How to Secure Zoom from ELUSIVE COMET Remote Attacks
 Tran Hoang Phong
Tran Hoang Phong
Researchers have warned about the ELUSIVE COMET campaign, a method of attack targeting Zoom's remote control feature. This article will analyze the attack method and propose specific defensive measures that organizations can apply to protect themselves.
Background
Two Twitter accounts approached the CEO of a company, inviting them to participate in a series of "Bloomberg Crypto" programs—a very suspicious situation. The attackers refused to communicate via email and only instructed scheduling meetings through fake Calendly pages. It was these procedural anomalies—rather than technical signs—that revealed the true nature of the attack.
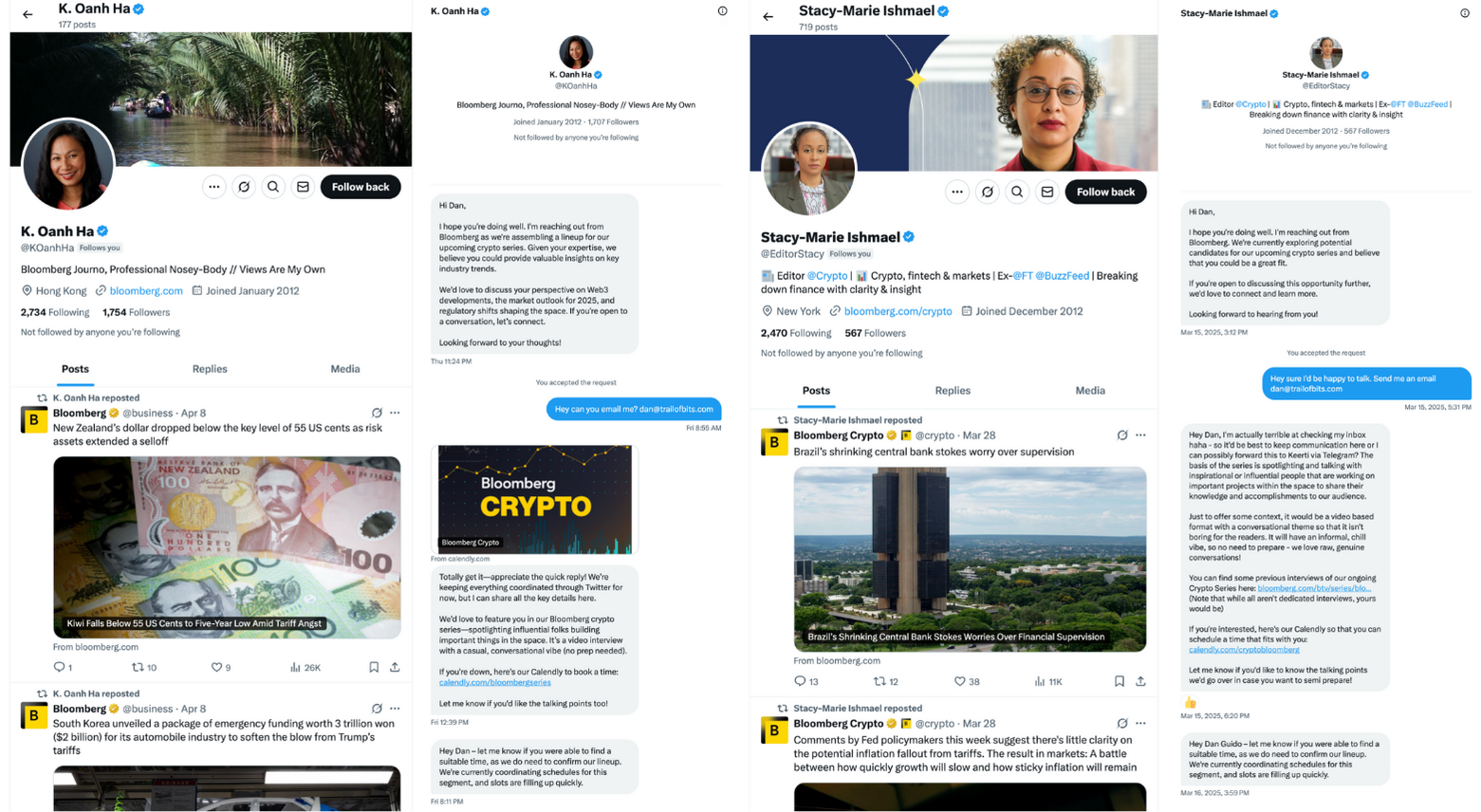
Figure 1. X messages from the scammer introducing the crypto program
ELUSIVE COMET's method is similar to the technique that caused the $1.5 billion hack at Bybit in February, where attackers did not exploit software vulnerabilities but instead took advantage of operational processes. This indicates that the blockchain industry is facing significant operational security risks, where attacks targeting humans are becoming a greater threat than software vulnerabilities.
