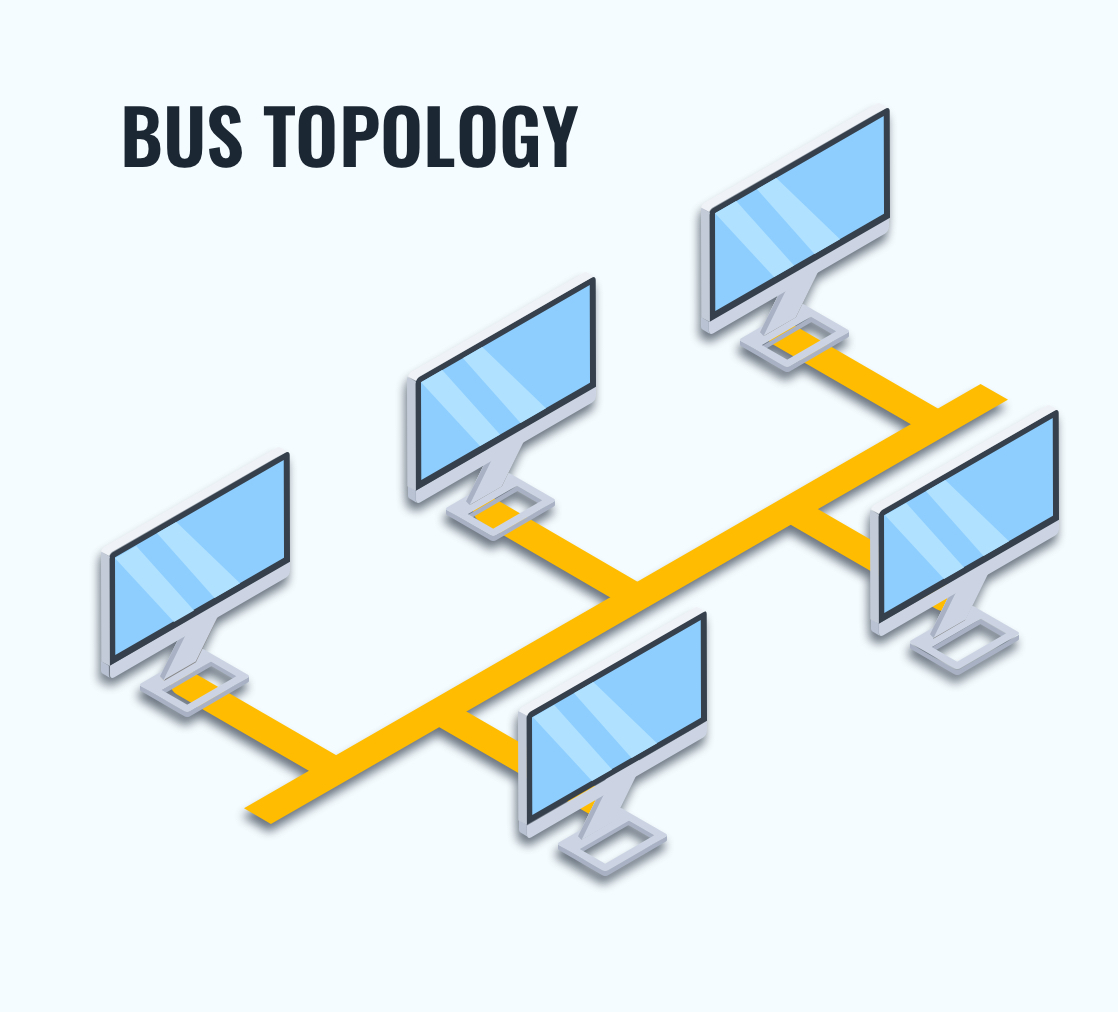
Bus Topology :
Every computer and network type in device is connected to a single cable.
It is bi-directional.
If the backbone fails, the entire network goes down.
