Understanding the Risk Management System and Its Importance
 Community Contribution
Community Contribution
A risk management system provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Organizations use this system to address uncertainties and protect their operations. Effective risk management plays a crucial role in achieving strategic goals while ensuring operational resilience.
Proactive risk management helps organizations align opportunities with their objectives.
A reactive approach often leads to missed opportunities and project failures, which can harm success.
Credit rating agencies now assess companies based on their risk management processes, linking robust practices to financial stability.
By adopting a proactive stance, organizations not only safeguard their interests but also position themselves for long-term growth.
The fastest way to build a risk management system — try RisingWave.
Key Takeaways
A risk management system helps find and fix risks early.
Managing risks early connects chances with goals, boosting growth.
Involving others in risk planning builds teamwork and better choices.
Checking and updating risk plans often keeps them useful.
Using a risk system makes work easier and data more accurate.
Definition and Purpose of a Risk Management System
What is a Risk Management System?
A risk management system is a structured framework designed to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact an organization's objectives. It provides a systematic approach to managing uncertainties, ensuring that potential threats are addressed proactively. This system encompasses various processes, tools, and methodologies tailored to an organization's specific needs.
Constructing a sustainable risk management system relies on correctly diagnosing and designing a model that works for an organization’s risk-based approach to risk identification and mitigation. It defines the process of quality control-directed monitoring activities and recommends periodic review necessary to assure sustained improvement and control necessary to sustain the Quality by Design (QbD)/QMS model.
Organizations often adopt globally recognized frameworks such as ISO 31000 or COSO ERM to guide their risk management process. These frameworks emphasize governance, culture, and a systematic approach to risk handling.
| Framework | Key Features |
| COSO ERM | - Governance and culture |
| - Strategy and objective-setting | |
| - Performance | |
| - Review and revision | |
| - Information, communication, and reporting | |
| ISO 31000 | - Universal applicability |
| - Comprehensive coverage | |
| - Guideline-based |
By implementing these frameworks, organizations can align their risk management practices with international standards, ensuring consistency and effectiveness.
The Purpose of Risk Management in Organizations
The primary purpose of risk management is to minimize potential risks to an acceptable level before they occur. This proactive approach ensures that organizations can anticipate and address threats that may negatively affect their operations, finances, or reputation. Risk management also plays a crucial role in enhancing organizational stability and resilience.
A study analyzing risk management systems in France, Germany, and the United Kingdom found that effective risk management positively influences firm performance. The research highlighted the importance of risk management committees in maintaining stability and mitigating the negative effects of debt on performance.
Organizations across various industries have demonstrated the importance of risk management in achieving their goals. For example:
A regional transportation company reduced accident rates and insurance premiums by implementing a comprehensive risk management strategy.
A mid-sized insurance firm improved profitability by enhancing its practices to address natural disaster-related claims.
A luxury brand in Europe aligned with ISO 31000 standards to manage market volatility effectively.
Risk management ensures compliance with regulations, protects assets, and fosters a culture of accountability. It also supports enterprise risk management by integrating risk considerations into strategic decision-making processes. By adopting a robust risk management system, organizations can navigate uncertainties and achieve long-term success.
Key Components of a Risk Management System
Risk Identification
Risk identification serves as the foundation of any risk management system. It involves pinpointing potential risks that could disrupt organizational objectives. Effective identification enhances awareness of risk identification and allows businesses to address vulnerabilities before they escalate.
Organizations often use structured techniques to identify risks. For example:
General Motors (GM) recognized a strategic vulnerability in its supply chain for EV battery materials. This led to a $150 million investment in a Canadian mining company to mitigate risks.
Change Healthcare detected a ransomware attack in progress, highlighting the importance of early identification to prevent disruptions.
UnitedHealthcare reviewed exposure points after a targeted attack on its CEO, emphasizing the need for proactive measures.
These examples demonstrate how identifying risks early can protect assets and ensure operational continuity. Communication and consultation play a vital role in this process, engaging stakeholders and raising awareness about business risks.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment evaluates the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This step prioritizes actions by categorizing risks based on their severity. Organizations use tools like risk matrices and risk scores to streamline the evaluation process.
A risk matrix visually categorizes risks, helping teams identify critical threats quickly. Risk scores assign numerical values to risks, calculated by multiplying likelihood and impact. Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) further supports decision-making by comparing mitigation costs against potential benefits.
