What is Web 3.0?
 NonStop io Technologies
NonStop io Technologies
Introduction:
Web 3.0 is the next evolution of the web which is based on Blockchain technology. It is also referred to as the “Decentralized Web”, which allows users more privacy and security towards their data.
Let’s dig more into the evolution of the World Wide Web.
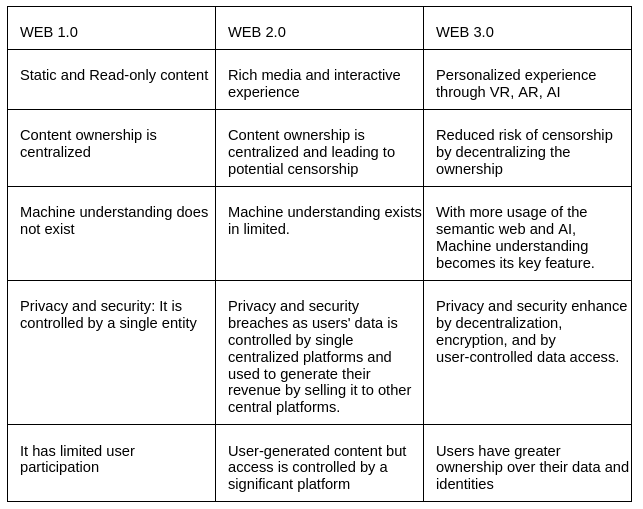
WEB 1.0 (1980s — ~2000): Web 1.0 is the foundational stage of the World Wide Web, it is characterized by static web pages and it was a “Read-only” web. It has centralized publishing and it has narrow user interaction. It offers negligible personalization and customization. Search engines and web directories play a crucial role in the era of Web 1.0.
WEB 2.0 (~2000 — ~2014): Web 2.0 was the next step towards the evolution of the World Wide Web. It allows users to create and share their content over the internet. It is the participative social web. It offers free information sorting, allowing users to retrieve and classify data collectively.
WEB 3.0 (~2014): Web 3.0 represents the vision of the internet which goes beyond the capabilities of Web 2.0 and allows users to control their data in a decentralized manner. It lacks arbitrary central authority over the user’s data. In theory, it shows the more democratic way of using the user’s information or data.
Understanding Web 3.0:
The core principles of Web3.0 are :
DECENTRALIZATION: It is nothing but to distribute the power, control, authority, or decision-making away from one centralized system to multiple nodes/participants. It provides a more democratic, transparent, and secure approach toward various systems and sectors to reduce the power of one centralized system and allow greater participation and innovation from a wide range of participants.
SEMANTIC WEB: It is the technology that aims to organize information in such a way that it is understood by machines. In the semantic web, the information is linked and structured in such a way that the user can get more meaningful and relevant search results. The results of this semantic web are more efficient and improved in decision-making.
AI/ML: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are the abilities of machines to perform the tasks which typically require human cognitive functions. It mainly includes the algorithms and methodologies that aim to mimic human intelligence and problem-solving abilities. It also includes NLP(Natural language Processing).

Pic credits : Google images
Key Features that distinguish WEB 3.0 from its predecessors:
Decentralization and Blockchain:
1. Role of decentralization in Web 3.0.
Decentralization plays a core role in Web 3.0 from its predecessors. It empowers users to have greater control over their data. Users can grant and revoke access to their data, enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of data breaches.
Decentralized systems are mainly based on the consensus method, promoting trust and transparency amongst users. Block-chain-based platforms ensure that the transactions/actions happening are recorded immutably. These systems are more resistant to censorship. They are more open to collaboration and innovation. These systems reduce the barrier to access the data, users can access such services from various parts of the world as it is not dependent on a single central system.
Decentralized systems empower users to participate more in decision-making, content creation, and governance.
2. Role of blockchain technology and its impact on the new web paradigm:
Blockchain technology is nothing but a distributed ledger system that holds the records of every action/transaction that are happening on the platforms and store that information in the blocks.
The word blockchain itself represents the meaning that the data is stored in sequential blocks that are linked together in a chain.
Now the question that arises here is how the data is stored in the blockchain.
Here each block consists of 3 main keys :
Hash — the secure has a key,
Data — The information which you have stored or transferred,
Previous hash — the hash of the previous block from where the information has come
This technology provides security through public and private keys to provide secure access and authentication.
Real-life examples of DApps
Uniswap: It is the DApp that allows users to directly trade cryptocurrencies from their wallets.
Patientory: It stores and manages the user's healthcare information.
Power Ledger: A platform to trade renewable energy, etc
Challenges and Future Prospects:
Despite such usability Web 3.0 faces one major problem and that is scalability along with environmental impact, and legal uncertainty we will be discussing issues in depth in upcoming blogs.
Conclusion:
As we have seen we realized that Web 3.0 is still challenging and still evolving with the help of developers, researchers, and entrepreneurs, we can say that we are moving toward the new Era of the World wide web.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from NonStop io Technologies directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

NonStop io Technologies
NonStop io Technologies
Product Development as an Expertise Since 2015 Founded in August 2015, we are a USA-based Bespoke Engineering Studio providing Product Development as an Expertise. With 80+ satisfied clients worldwide, we serve startups and enterprises across San Francisco, Seattle, New York, London, Pune, Bangalore, Tokyo and other prominent technology hubs.