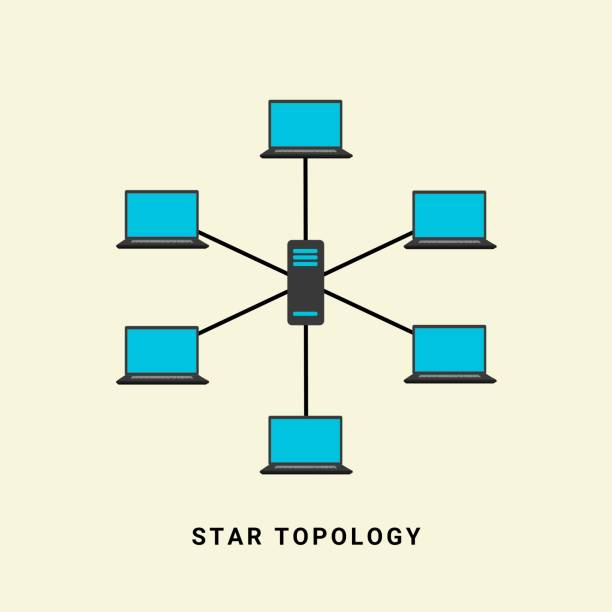
Star Topology :
All the nodes are connected to a single device known as a central device.
If the central device is damaged, then the whole network fails.
Star topology is very easy to install, manage and troubleshoot. It is commonly used in office and home networks.
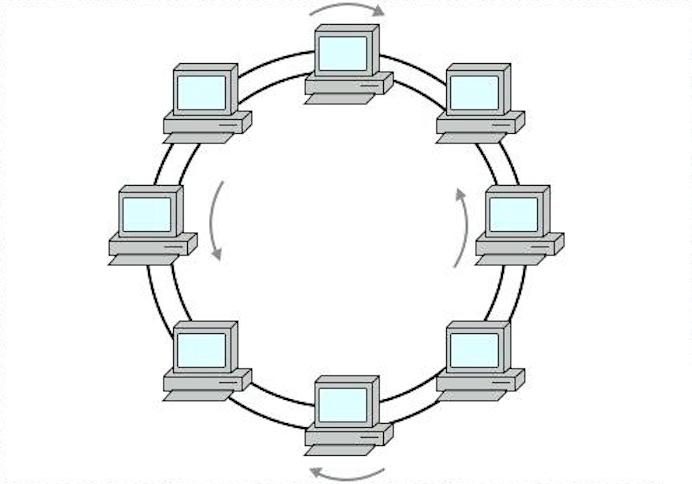
Ring Topology :
In ring topology if forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices. A number of repeaters are used for ring topology with a large number of nodes.
Star topology is very easy to install, manage and troubleshoot. It is commonly used in office and home networks.
If the single node is damaged, then the whole network fails.
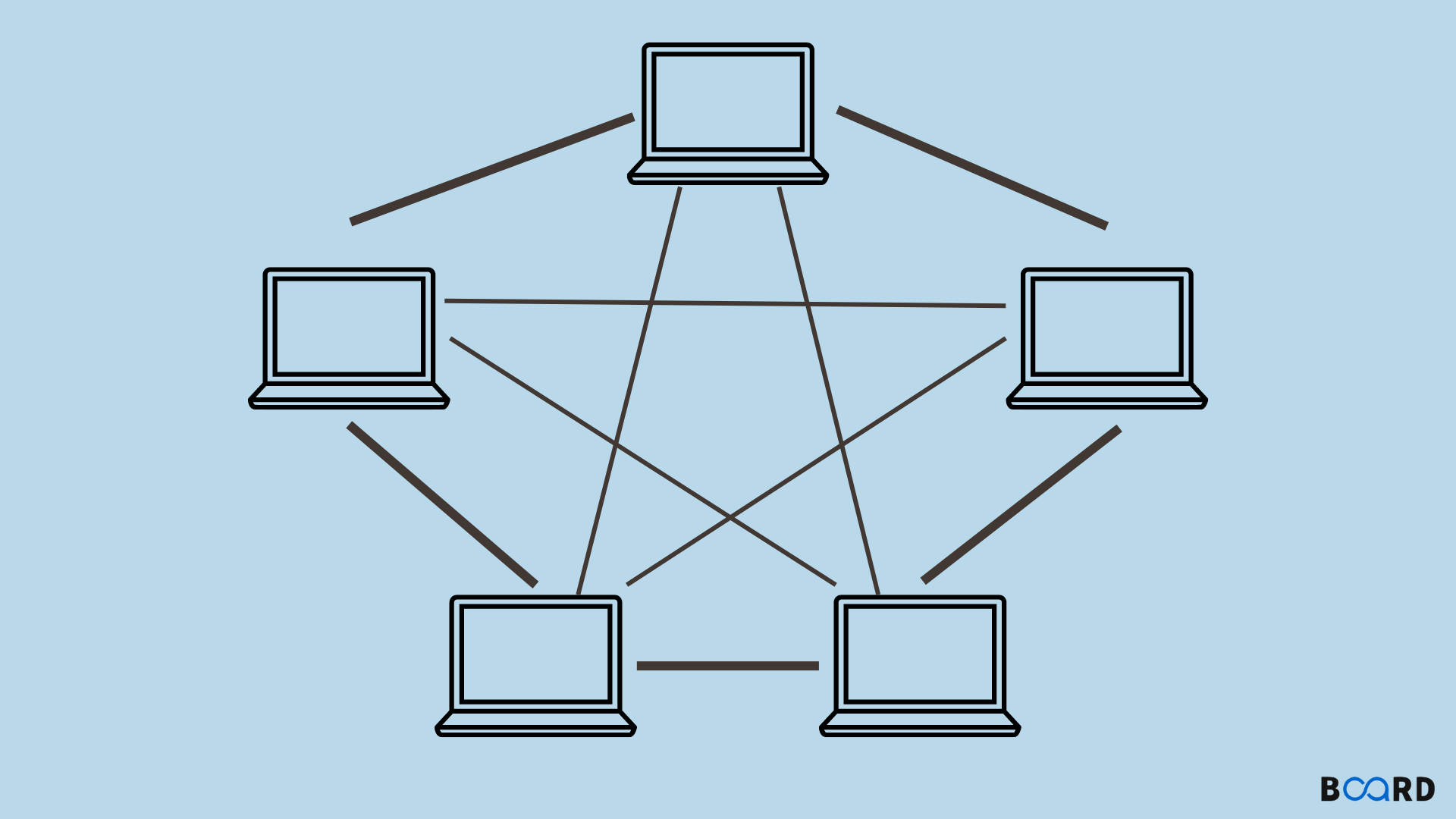
Mesh Topology :
Every device is connected to another device via a particular channel.
Mesh topology is rarely used as installation and configuration are difficult when connectivity gets more.
Mesh topology is rarely used as installation and configuration are difficult when connectivity gets more.
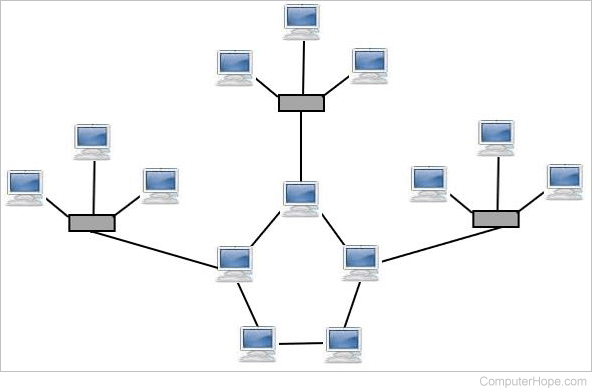
Tree Topology :
Tree topology is a combination of star and bus topology. It is also known as the expanded star topology.
Tree topology depends on the "main bus," and if it breaks, then the whole network gets damaged.
Error detection and correction are very easy in a tree topology.
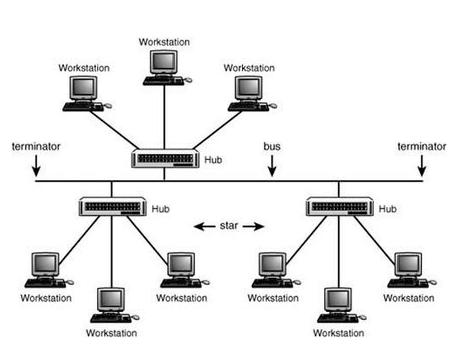
Hybrid Topology :
A combination of two or more topologies.
It provides flexibility as it can be implemented in a different network environment.
Complex to design and manage.conclusion
conclusion
Understanding computer networks is essential in today's interconnected world. Networks, ranging from small personal area networks to vast wide area networks, facilitate communication and data sharing across various devices and geographical locations. Each type of network, whether it's a LAN, CAN, MAN, or WAN, serves specific purposes and comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Additionally, the topology of a network, such as star, ring, or mesh, plays a crucial role in determining the network's efficiency, reliability, and ease of maintenance. By grasping these fundamental concepts, individuals and organizations can better design, implement, and manage their network infrastructures to meet their specific needs.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tambadkar Rohit Yashwant directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tambadkar Rohit Yashwant
Tambadkar Rohit Yashwant
Learning DevOps Engineer passionate about cloud computing, containerization, and automation. Currently exploring Docker, AWS, and CI/CD pipelines to build scalable and efficient workflows. Documenting my learning journey in blog. stay tuned with me for learning.