What is a Server, Can Anyone Make It, and Why Do Companies Have It?
 Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
In today’s digital age, servers are an essential part of the online world. From hosting websites to managing business operations, servers play a crucial role in ensuring smooth connectivity and functionality. But what exactly is a server? Can anyone create one? And why do companies rely on them? What is a Server?
A server is essentially a specialized computer designed to provide services or resources to other computers, known as "clients," over a network. Think of it as the backbone of the internet and IT systems that "serves" data, files, applications, or websites whenever requested. For example:
When you visit a website, your browser sends a request to the server hosting that website. The server processes this request and sends back the webpage for you to view.
Servers also handle emails, store files, and even run applications like video streaming platforms or online games.
Unlike regular computers (like laptops or desktops), servers are optimized for continuous operation and high performance. They often lack peripherals like screens or keyboards because they are managed remotely through command-line interfaces or specialized software.
Types of Servers
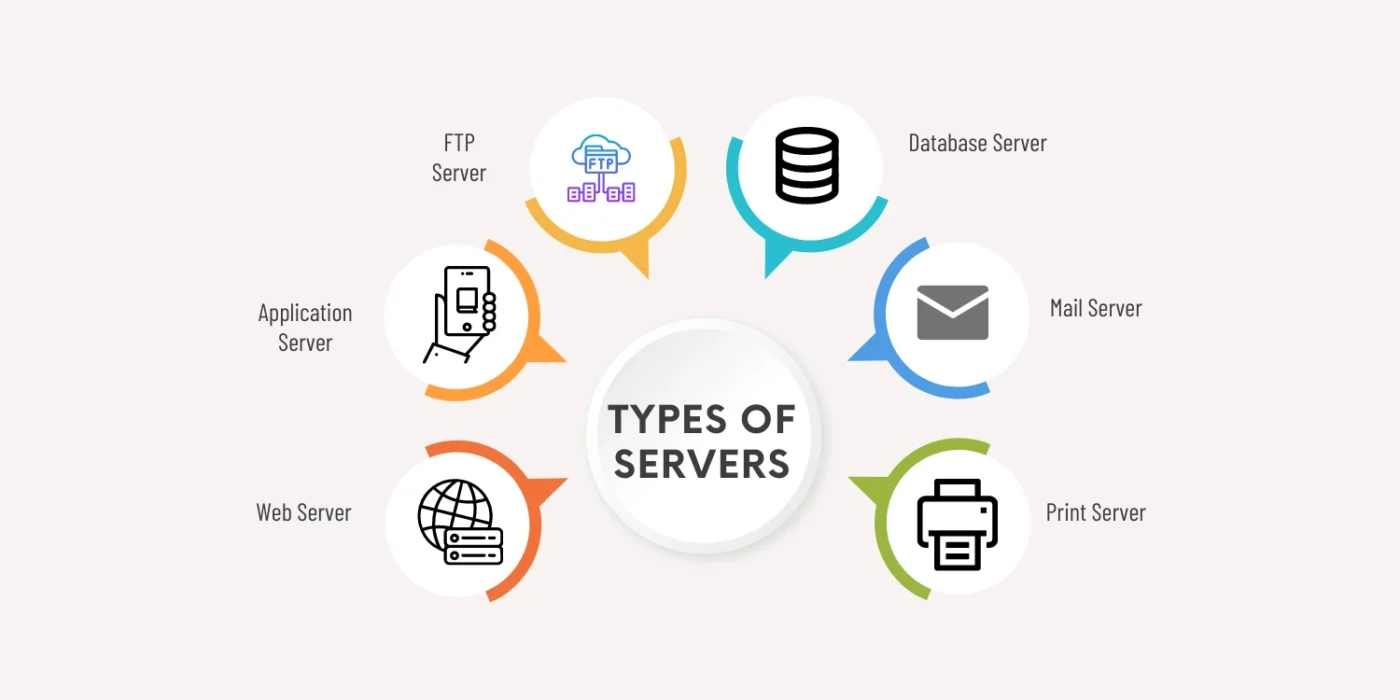
Servers come in various types depending on their function. Here are some common ones:
Web Servers: These host websites and deliver web pages to users via browsers.