Exploitation Scenario
Understanding Zoom's Remote Control Feature
ELUSIVE COMET's attack exploits Zoom's remote control feature—a function that allows participants to control another's computer if granted permission. When a control request is sent, a dialog box simply states, “$PARTICIPANT is requesting remote control of your screen.”
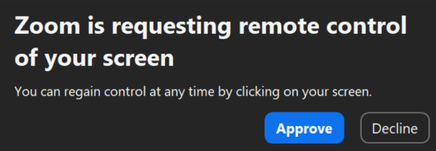
Figure 2. Example of Zoom remote control request dialog showing a forged name “Zoom” as the requester
The attack exploits this feature through a simple yet effective social engineering trick:
The attacker arranges a seemingly legitimate meeting.
During screen sharing, they request remote control.
They change their display name to “Zoom” to make the request look like a system notification.
If granted permission, they can install malware, steal data, or hijack cryptocurrency.
What makes this attack particularly dangerous is the similarity between the permission request dialog and other harmless Zoom notifications. Users accustomed to clicking "Approve" can easily grant full computer access without realizing the consequences.

Figure 3. Fake Calendly page used to schedule fake "Bloomberg Crypto" interviews
Why the Attack Succeeds (Even with Security Experts)
The ELUSIVE COMET campaign succeeds by cleverly exploiting human behavioral psychology through a combination of fake social credibility, time pressure, and confusing interfaces. The attack occurs in a business negotiation context, catching victims off guard; the permission request dialog does not clearly warn of risks; and the habit of accepting Zoom requests leads users to act instinctively; while the victim's focus is primarily on the meeting content rather than security alerts.
This tactic targets operational vulnerabilities rather than exploiting technical ones.
IOCs Related to the ELUSIVE COMET Campaign
Twitter: @KOanhHa and @EditorStacy
Email: bloombergconferences[@]gmail.com
Zoom Meeting URL:
https://us06web[.]zoom[.]us/j/84525670750Calendly Links:
calendly[.]com/bloombergseriesandcalendly[.]com/cryptobloomberg
Recommendations
FPT Threat Intelligence recommends several ways for organizations and individuals to prevent this particularly dangerous attack campaign:
To protect your organization from this attack vector, we recommend deploying the following tools:
create_zoom_pppc_profile.bash: create a system profile to block Zoom from requesting Accessibility permissions.
disable_zoom_accessibility.bash: check and remove Accessibility permissions granted to Zoom.
uninstall_zoom.bash: completely remove Zoom from computers within the organization.
Network Monitoring and Intrusion Detection: Deploy network monitoring systems (NIDS/NDR) to detect abnormal traffic and behavior related to ransomware.
Secure Data Backup: Ensure offline backups are available to recover data when encrypted.
System Updates: Apply the latest patches and security updates to fix exploited vulnerabilities.
Access Management: Limit user access rights, apply network segmentation to prevent lateral movement within the system.
Account Security: Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Data Encryption: Implement encryption for sensitive data to protect against theft or leakage.
Reduce Attack Surface: Disable unnecessary functions to reduce exploitation risk.
Enhance Security Awareness: Train employees on security risks and common cyber attack methods.
References
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tran Hoang Phong directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tran Hoang Phong
Tran Hoang Phong
Just a SOC Analyst ^^