Motherboard
 Megha Prabhakar
Megha Prabhakar
A motherboard is large circuit board inside a general purpose computing system. It's the main components of a computing system where all the important components get connected to it.
Functional description of motherboard
The various functions of a motherboard includes:
Connect components: The motherboard connects the CPU, GPU, and other components.
Provide power: The motherboard provides power to each components.
Facilitate communication: The motherboard allows components to communicate with each other.
Stores BIOS settings: The motherboard's BIOS settings are store din a CMOS battery which is also known as the memory battery.
Provide interfaces: The motherboard provides interfaces for connecting external devices like keyboards, mice, and printers.
Enhances performance: The motherboard boots the capabilities of a computer.
Improve reliability: A good motherboard boosts the overall reliability of the computer.
Enables productivity: The motherboard reduces effort duplication and simplifies work for computer users.
Form factor
The form factor of a motherboard refers to its size, shape and layout.
Types and features of form factor
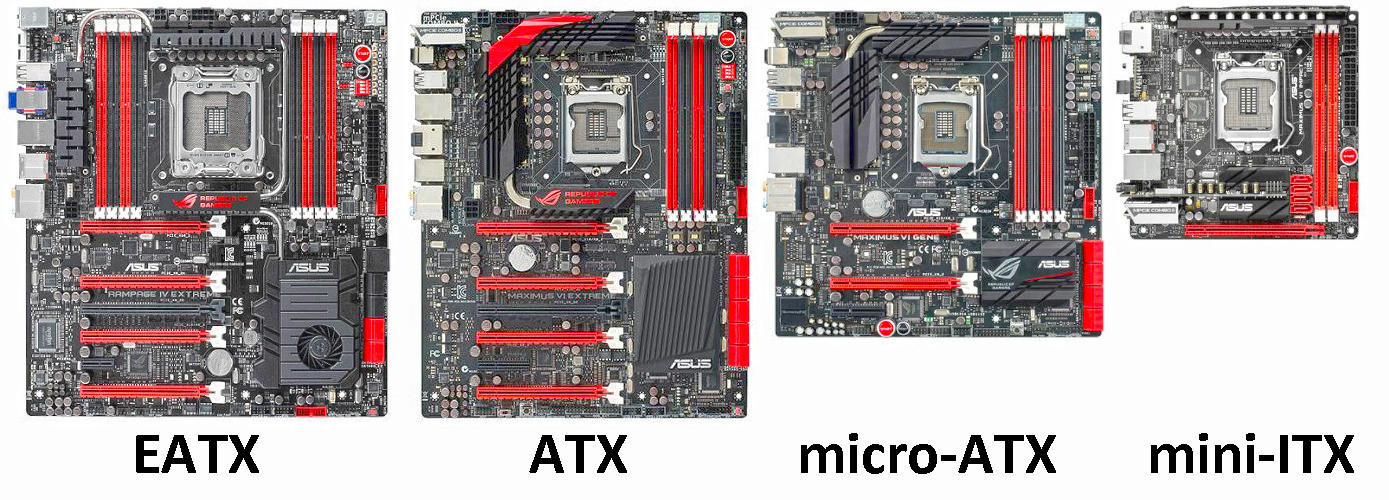
ATX
Size: 305mm × 244mm (12 × 9.6 inches)
Expansion slots: 7-8 slots (PCIe, PCI, AGP)
RAM: 4-8 DIMM slots
Storage: 4-6 SATA ports, 2-4 IDE ports
Power connectors: 24-pin ATX power connectors, 4-8 pin EPS power connector
Cooling: Supports large CPU cooler and multiple case fans
Applications: Used in Gaming PCs, work stations, servers, high-end desktops etc.
Micro ATX
Size: 244mm × 244mm (9.6× 9.6 inches)
Expansion slots: 4-5 slots (PCIe, PCI)
RAM: 2-4 DIMM slots
Storage: 2-4 SATA ports, 1-2 IDE ports
Power connectors: 24-pin ATX power connectors
Cooling: Supports smaller CPU cooler and fewer case fans
Applications: Used in Gaming PCs, work stations, servers, high-end desktops etc.
