Browser Use & Scraping Browser: Achieving Maximum Effectiveness of AI Agent
 Scraper0024
Scraper0024
Scraping Browser has become the go-to tool for daily data extraction and automation tasks. By integrating Browser-Use with Scrapeless Scraping Browser, you can overcome browser automation limitations and avoid blocks.
In this article, we’ll build an automated AI Agent tool using Browser-Use and Scrapeless Scraping Browser to perform automated data scraping. You’ll see how it saves you time and effort, making automation tasks a breeze!
You will learn:
What is Browser-Use, and how does it help build AI agents?
Why can Scraping Browser effectively overcome the limitations of Browser-Use?
How to build a block-free AI agent using Browser-Use and Scraping Browser?
What Is Browser-Use?
Browser-Use is a Python-based AI browser automation library designed to empower AI agents with advanced browser automation capabilities. It can recognize all interactive elements on a webpage and allows agents to interact with the page programmatically—performing common tasks like search, clicking, form-filling, and data scraping. At its core, Browser-Use converts websites into structured text and supports browser frameworks like Playwright, greatly simplifying web interactions.
Unlike traditional automation tools, Browser-Use combines visual understanding with HTML structure parsing, allowing AI agents to control the browser using natural language instructions. This makes the AI more intelligent in perceiving page content and efficiently executing tasks. Additionally, it supports multi-tab management, element interaction tracking, custom action handling, and built-in error recovery mechanisms to ensure the stability and consistency of automation workflows.
More importantly, Browser-Use is compatible with all major large language models (such as GPT-4, Claude 3, Llama 2). With LangChain integration, users can simply describe tasks in natural language, and the AI agent will complete complex web operations. For users seeking AI-driven web interaction automation, this is a powerful and promising tool.
Limitations of Browser-Use in AI Agent Development
As mentioned above, Browser-Use doesn’t work like a magic wand from Harry Potter. Instead, it combines visual input with AI control to automate browsers using Playwright.
Browser-Use inevitably comes with some drawbacks, but these limitations do not stem from the automation framework itself. Rather, they arise from the browsers it controls. Tools like Playwright launch browsers with specific configurations and tools for automation, which can also be exposed to anti-bot detection systems.
As a result, your AI agent may frequently encounter CAPTCHA challenges or blocked pages such as “Sorry, something went wrong on our end.” To unlock the full potential of Browser-Use, thoughtful adjustments are required. The ultimate goal is to avoid triggering anti-bot systems to ensure your AI automation runs smoothly.
After extensive testing, we can confidently say: Scraping Browser is the most effective solution.
What Is Scrapeless Scraping Browser?
Scraping Browser is a cloud-based, serverless browser automation tool designed to solve three core problems in dynamic web scraping: high concurrency bottlenecks, anti-bot evasion, and cost control.
It consistently provides a high-concurrency, anti-blocking headless browser environment to help developers easily scrape dynamic content.
It comes with a global proxy IP pool and fingerprinting technology, capable of automatically solving CAPTCHA and bypassing blocking mechanisms.
Built specifically for AI developers, Scrapeless Scraping Browser features a deeply customized Chromium core and a globally distributed proxy network. Users can seamlessly run and manage multiple headless browser instances to build AI applications and agents that interact with the web. It eliminates the constraints of local infrastructure and performance bottlenecks, allowing you to fully focus on building your solutions.
How Do Browser-Use and Scraping Browser Work Together?
When combined, developers can use Browser-Use to orchestrate browser operations while relying on Scrapeless’s stable cloud service and powerful anti-blocking capabilities to reliably acquire web data.
Browser-Use offers simple APIs that allow AI agents to “understand” and interact with web content. For example, it can use LLMs like OpenAI or Anthropic to interpret task instructions and complete actions such as searches or link clicks in the browser via Playwright.
Scrapeless’s Scraping Browser complements this setup by addressing its weaknesses. When dealing with large websites with strict anti-bot measures, its high-concurrency proxy support, CAPTCHA solving, and browser emulation mechanisms ensure stable scraping.
In summary, Browser-Use handles intelligence and task orchestration, while Scrapeless provides a robust scraping foundation, making automated browser tasks more efficient and reliable.
How to Integrate a Scraping Browser with Browser-Use?
