🔐 Building a Secure and Scalable AWS VPC with Private Subnets and NAT Gateways
 paritosh pati
paritosh patiWhen building production-grade infrastructure on AWS, it's essential to design your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with security, high availability, and internet access control in mind. In this post, I’ll walk you through a practical and powerful architecture: a VPC with private subnets, NAT gateways, and a load balancer, based on AWS’s recommended best practices.
Whether you’re new to VPCs or looking to refine your existing setup, this guide is for you.
🚧 What We're Building
A multi-AZ, secure VPC setup with:
🔹 Public and private subnets across 2 Availability Zones
🔹 NAT Gateways to allow internet-bound traffic from private subnets
🔹 An Application Load Balancer (ALB) in the public subnets
🔹 Auto Scaling Group for app instances in private subnets
🔹 A VPC Endpoint for Amazon S3 to avoid public internet traffic
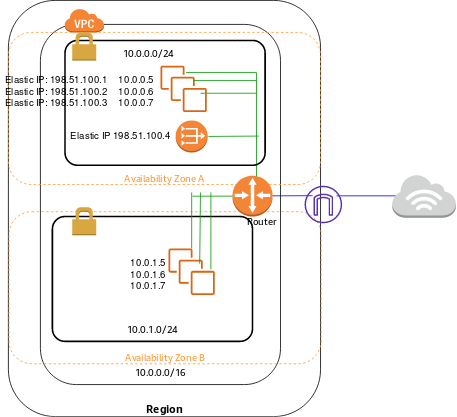
🧱 VPC Architecture Breakdown
🔸 Subnets
Public Subnets (1 in each AZ): Host ALB and NAT Gateways
Private Subnets (1 in each AZ): Host EC2 application instances
🔸 NAT Gateways
Used to allow private subnet instances to initiate outbound traffic to the internet (e.g., to pull updates), without exposing them to inbound internet traffic.
🔸 Load Balancer
The Application Load Balancer distributes incoming web traffic across EC2 instances in the private subnets.
🔸 VPC Endpoint
A gateway endpoint for Amazon S3 enables private instances to access S3 without traversing the internet, improving both security and latency.
🛠️ Step-by-Step Setup
Step 1: Create the VPC and Subnets
Create a VPC (e.g.,
10.0.0.0/16)Add 2 public subnets (e.g.,
10.0.1.0/24,10.0.2.0/24)Add 2 private subnets (e.g.,
10.0.3.0/24,10.0.4.0/24)Associate subnets with different AZs for high availability
Step 2: Set Up NAT Gateways
Launch NAT Gateways in each public subnet
Associate Elastic IPs
Update private subnet route tables to send internet-bound traffic through their respective NAT Gateway
Step 3: Configure the Internet Gateway
Attach an Internet Gateway to the VPC
Update public subnet route tables to point
0.0.0.0/0to the Internet Gateway
Step 4: Launch Application EC2 Instances
Use a Launch Template for consistent configuration
Place EC2 instances into Auto Scaling Group across private subnets
Step 5: Set Up an Application Load Balancer
Launch an ALB in public subnets
Create a target group that includes private EC2 instances
Add listeners (e.g., HTTP on port 80)
Step 6: Add a VPC Endpoint for Amazon S3
Create a gateway VPC endpoint for S3
Add routes to the private subnet route tables pointing S3 traffic (
pl-xxxx) to the endpoint
🧪 Testing the Setup
🟢 Confirm that traffic to the ALB is routed to private EC2 instances
🟢 Verify private instances can access the internet via NAT Gateways
🟢 Check that S3 access works through the VPC endpoint (e.g., use AWS CLI from an instance)
🔐 Security Best Practices
Use security groups to restrict traffic:
ALB accepts HTTP/HTTPS
EC2 only accepts traffic from ALB SG
Keep network ACLs simple or default unless needed
Use VPC Flow Logs for monitoring and audits
Follow least privilege access policies, especially for IAM roles and S3 permissions
💡 Tips & Best Practices
🧩 Multi-AZ setup ensures high availability
📉 Monitor NAT Gateway data transfer costs
🔍 Use Reachability Analyzer to troubleshoot routing or firewall issues
📊 Use CloudWatch alarms and dashboards for visibility
🧹 Cleanup
If this is for learning purposes:
Terminate instances
Delete the ALB, NAT Gateways, and route tables
Delete subnets, VPC, and other associated resources
🚀 Conclusion
This architecture provides a secure, scalable, and fault-tolerant foundation for running web apps or APIs on AWS. With private subnets, NAT gateways, load balancing, and scaling, it’s a production-ready solution trusted by many.
If you’re building in AWS, this is a great pattern to start with.
Refer to this good video from Abhishek Veeramalla
https://youtu.be/iSOfkw_YyOU?si=-fCsOz0722pTfa3z&t=8829
Let me know if you’d like a Terraform or CloudFormation version of this!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from paritosh pati directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
