Data science lifecycle
 Ian Santillan
Ian Santillan
The Team Data Science Process (TDSP) is an agile, iterative data science methodology to deliver predictive analytics solutions and intelligent applications efficiently. TDSP helps improve team collaboration and learning by suggesting how team roles work best together. TDSP includes best practices and structures from Microsoft and other industry leaders to help toward successful implementation of data science initiatives. The goal is to help companies fully realize the benefits of their analytics program.
Key components of the TDSP
TDSP has the following key components:
A data science lifecycle definition
A standardized project structure
Infrastructure and resources recommended for data science projects
Tools and utilities recommended for project execution
Data science lifecycle
The Team Data Science Process (TDSP) provides a lifecycle to structure the development of your data science projects. The lifecycle outlines the full steps that successful projects follow.
If you are using another data science lifecycle, such as CRISP-DM, KDD, or your organization’s own custom process, you can still use the task-based TDSP in the context of those development lifecycles. At a high level, these different methodologies have much in common.
This lifecycle has been designed for data science projects that ship as part of intelligent applications. These applications deploy machine learning or artificial intelligence models for predictive analytics. Exploratory data science projects or improvised analytics projects can also benefit from using this process. But in such cases some of the steps described may not be needed.
Five lifecycle stages
The TDSP lifecycle is composed of five major stages that are executed iteratively. These stages include:

The TDSP lifecycle is modeled as a sequence of iterated steps that provide guidance on the tasks needed to use predictive models. You deploy the predictive models in the production environment that you plan to use to build the intelligent applications. The goal of this process lifecycle is to continue to move a data-science project toward a clear engagement end point. Data science is an exercise in research and discovery. The ability to communicate tasks to your team and your customers by using a well-defined set of artifacts that employ standardized templates helps to avoid misunderstandings. Using these templates also increases the chance of the successful completion of a complex data-science project.
For each stage, we provide the following information:
Goals: The specific objectives.
How to do it: An outline of the specific tasks and guidance on how to complete them.
Artifacts: The deliverables and the support to produce them.
The goals, tasks, and documentation artifacts for each stage of the lifecycle in TDSP are described in the Team Data Science Process lifecycle topic. These tasks and artifacts are associated with project roles:
Solution architect
Project manager
Data engineer
Data scientist
Application developer
Project lead
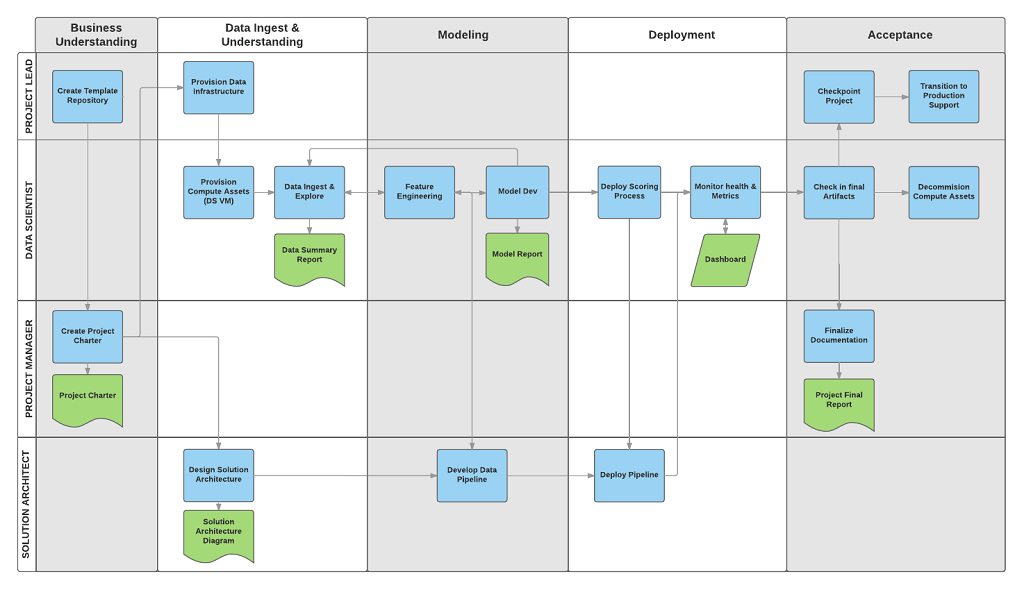
The following diagram provides a grid view of the tasks (in blue) and artifacts (in green) associated with each stage of the lifecycle (on the horizontal axis) for these roles (on the vertical axis).