Mini ITX
Size: 170mm × 170mm (6.7 × 6.7 inches)
Expansion slots: 1-2 slots (PCIe)
RAM: 2-4 DIMM slots
Storage: 2-4 SATA ports
Power connectors: 24-pin ATX power connectors or DC power jack
Cooling: Supports small CPU cooler and limited case fans
Applications: Used in mini-PCs, media centers, embedded system, retro gaming console etc.
Nano-ITX
Size: 120mm × 120mm (4.7 × 4.7 inches)
Expansion slots: 0-1 slot (PCIe)
RAM: 1-2 DIMM slots
Storage: 1-2 SATA ports
Power connectors: DC power jack
Cooling: Supports tiny CPU cooler and limited case fans
Applications: Used in ultra compact PCs, IoT devices, wearables, industrial control system etc.
Pico-ITX
Size: 100mm × 72mm (3.9 × 2.8 inches)
Expansion slots: 0 slots
RAM: 1 DIMM slot
Storage: 1 SATA ports
Power connectors: DC power jack
Cooling: Supports tiny CPU cooler and very limited case fans
Applications: Used in ultra-embedded systems, robotics, medical devices, aerospace etc.
Functional components of Motherboard
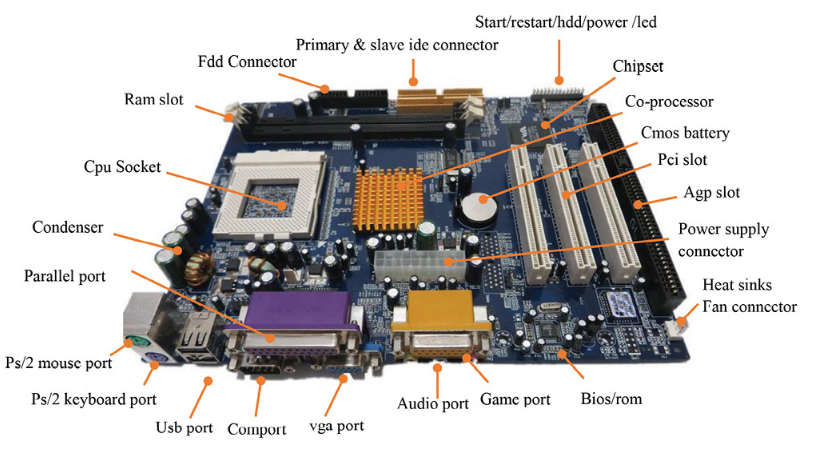
CPU Socket: Slot where the CPU is installed.
RAM Slot: Slot that hold the RAM modules.
Chipset: Acts as the communication center and traffic controller,managing data flow b/w CPU, memory etc.
Northbridge : manages high-speed communication b/w the CPU, RAM, and graphics card.
Southbridge : manages low-speed peripherals like SATA drives, USB ports etc.
Expansion Slot: Slot where additional cards can be installed to extend the copmuter’s capabilities.
BIOS/ UEFI chip: Stores the BIOS firmware, which initializes the computer during boot-up.
Storage connectors:
SATA: connects storage devices like HDD and SSD.
NVMe: high-speed interface for SSDs.
Power connectors: Connectors for supplying power from the PSU to motherboard, and other components.
I/O Ports: Ports for external devices such as USB, HDMI, Ethernet, audio jack, and others, allowing connectivity to peripherals like keyboard, mice etc.
Cooling Fans: Spread the heat (generated by the components) in surrounding or out of the cabinet
CMOS Battery: Powers the CMOS chip, which stores the system time and date, and BIOS settings.
CPU and CPU socket
CPU
Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the main component of the system that performs all the software (arithmetic & logical) operations. It is also called the brain of computer system.
CPU Socket
CPU socket is the slot used to connect the micro processor, allowing for the CPU to be installed or replaced more easily on the motherboard.
Types of CPU sockets
LGA
LGA stands for Land Grid Array. It has pads on the CPU that matches the pins in the socket.
