🔒Network+ Day 2 of Cybersecurity Learning – Demystifying IDS/IPS, DHCP, DNS, OSI, and More!
 Narayan Joshi
Narayan Joshi
Welcome to Day 2 of my cybersecurity journey! Today was an absolute firehose of concepts—but stick with me, because by the end of this blog, you’ll feel like a mini network guru 😎. I covered everything from how your PC talks to the internet, to how we catch sneaky intruders. Let’s dive in!
🕵️♂️ IDS vs IPS vs HIDS – Who's Watching Your Network?
Ever wondered how networks catch threats before they become disasters? That’s where IDS and IPS come in!
✅ IDS – Intrusion Detection System
Think of IDS like a security guard watching CCTV footage. It detects suspicious traffic and raises the alarm, but doesn't act—just warns you something's fishy.
Follows predefined rules or ML models
Alerts on abnormal activity (but doesn’t block it)
🛡️ IPS – Intrusion Prevention System
IPS is the bodyguard who jumps in to block the threat. It watches, detects, and acts in real-time.
Blocks, halts, or drops malicious traffic
Protects in real-time—no waiting!
🧍♂️ HIDS – Host-Based Intrusion Detection System
HIDS is like IDS but for a single machine. It’s limited to monitoring just that device (host), watching internal logs and system behavior.
🌐 Modem, Hub, Router, VPN Concentrator – What Connects What?
Let’s clear up the confusion between all these boxes blinking in your networking cabinet.
📡 Modem
Converts digital data to analog (modulation) and vice versa (demodulation)
Connects your home/office to the internet
🔁 Hub
Basic device that broadcasts data to all connected devices
No intelligence, just a repeater
🚪 Router
Connects different networks together (e.g., LAN to WAN)
Assigns IPs within your LAN (via DHCP)
🔐 VPN Concentrator
Ever work from home and still need secure access to your office files? Enter VPN Concentrators!
Creates secure VPN tunnels for remote access
Uses encryption like SSL/TLS
Ideal for large enterprises with many remote employees
🚦 Packet Shapers and Content Filters – The Internet Traffic Cops
🧠 Packet Shaper
Manages traffic flow so important stuff goes first (like video calls) and cat memes get sent after.
Ensures QoS (Quality of Service)
Prioritizes critical traffic
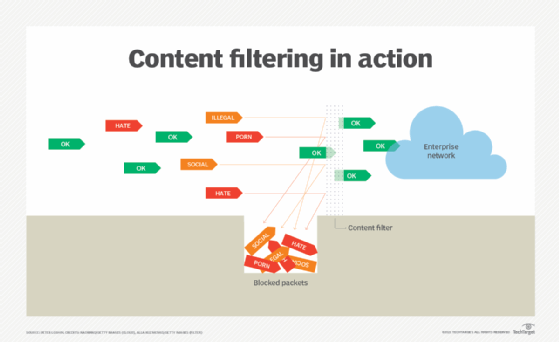
🚫 Content Filters
Keeps the network safe and focused:
Blocks inappropriate or unsafe content
Used in schools and businesses to restrict access
Works via keywords, URLs, and categories
📶 AP (Access Point) – Wireless Gateways
An Access Point connects your wireless devices to a wired network.
Enables Wi-Fi connectivity
Acts as a bridge between LAN and wireless devices
💡 DHCP – The Auto-IP Wizard
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) handles the headache of assigning IP addresses to every device.
Here’s how it works (think of it like finding a seat at a restaurant):
Discover – Client says: “Hey, any free IPs?”
Offer – Server: “Yeah, take this one!”
Request – Client: “I want that IP, please.”
Acknowledge – Server: “You got it!”
Other cool terms:
DHCP Lease – How long you can “keep” that IP
DHCP Reservation – Like pre-booking a seat with your name on it
Scope – The range of IPs available to assign
📋 DHCP Configuration on Windows Server 2012
Setting up DHCP is like preparing a buffet:
Install the DHCP role via Server Manager
Configure your scope (IP range)
Define lease duration, exclusions, and activate
Done right, this setup automates IP management beautifully!

🌍 DNS – The Internet’s Phonebook
Imagine if you had to remember IP addresses for every site—yikes. DNS makes life easier!
🧠 What DNS Does
Converts human-friendly names (like
google.com) to IP addresses (142.250.190.14)Uses caching for faster lookup
Works with record types like:
A– IPv4 addressAAAA– IPv6MX– Mail serversCNAME– AliasesPTR– Reverse DNS

🤔 What is Dynamic DNS?
Let’s say your home camera’s IP keeps changing. DDNS lets you bind it to a custom domain like mycamera.ddns.net, so you can always access it—even if the IP changes.
🧬 OSI Model and TCP/IP – The Protocol Pizza
Let’s wrap up with the OSI Model, a framework that explains how data travels through networks in 7 layers.
Here’s a fun way to remember:
All People Seem To Need Data Processing
(Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical)
When Alice sends Bob an email:
Alice writes it (Application Layer)
It’s prepared and segmented (Presentation, Session, Transport)
Routed through networks (Network, Data Link)
Finally reaches Bob's device (Physical Layer)
The TCP/IP model simplifies it into 4 layers:
Application
Transport
Internet
Network Access
Both models describe the same journey—just differently!
🚀 Wrapping Up
From catching cyber intruders to building IP magic, today was full of powerful concepts. Whether you’re a cybersecurity newbie or brushing up your skills, understanding these networking fundamentals is essential.
Want to geek out with me every day as I learn more? Follow along!

📚 Stay curious
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Narayan Joshi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Narayan Joshi
Narayan Joshi
I have a strong and evolving interest in cybersecurity and ethical hacking, proven by my top 1% rank on TryHackMe, completion of SOC Fundamentals, multiple Udemy courses, and active participation in CTF programs and practical hacking series. Currently, I work as a Cybersecurity Associate at Sattrix Information Security, where I serve as an ArcSight Administrator and have hands-on experience with SIEM tools like Splunk and NewEvol. Alongside cybersecurity, I also have a background in web development with experience in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Python scripting. I’m deeply committed to continuous learning and real-world application, with a consistent track record of completing certifications and challenges. Despite ongoing health challenges that impact productivity, I remain focused on deepening my expertise and building a successful career in cybersecurity and ethical hacking.


