Understanding the Scrum Process: A Beginner's Guide
 Iresh Ekanayaka
Iresh EkanayakaScrum is an Agile framework used to develop and deliver products iteratively and incrementally. It helps teams work collaboratively and respond to change effectively. This guide provides an overview of the Scrum process and its key components.
1. Scrum Framework Overview
Scrum follows an iterative approach, breaking down work into fixed time periods called Sprints. Each Sprint results in a potentially shippable product increment. The process involves specific roles, events, and artifacts.
Key Roles in Scrum:
Product Owner: Defines product goals, prioritizes backlog items, and ensures value delivery.
Scrum Master: Facilitates Scrum processes, removes impediments, and ensures adherence to Agile principles.
Development Team: Cross-functional team responsible for delivering increments.
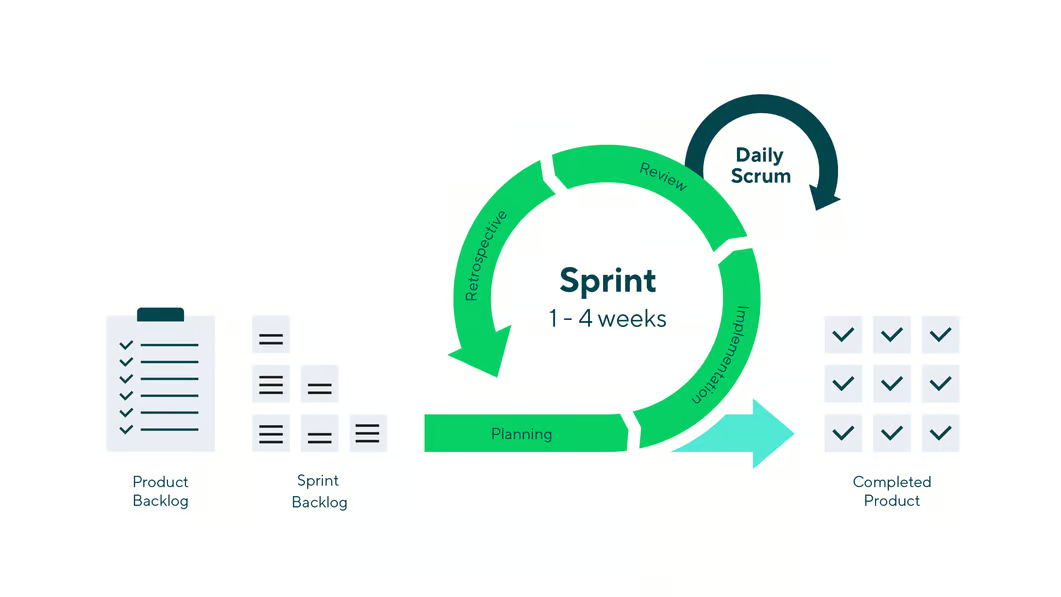
2. Scrum Process Flow
2.1 Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is a prioritized list of features, improvements, and fixes required for the product. The Product Owner maintains and refines this backlog continuously.
2.2 Backlog Refinement (Backlog Grooming)
Backlog Refinement (also known as Backlog Grooming) is an ongoing activity where the team discusses and clarifies backlog items, breaks them into smaller tasks, and estimates their effort.
2.3 Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is the meeting where the team selects backlog items for the upcoming Sprint. The key outputs of Sprint Planning include:
Sprint Goal: Defines the purpose of the Sprint.
Sprint Backlog: A subset of Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint.
Task Breakdown: Identifying the necessary tasks to complete selected items.
2.4 Sprint Execution
The Sprint is a time-boxed iteration (typically 1-4 weeks) where the team works on Sprint Backlog items. The team holds Daily Standup (Daily Scrum) Meetings to sync progress and discuss roadblocks.
2.5 Increment
By the end of the Sprint, the team delivers a Potentially Shippable Product Increment that meets the Definition of Done (DoD).
2.6 Sprint Review
The Sprint Review is held at the end of the Sprint, where the team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and gathers feedback.
2.7 Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective follows the Sprint Review and is aimed at process improvement. The team discusses what went well, what didn’t, and how they can improve future Sprints.
3. Summary of Scrum Process Steps
Product Backlog Creation: Product Owner maintains and prioritizes backlog items.
Backlog Refinement: Team refines and estimates backlog items.
Sprint Planning: Team selects work for the Sprint and sets a goal.
Sprint Execution: Development occurs, guided by Daily Standups.
Increment Creation: A potentially shippable product increment is produced.
Sprint Review: Team showcases work and receives feedback.
Sprint Retrospective: The team reflects and improves the process.
Repeat: The process continues in cycles until the product is completed.
Scrum ensures adaptability, continuous improvement, and consistent product delivery. By following these steps, teams can efficiently manage their work and deliver high-value products in an Agile environment.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Iresh Ekanayaka directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