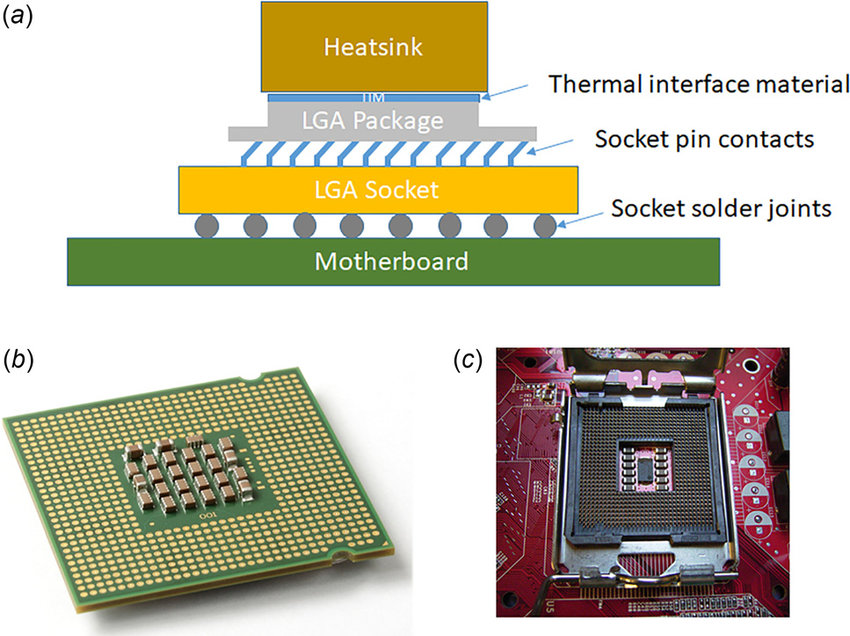
PGA
PGA stands for Pin Grid Array.This consists of multiple pins on the CPU that matches the holes in the socket.
BGA
BGA stands for Ball Grid Array. It has balls on the CPU that are soldered to the socket.
Overview of microarchitecture of INTEL and AMD CPU.
Microarchitecture refers to the internal design and organizations of the CPU components which executes the instructions and perform the necessary calculations.
Here is the overview of microarchitecture of :
Intel CPU
NetBurst (2000-2008)
Pipeline stages: 20-31 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Introduced
Execution Units: 4-6 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
Core (2006-2010)
Pipeline stages: 14-16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 4-6 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
Sandy Bridge (2011-2013)
Pipeline stages: 14+16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 6-8 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
AVX instructions: Introduced
Skylake (2015-2019)
Pipeline stages: 14-16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 8-10 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
DDR4 memory support: Introduced
Ice Lake (2019-present)