For instance, a transportation company used risk matrices to reduce accident rates and insurance premiums. This approach ensures that resources focus on addressing the most significant risks, improving overall efficiency.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Risk mitigation involves implementing strategies to manage potential risks effectively. Organizations can choose from several approaches, including avoidance, reduction, transfer, or acceptance. Each strategy depends on the nature and severity of the risk.
For example, GM's investment in a mining company represents a risk reduction strategy, addressing supply chain vulnerabilities. Similarly, Change Healthcare's response to ransomware attacks highlights the importance of reducing cybersecurity risks.
Monitoring and review ensure that mitigation strategies remain effective over time. Regular evaluations allow organizations to adapt to changing circumstances and maintain resilience. By prioritizing mitigation, businesses safeguard their operations and enhance stakeholder confidence.
Risk Monitoring and Review
Risk monitoring and review form a critical part of an effective risk management system. This process ensures that organizations continuously evaluate their risk environment and the effectiveness of their mitigation strategies. By doing so, they can adapt to changes and maintain resilience in the face of uncertainties.
Organizations use systematic data collection to track key risk indicators (KRIs). These indicators provide measurable and predictable insights into potential risks. Setting thresholds for KRIs helps trigger alerts when risk levels exceed acceptable limits. For example, a financial institution might monitor credit default rates and establish a threshold to signal when intervention is necessary. Involving stakeholders in the development of KRIs ensures alignment with organizational goals and fosters accountability.
| Evidence | Description |
| Systematic Data Collection | Emphasizes the importance of systematically collecting data on KRIs to ensure they are measurable, predictable, and comparable. |
| Setting Thresholds | Highlights the need for establishing thresholds that trigger alerts when risk levels exceed acceptable limits. |
| Stakeholder Involvement | Stresses the necessity of involving key stakeholders in the KRI development process to ensure alignment with organizational goals. |
Effective monitoring and review processes validate the KRI framework. They also track and report on KRIs to ensure transparency. Organizations identify and document exceptions or breaches to KRIs, enabling timely corrective actions. For instance, a manufacturing company might monitor equipment failure rates and document any deviations to prevent production delays.
Regular reviews of risk management strategies ensure they remain relevant and effective. This iterative process allows organizations to refine their approaches and address emerging risks. By prioritizing monitoring and review, businesses can enhance their ability to navigate uncertainties and achieve long-term success.
Benefits of Implementing a Risk Management System

Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Organizations face increasing regulatory demands across industries. A robust risk management plan ensures compliance with these regulations, reducing the likelihood of penalties and reputational damage. By integrating compliance into their risk management processes, businesses can proactively address regulatory changes and maintain operational integrity.
Statistics highlight the challenges organizations face in meeting compliance requirements. For instance:
| Statistic | Description |
| 70% | Service organizations need to demonstrate compliance with at least six different frameworks. |
| 60% | Businesses struggle to keep up with compliance and regulatory requirements. |
| 76% | Compliance managers manually track regulatory changes. |