Standardized project structure
Having all projects share a directory structure and use templates for project documents makes it easy for the team members to find information about their projects. All code and documents are stored in a version control system (VCS) like Git, TFS, or Subversion to enable team collaboration. Tracking tasks and features in an agile project tracking system like Jira, Rally, and Azure DevOps allows closer tracking of the code for individual features. Such tracking also enables teams to obtain better cost estimates. TDSP recommends creating a separate repository for each project on the VCS for versioning, information security, and collaboration. The standardized structure for all projects helps build institutional knowledge across the organization.
We provide templates for the folder structure and required documents in standard locations. This folder structure organizes the files that contain code for data exploration and feature extraction, and that record model iterations. These templates make it easier for team members to understand work done by others and to add new members to teams. It is easy to view and update document templates in markdown format. Use templates to provide checklists with key questions for each project to insure that the problem is well defined and that deliverables meet the quality expected. Examples include:
a project charter to document the business problem and scope of the project
data reports to document the structure and statistics of the raw data
model reports to document the derived features
model performance metrics such as ROC curves or MSE
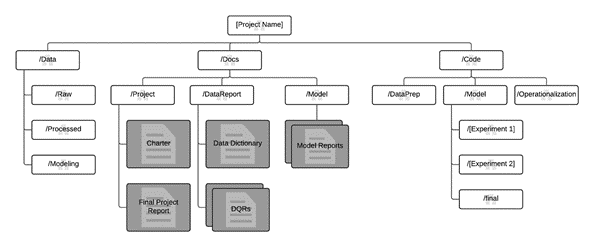
The directory structure can be cloned from GitHub.
Infrastructure and resources for data science projects
TDSP provides recommendations for managing shared analytics and storage infrastructure such as:
cloud file systems for storing datasets
databases
big data (SQL or Spark) clusters
machine learning service
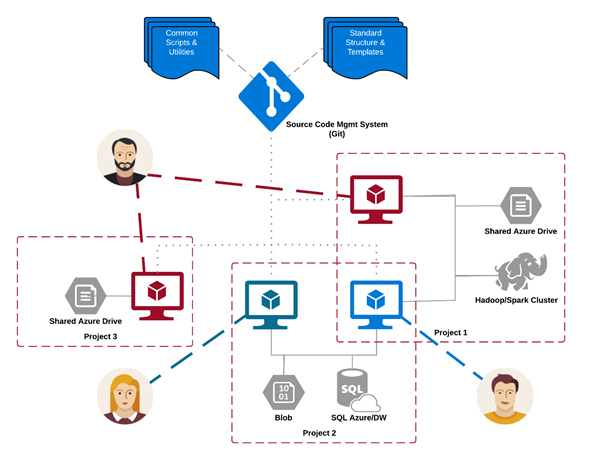
The analytics and storage infrastructure, where raw and processed datasets are stored, may be in the cloud or on-premises. This infrastructure enables reproducible analysis. It also avoids duplication, which may lead to inconsistencies and unnecessary infrastructure costs. Tools are provided to provision the shared resources, track them, and allow each team member to connect to those resources securely. It is also a good practice to have project members create a consistent compute environment. Different team members can then replicate and validate experiments.
Here is an example of a team working on multiple projects and sharing various cloud analytics infrastructure components.
Tools and utilities for project execution
Introducing processes in most organizations is challenging. Tools provided to implement the data science process and lifecycle help lower the barriers to and increase the consistency of their adoption. TDSP provides an initial set of tools and scripts to jump-start adoption of TDSP within a team. It also helps automate some of the common tasks in the data science lifecycle such as data exploration and baseline modeling. There is a well-defined structure provided for individuals to contribute shared tools and utilities into their team’s shared code repository. These resources can then be leveraged by other projects within the team or the organization. Microsoft provides extensive tooling inside Azure Machine Learning supporting both open-source (Python, R, ONNX, and common deep-learning frameworks) and also Microsoft’s own tooling (AutoML).
Reference
AI Plan - Process to plan for AI adoption - Cloud Adoption Framework | Microsoft Learn
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ian Santillan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ian Santillan
Ian Santillan
Data Architect ACE - Analytics | Leading Data Consultant for North America 2022 | Global Power Platform Bootcamp 2023 Speaker | Toronto CDAO Inner Circle 2023