Exploring Different Types of Computer Networks
 Rahul Kumar
Rahul Kumar
Computer networks can be small or large, connecting just two devices in a room or covering entire continents. They are mainly categorized by geographical area, data transfer distance, and how they are used.
Let’s explore the five basic types of networks, starting from the smallest and going to the largest:
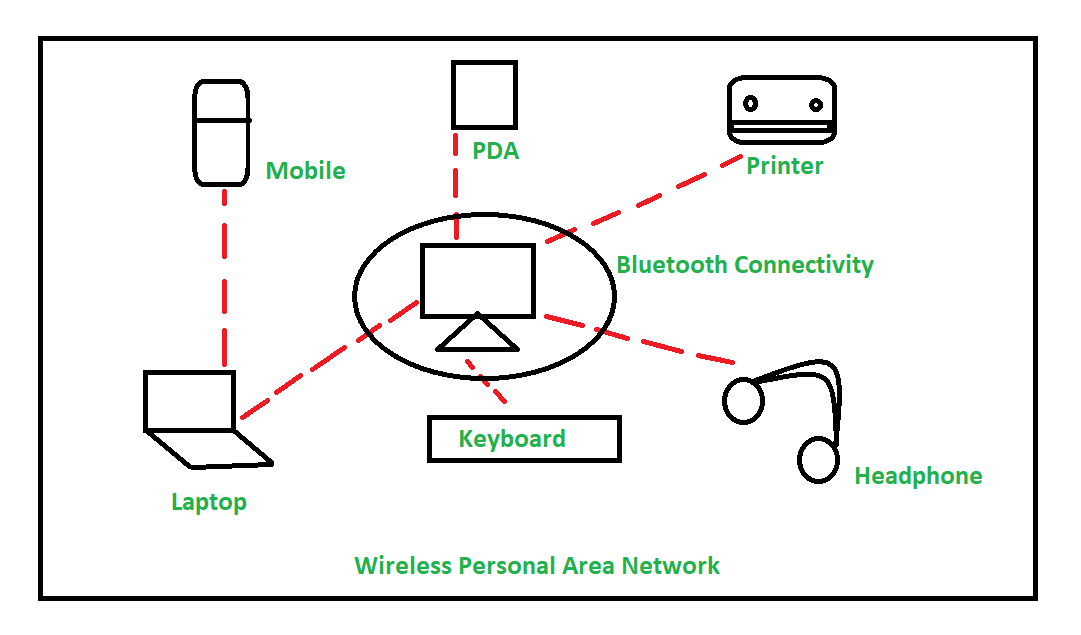
🧩 1. PAN – Personal Area Network
Full Form: Personal Area Network
Range: A few meters
Purpose: Connecting personal devices that are close to each other
Example: Bluetooth between phone and smartwatch, infrared remotes, or file sharing via AirDrop.
🔍 Use Case: Great for personal use — low range, low power, direct communication.
✅ Pros:
Easy setup, no complex hardware
No need for internet or routers
Low power consumption
❌ Cons:
Very limited range
Low data transfer speeds
Prone to interference
🏠 2. LAN – Local Area Network
Full Form: Local Area Network
Range: Up to 1 kilometer
Purpose: Connecting devices within a building or small campus
Example: Your Wi-Fi network at home, or an office network connecting computers, printers, and servers.
🔍 Use Case: Enables file sharing, gaming, printing, and local communication. Reliable, fast, and usually managed by a single organization.
✅ Pros:
Fast data transfer speeds (up to gigabit)
Secure and easily manageable
Enables printer/file sharing, multiplayer gaming, etc.