Database Servers: They store and manage databases, allowing applications to access structured data efficiently.
File Servers: These are used for storing and sharing files across a network.
Mail Servers: They handle email communication by sending, receiving, and storing emails.
Application Servers: These host software applications that users access remotely.
Each type of server is tailored for specific tasks but operates on the same basic principle: serving resources to clients.
Can Anyone Make a Server?
You don’t need to be an IT expert to create your own server. With some basic understanding and the right tools, almost anyone can set up a server for personal or small-scale use. Here’s how:
What You Need
Hardware: You can use an old computer or purchase dedicated hardware like a physical server or virtual server.
- Minimum requirements include a processor (300MHz or higher), sufficient RAM (64MB or more), and storage space.
Network Router: A router connects your server to the internet or local network.
Ethernet Cable: This ensures stable connectivity between your server and other devices.
Operating System: Servers often run specialized operating systems like Linux (popular for servers), Windows Server, or macOS Server.
Steps to Create Your Own Server
Determine Your Requirements: Decide what you want your server to do—host a website, store files, or manage emails.
Set Up Hardware: Install necessary components like RAM, storage drives, and connect it to your router using Ethernet cables.
Install Server Software: Choose an operating system suited for servers (e.g., Ubuntu Server) and install it on your machine.
Configure Network Settings: Set up IP addresses and network protocols to ensure smooth communication between devices.
Secure Your Server: Install firewalls, encryption tools, and antivirus software to protect against cyber threats.
Maintain Your Server: Regularly update software and monitor performance to ensure reliability.
While setting up a personal server is achievable, managing larger-scale servers requires expertise in networking and security.
Why Do Companies Have Servers?
Servers are indispensable for businesses of all sizes because they centralize operations, improve efficiency, and enhance security. Here are some key reasons why companies rely on servers:
1. Centralized Data Management
Servers allow businesses to store all their critical data in one central location rather than scattering it across individual devices. This makes it easier for employees to access files, collaborate on projects, and share information securely.
2. Enhanced Security
With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, businesses need robust security measures to protect sensitive information like customer data or financial records. Servers come equipped with features like firewalls, encryption protocols, and access controls that safeguard against unauthorized access.
3. Reliability and Uptime
For businesses that operate online (e.g., e-commerce stores), downtime can lead to lost revenue and damaged reputation. Servers are designed for continuous operation with minimal disruptions—thanks to features like load balancing and failover systems.
4. Remote Access
Modern workplaces often have employees working from different locations or remotely. Servers enable secure remote access to company resources such as files, applications, or databases via Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
5. Scalability
As businesses grow, their IT needs expand too—whether it’s increased storage capacity or higher processing power for handling more users. Cloud servers offer scalability by allowing companies to rent additional resources without investing in physical hardware.
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Servers play a vital role in ensuring business continuity during unexpected events like hardware failure or natural disasters. Backup servers store copies of critical data that can be restored quickly if needed.
7. Improved Performance
Servers offload heavy tasks from individual computers (like running complex applications), freeing up memory and processing power on those devices.
8. Professional Image
Having dedicated servers allows businesses to host their own websites or email systems rather than relying on third-party providers—presenting a more professional image to customers.
On-Premise vs Cloud Servers
Businesses can choose between two main types of server setups:
On-Premise Servers
Physical servers maintained in-house by the company.
Offer complete control over data, but require significant investment in hardware and expertise for maintenance.
Cloud Servers
Virtual servers provided by third-party services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Cost-effective with high scalability but involve storing data off-site.
The choice depends on factors like budget, security requirements, and scalability needs.
A server is a specialized computer that provides resources or services over a network.
Anyone can create their own server with basic tools and knowledge.
Companies rely on servers for centralized data management, enhanced security, reliability, scalability, remote access capabilities, backup solutions, improved performance, and professional branding.
Whether you’re an individual exploring tech possibilities or a business looking to optimize operations, understanding servers opens up endless opportunities in today’s interconnected world!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aakashi Jaiswal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Coder | Winter of Blockchain 2024❄️ | Web-Developer | App-Developer | UI/UX | DSA | GSSoc 2024| Freelancer | Building a Startup | Helping People learn Technology | Dancer | MERN stack developer