Pipeline stages: 14-16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 10-12 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
DDR5 memory support: Introduced
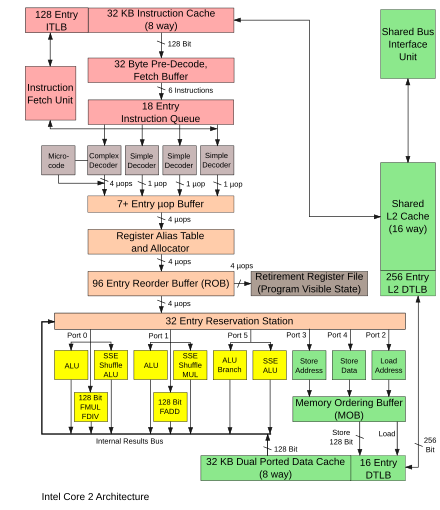
Microarchitecture of Intel Core CPU:
AMD CPU
K8 (2003-2009)
Pipeline stages: 12-15 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Introduced
Execution Units: 3-4 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 2-Level cache hierarchy
Bulldozer (2011-2012)
Pipeline stages: 15-17 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 4-6 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 2-Level cache hierarchy
Modular design: Introduced
Zen (2017-2019)
Pipeline stages: 14-16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 6-8 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
SMT ( Simultaneous Multithreading): Introduce
Zen 2 (2019- present)
Pipeline stages: 14-16 stages
Out-of-Order execution (OoOE): Improved
Execution Units: 8-10 execution units
Cache hierarchy: 3-Level cache hierarchy
PCIe 4.0 support: Introduced
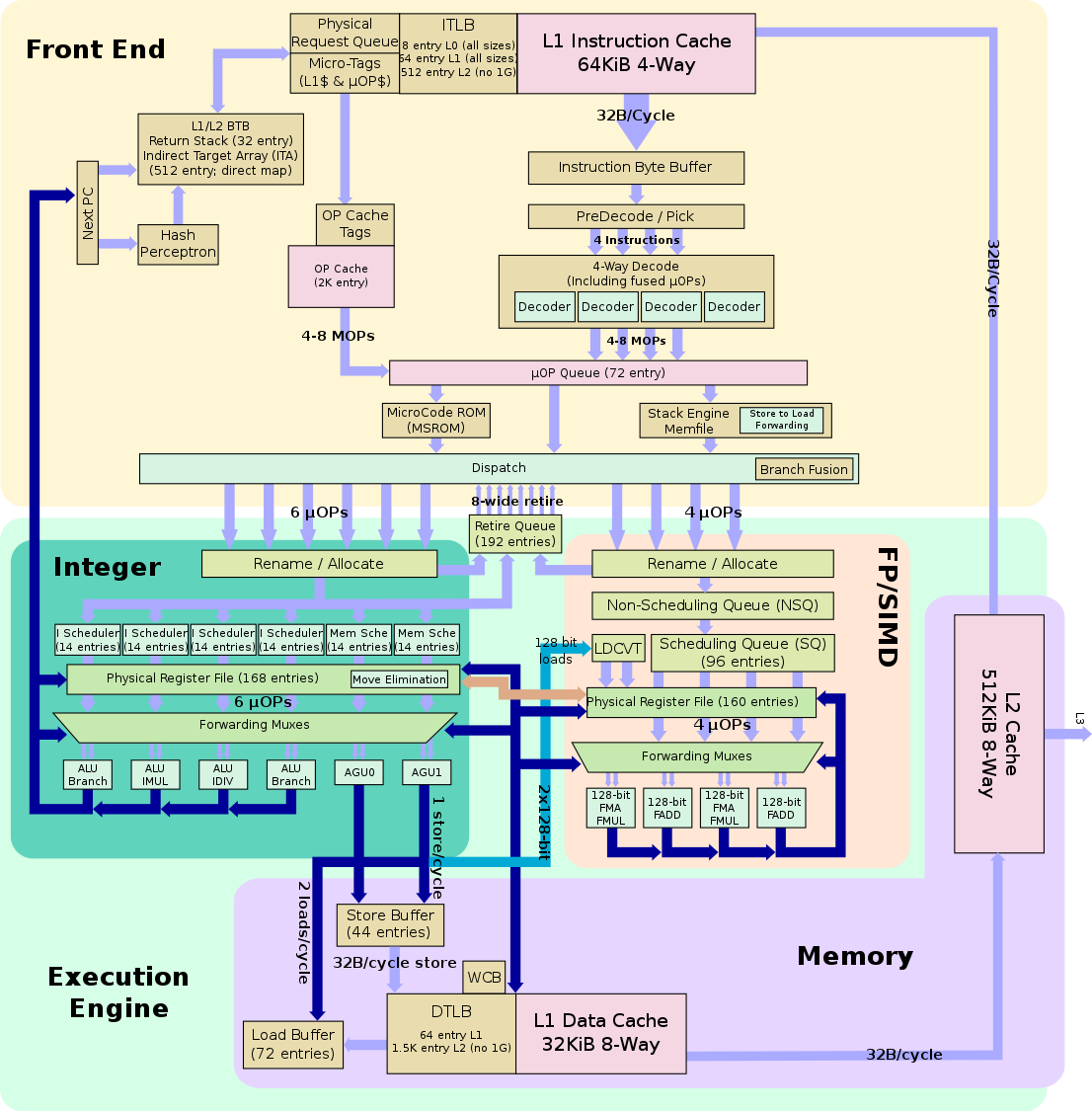
Microarchitecture of Zen CPU:
Conclusion
Motherboard is the essential part of a computing system as it controls the actions of components inside it.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Megha Prabhakar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