| 35% | Risk executives see compliance risk as a major threat to growth. |
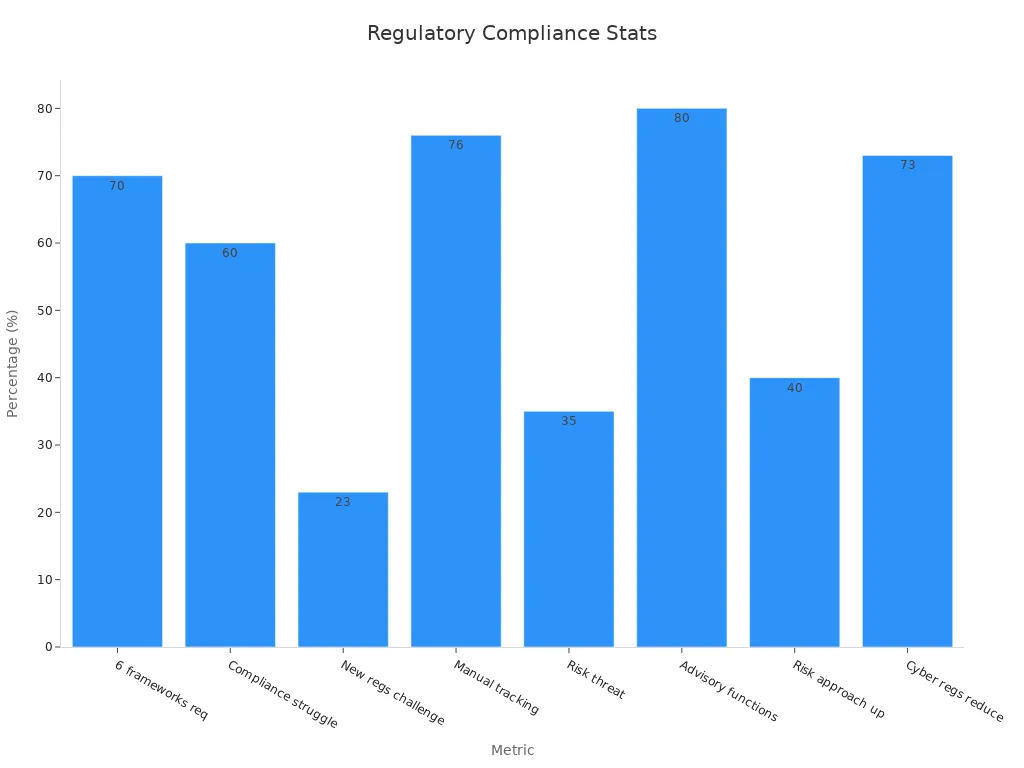
Effective risk management helps organizations streamline compliance processes. For example, automated systems can track regulatory updates, reducing manual effort and ensuring timely adherence. This approach not only minimizes compliance risks but also fosters trust among stakeholders.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Implementing a risk management plan significantly improves operational efficiency. By identifying and addressing potential risks early, organizations can optimize resources and reduce waste. Improved data management, for instance, has led to a 5-15% reduction in annual data spend for many businesses. Additionally, project controls help prevent delays and ensure projects stay on track.
A detailed analysis of operational challenges and solutions reveals the tangible benefits of risk management:
| Challenge | Solution and Result |
| User Resistance & Data Quality | Introduced peer mentors and automated validation checks, leading to 85% active user participation and a 60% drop in data errors. |
| System Performance | Applied load balancing and optimization techniques, cutting response times by 40%. |
These improvements demonstrate how effective risk management enhances productivity and reduces costs. Organizations that regularly test their incident response plans report significant cost savings. According to IBM, businesses with an incident response team save an average of $2.66 million, representing a 58% reduction in costs.
Building Stakeholder Confidence
A well-implemented risk management system builds confidence among stakeholders, including investors, employees, and customers. Organizations that prioritize risk management demonstrate their commitment to stability and long-term growth. This assurance fosters trust and strengthens relationships with key stakeholders.
Surveys reveal the impact of risk management on stakeholder confidence:
Organizations investing over $10 million in risk management rate their programs as excellent or good.
Integrated risk management programs correlate with higher growth rates. About one-third of organizations with a CAGR over 5% have highly integrated risk programs.
The presence of risk management in board meetings boosts leaders' confidence in risk data. In fact, 88% of leaders express strong confidence when risk management is frequently discussed.
By integrating risk management into strategic decision-making, businesses can align their objectives with stakeholder expectations. This alignment not only enhances credibility but also positions organizations as reliable and forward-thinking entities in their respective industries.
Reducing Financial and Operational Risks
Reducing financial and operational risks is a critical objective for organizations aiming to maintain stability and achieve long-term success. A well-structured risk management plan minimizes losses by identifying vulnerabilities and implementing strategies to address them effectively.
Quantitative risk analysis plays a significant role in reducing financial uncertainties. This method uses statistical techniques to evaluate risks, translating probabilities and impacts into measurable quantities. By forecasting potential outcomes, organizations can make informed decisions that minimize losses. For example, a company facing fluctuating market conditions might use quantitative analysis to predict revenue changes and adjust its financial strategies accordingly.
The FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) model provides a structured approach to quantifying information risks. This model helps organizations evaluate operational risks by breaking them into measurable components. For instance, a manufacturing firm might use the FAIR model to assess risks related to equipment downtime, enabling it to implement preventive maintenance schedules and reduce disruptions.