❌ Cons:
Limited to local space
Setup can get costly in large offices
Requires network admin in bigger environments

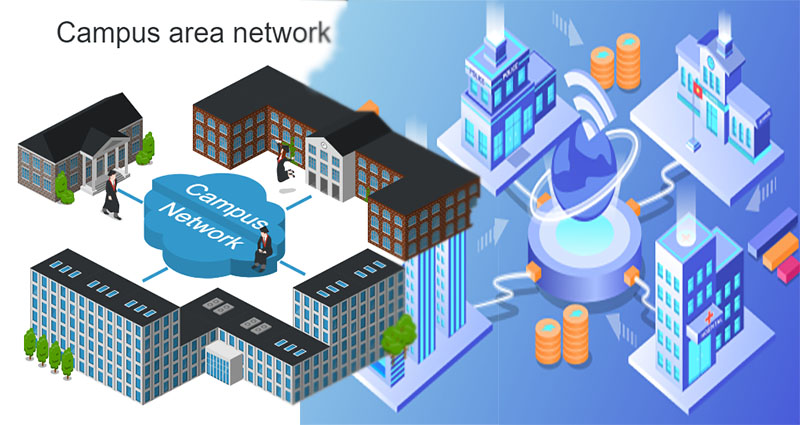
🏢 3. CAN – Campus Area Network
Full Form: Campus Area Network
Range: Covers multiple LANs across a campus or organization
Purpose: Bridges LANs within a geographic area like a university, tech park, or military base
Example: A university’s IT network that links multiple buildings — libraries, labs, dorms, administration — under one central control.
🔍 Use Case: Optimized for institution-level performance with centralized network resources like data centers, security systems, and internal portals.
✅ Pros:
Centralized control over entire campus
Cost-efficient compared to multiple isolated LANs
Seamless internal data sharing
❌ Cons:
Needs skilled IT team to manage
Hardware failure can affect multiple buildings
Vulnerable to internal misuse if not secured
🏙️ 4. MAN – Metropolitan Area Network
Full Form: Metropolitan Area Network
Range: Entire city or metro region
Purpose: Connecting multiple CANs and LANs across urban areas
Example: City-wide broadband by ISPs, or an inter-building government data network.
🔍 Use Case: Ideal for cities needing centralized communication, surveillance, or public Wi-Fi across multiple zones.
✅ Pros:
High-speed connectivity across urban areas
Ideal for public services and large-scale enterprises
Reduces the need for individual network setups
❌ Cons:
High infrastructure cost (fiber laying, switching equipment)
Complex to maintain and troubleshoot
Risk of central-point failure

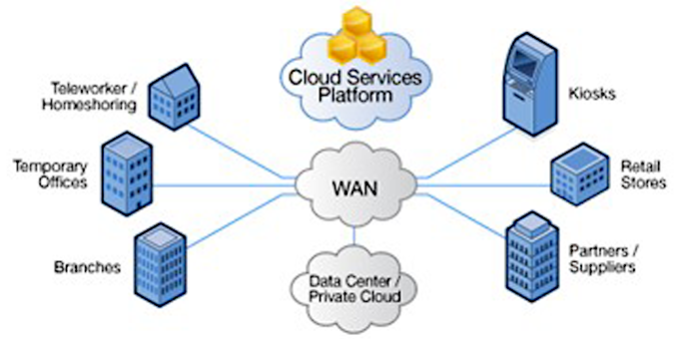
🌍 5. WAN – Wide Area Network
Full Form: Wide Area Network
Range: Country to global scale
Purpose: Long-distance communication and connectivity
Example: The Internet, multinational corporate networks, banking backbones.
🔍 Use Case: Powers cross-border operations, cloud computing, and global commerce. Uses leased lines, satellites, undersea cables.
✅ Pros:
Enables global communication and cloud access
Connects branch offices, remote users, and data centers
Scalable across regions
❌ Cons:
Expensive to build and operate
Security is a major challenge
Latency and downtime risks are higher
| Type | Full Form | Range | Examples | Pros | Cons |
| PAN | Personal Area Network | A few meters | Bluetooth between phone & earbuds | Easy to set up, low power, no internet needed | Very short range, low speed, easily interrupted |
| LAN | Local Area Network | Up to 1 km | Home Wi-Fi, office network | Fast, secure, good for file/printer sharing | Limited to small area, setup can be costly in larger setups |
| CAN | Campus Area Network | Several kilometers | University or corporate campus network | Centralized control, cost-effective across buildings | Requires skilled management, internal misuse risk |
| MAN | Metropolitan Area Network | City-wide | City broadband, metro rail networks | Covers large urban areas, great for public services | High setup & maintenance cost, complex infrastructure |
| WAN | Wide Area Network | Country to globe | The Internet, multinational bank networks | Global communication, cloud access, high scalability | Expensive, high latency risk, major security concerns |
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rahul Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
