The Biological Neuron Inspiration
 ukana ikpe
ukana ikpe
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, learners will be able to:
Understand the basic structure and function of a biological neuron.
Explain how information is processed and transmitted in the brain.
Recognize the analogy between biological and artificial neurons.
Appreciate why artificial neural networks are inspired by the brain’s architecture.
1. What Is a Neuron?

A neuron is a specialized cell in the human brain and nervous system responsible for transmitting information using electrical and chemical signals.
Humans have around 86 billion neurons, and these interconnected cells form the basis of cognition, perception, and control of the body.
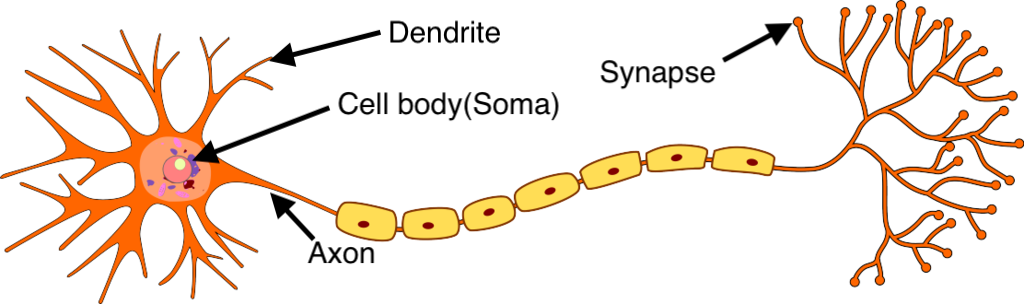
2. Structure of a Biological Neuron
A neuron has three main components:
1. Dendrites

Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
Think of them as inputs.
Signals come in the form of electrical impulses.
2. Cell Body (Soma)

The control center of the neuron.
Processes incoming signals from dendrites.
If the total input signal is strong enough, it triggers an action potential.
3. Axon

A long, cable-like structure that sends signals to other neurons.
Ends in terminal branches connected to other neurons’ dendrites.
These connections occur at synapses—tiny gaps where chemicals called neurotransmitters pass the signal from one neuron to another.
3. How Information Flows
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a biological neuron fires:
Signal received by dendrites.
Cell body integrates signals (adds up all incoming signals).
If the total exceeds a threshold, an action potential is triggered.
The signal travels down the axon.
Signal reaches synaptic terminals.
Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse.
The next neuron receives the signal via its dendrites.
This is called electrochemical transmission.
4. From Biology to Deep Learning

Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are not perfect replicas of the brain, but they are inspired by its structure:
| Biological Neuron | Artificial Neuron (Node) |
| Dendrites | Inputs |
| Soma (Cell body) | Weighted sum + activation |
| Axon | Output |
| Synapse | Connection (Weight) |
Biological process:
Input (dendrites) → Process (soma) → Output (axon) → Other neurons
Artificial neuron process:
Input (x) → Multiply with weights (w) → Sum → Apply activation function → Output (y)
Mathematically:
$$y = \sigma(w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + \dots + w_nx_n + b)$$
Where:
$$x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n = inputs$$
$$w_1, w_2, ... w_n = weight$$
b = bias (like a threshold)
σ\sigma = activation function (like decision to fire)
5. Why the Brain Is an Inspiration
The brain can learn from experience — artificial networks aim to do the same.
The brain processes massive amounts of data in parallel — ANNs try to emulate this.
Neurons are highly interconnected — just like the layers in deep neural networks.
6. Historical Context

In 1943, Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed the first mathematical model of a neuron.
In the 1950s, Frank Rosenblatt introduced the Perceptron, inspired by neurons.
Today’s deep networks are the descendants of these early bio-inspired models.
7. Summary
Biological neurons process and transmit signals using dendrites, a soma, and an axon.
Artificial neurons simplify this into inputs, a weighted sum, and an output.
Deep learning models are built using layers of artificial neurons to mimic the brain's learning process.
While artificial neurons are inspired by biology, they are much simpler and operate on mathematical principles.
Questions
What are the three main parts of a biological neuron?
What is the function of dendrites?
What role does the soma play in signal processing?
What is the artificial equivalent of a synapse?
How is the output of an artificial neuron typically computed?
Want To Master Deep Learning

Join The Mastering Deep Learning — a comprehensive, beginner-friendly deep learning journey where you'll:
✅ Build powerful neural networks
✅ Work on real-world projects (CV, NLP, GANs & more)
✅ Master PyTorch & Tensorflow from the ground up
✅ Get interview-ready for top tech companies
✅ Learn step-by-step — no prior experience needed!
Enroll today and turn your curiosity into real-world skill:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ukana ikpe directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ukana ikpe
ukana ikpe
Transformative Tech Leader | Serial Entrepreneur & Machine Learning Engineer Leveraging 3+ years of expertise in Machine Learning and a background in Web Development, I drive innovation through building, mentoring, and educating. Passionate about harnessing AI to solve real-world problems."