Financial risk management involves identifying and assessing potential financial threats. This process is essential for developing strategies that protect assets and ensure operational continuity. For example, a retail business might analyze credit risks associated with its suppliers. By doing so, it can diversify its supply chain and reduce dependency on high-risk vendors.
Operational risks often arise from inefficiencies or disruptions in processes. Organizations can address these risks by implementing robust monitoring systems and contingency plans. For instance, a logistics company might use real-time tracking to monitor shipments and respond quickly to delays. This proactive approach minimizes losses and enhances customer satisfaction.
A comprehensive risk management plan integrates financial and operational risk assessments into a unified framework. This integration ensures that organizations can address interconnected risks effectively. By adopting such a plan, businesses not only safeguard their financial health but also enhance their operational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations in Risk Management
Common Challenges in Implementing Risk Management
Organizations often encounter several obstacles when implementing risk management strategies. These challenges can hinder the effectiveness of their efforts and create vulnerabilities. The most common challenges include:
Limited visibility into risks: Data silos within organizations prevent a comprehensive understanding of potential risks. This lack of visibility can lead to missed threats.
Inconsistent risk management processes: Immature or poorly defined processes result in inconsistencies in identifying and managing risks.
Siloed risk management: Isolated practices across departments create gaps in the overall risk management framework.
Lack of executive buy-in: Insufficient leadership support makes it difficult to allocate resources for enterprise risk management (ERM).
Industry literature highlights additional challenges, particularly in laboratory environments. These include the need to comply with international standards, integrate risk management into daily operations, and focus on effective risk identification. Ongoing management and training also play a critical role in overcoming these obstacles. Without addressing these issues, organizations may struggle to build a robust risk management system.
Limitations of Risk Management Systems
Risk management systems, while essential, have inherent limitations that organizations must acknowledge. These limitations can affect their ability to predict and mitigate risks effectively. The table below outlines some of the most significant constraints:
| Limitation | Description |
| Incomplete Data and Information | Limited data availability and quality hinder accurate risk assessment, especially for emerging technologies or unprecedented events. |
| Uncertainty and Complexity | Interconnected risks and unpredictable outcomes complicate the development of comprehensive mitigation strategies. |
| Assumption of Normal Distribution | Traditional methods often assume normal distribution, underestimating the severity of extreme events and leaving organizations vulnerable. |
| Behavioral Biases | Cognitive biases distort risk assessments, leading to improper resource allocation and ineffective strategies. |
| Lack of Integration | Siloed risk management processes hinder effective decision-making and create inefficiencies. |
| Difficulty in Quantifying Intangible Risks | Intangible risks, such as reputational damage, are hard to measure objectively, leading to potential underestimation. |
| Lack of Predictive Power | Risk management systems cannot predict all future events, emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring and adaptive strategies. |
| Overemphasis on Short-Term Risks | Focusing on immediate threats often results in neglecting long-term strategic risks, which are crucial for sustained success. |
These limitations highlight the importance of adopting a dynamic and adaptive approach to risk management. Organizations must continuously refine their strategies to address emerging challenges and ensure resilience.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
Setting Clear Objectives and Goals
Establishing clear objectives is fundamental to effective risk management. Objectives provide a roadmap for identifying and addressing risks that could hinder organizational success. They also ensure alignment between risk management strategies and broader business goals.
Organizations should define objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a company aiming to reduce cybersecurity risks might set a goal to implement advanced encryption protocols within six months. This clarity enables teams to focus their efforts and measure progress effectively.
Regularly revisiting objectives ensures they remain relevant in dynamic environments. Businesses can adapt their goals to address emerging risks, ensuring resilience and long-term success.
Engaging Stakeholders in the Process
Stakeholder engagement enhances the effectiveness of risk management processes. Involving stakeholders fosters collaboration, improves decision-making, and ensures that risk strategies address diverse perspectives.
A study across sectors demonstrated the impact of stakeholder involvement:
| Evidence Description | Impact on Risk Management Process |
| Stakeholder involvement was a key strength in the review process. | It facilitated the identification of relevant research questions and enhanced the overall impact of the evidence produced. |
| The review process addressed a high volume of relevant questions in a timely manner. | This transparency and tailored approach improved decision-making in policy and clinical contexts. |
Organizations can engage stakeholders through workshops, surveys, and regular communication. These methods encourage active participation and build trust. For instance, a healthcare provider might involve clinicians and patients in identifying risks related to treatment protocols. This collaborative approach ensures that risk management strategies are comprehensive and effective.
Utilizing a Risk Management Information System
A risk management information system (RMIS) streamlines the risk management process by providing tools for data collection, analysis, and reporting. It enhances accuracy, improves workflows, and supports better decision-making.
The benefits of using an RMIS include:
| Benefit | Description |
| Enhanced data accuracy | Improves the quality and consistency of risk-related information. |
| Improved client communication | Provides clearer, more transparent updates to clients. |
| Streamlined workflows | Increases productivity through more efficient processes. |
| Better risk identification | Helps spot potential issues earlier and develop effective mitigation strategies. |
| Precise insurance program design | Enables tailored insurance solutions based on accurate data. |
Organizations can leverage RMIS to monitor risks in real-time, enabling proactive responses to emerging threats. For example, a logistics company might use RMIS to track shipment delays and adjust delivery schedules promptly. This system not only reduces operational risks but also enhances stakeholder confidence.
By integrating RMIS into their risk management framework, businesses can optimize their processes and achieve their objectives more effectively.
Emphasizing Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of effective risk management. Organizations must regularly refine their processes to adapt to evolving challenges and maintain resilience. This approach ensures that risk strategies remain relevant and effective over time.
Several models have proven successful in fostering continuous improvement. The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is widely applied to promote risk-oriented thinking. This model emphasizes planning actions, implementing them, reviewing outcomes, and refining processes. By focusing on development, organizations can achieve measurable results and enhance their risk management systems.
Quality Risk Management (QRM) also plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of products and services. Advanced strategies and tools enable firms to manage risks effectively while staying competitive and compliant. Mature Model Risk Management (MRM) processes further support this goal by integrating validation tools within governance frameworks. Automation and standardization of validation procedures ensure consistency and improve efficiency.
Automation is a critical component of continuous improvement. Firms must automate repetitive tasks and standardize procedures to reduce errors and save time. For example, model validators are evolving into model risk managers, taking on broader responsibilities within organizations. This shift highlights the importance of aligning roles with strategic objectives.
Consistency across validation units is another essential factor. Standardized practices eliminate discrepancies and foster a unified approach to risk management. Organizations that prioritize consistency can better address uncertainties and achieve long-term success.
By embracing continuous improvement, businesses can strengthen their risk management frameworks. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also positions organizations for sustained growth and stability.
A risk management system provides a structured framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Its purpose lies in safeguarding organizational objectives and fostering resilience. By implementing effective risk management, organizations experience an increased likelihood of achieving objectives, ensuring compliance, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Successful risk management also builds stakeholder confidence and reduces financial vulnerabilities. Organizations with advanced risk maturity engage in sustainable decision-making, which strengthens their market position. Higher maturity levels enhance reliability and trustworthiness, offering a competitive edge.
Overcoming challenges and adopting best practices remain essential for long-term success. Continuous improvement, stakeholder engagement, and the use of advanced tools ensure that risk strategies remain relevant and effective. These efforts collectively contribute to a stable and prosperous future.
FAQ
What is the first step in implementing a risk management system?
The first step involves identifying potential risks. Organizations should analyze their operations, processes, and external environment to pinpoint vulnerabilities. This foundational step ensures a comprehensive understanding of possible threats.
How does risk management improve decision-making?
Risk management provides structured data and insights. These tools help organizations evaluate potential outcomes and make informed decisions. By understanding risks, businesses can prioritize actions and allocate resources effectively.
Can small businesses benefit from risk management systems?
Yes, small businesses gain significant advantages. Risk management helps them identify vulnerabilities, reduce financial losses, and ensure compliance. It also enhances operational efficiency, enabling them to compete effectively in their markets.
What tools are commonly used in risk assessment?
Organizations often use risk matrices, risk scores, and cost-benefit analysis. These tools help evaluate the likelihood and impact of risks. They also support prioritization, ensuring that critical threats receive immediate attention.
How often should organizations review their risk management strategies?
Organizations should review their strategies regularly. Quarterly or annual reviews ensure that risk management processes remain relevant. Frequent evaluations help address emerging threats and adapt to changing circumstances.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Community Contribution directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