Step 1. Get Scrapeless API Key
Register and log in to the Scrapeless Dashboard.
Navigate to "Settings".
Click "API Key Management".
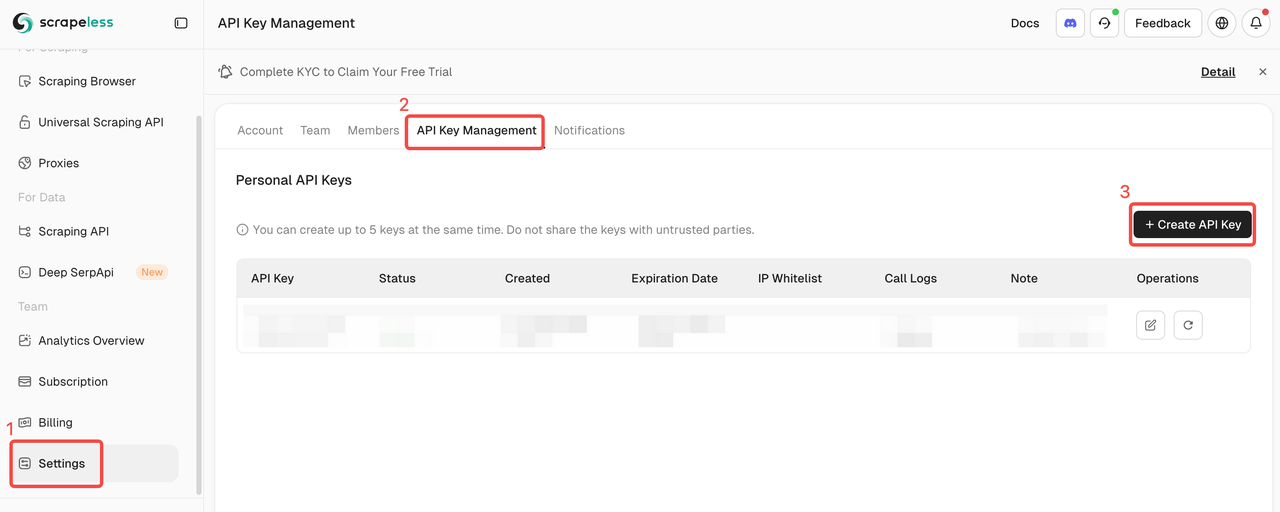
Then copy and set the SCRAPELESS_API_KEY environment variables in your .env file.
To enable AI features in Browser-Use, you need a valid API key from an external AI provider. In this example, we will use OpenAI. If you haven't generated an API key yet, follow OpenAI's official guide to create one.
The OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variables in your .env file are required too.
Disclaimer: The following steps focus on how to integrate OpenAI, but you can adapt the following to your needs, just make sure to use any other AI tool supported by Browser-Use.
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key
SCRAPELESS_API_KEY=your-scrapeless-api-key
💡Remember to replace the sample API key with your actual API key
Next, import ChatOpenAI in your program: langchain_openaiagent.py
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
Note that Browser-Use relies on LangChain to handle AI integration. Therefore, even if you haven't explicitly installed langchain_openai in your project, it is already available for use.
gpt-4o sets up the OpenAI integration with the following model:
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o")
No additional configuration is required. This is because langchain_openai automatically reads the API key from the environment variable OPENAI_API_KEY.
For integration with other AI models or providers, see the official Browser-Use documentation.
Step 2. Install Browser Use
With pip (Python at least v.3.11):
pip install browser-use
For memory functionality (requires Python<3.13 due to PyTorch compatibility):
pip install "browser-use[memory]"
Step 3. Set up Browser and Agent Configuration
Here’s how to configure the browser and create an automation agent:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
import asyncio
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from browser_use import Agent, Browser, BrowserConfig
from pydantic import SecretStr
task = "Go to Google, search for 'Scrapeless', click on the first post and return to the title"
SCRAPELESS_API_KEY = os.environ.get("SCRAPELESS_API_KEY")
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
async def setup_browser() -> Browser:
scrapeless_base_url = "wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser"
query_params = {
"token": SCRAPELESS_API_KEY,
"session_ttl": 1800,
"proxy_country": "ANY"
}
browser_ws_endpoint = f"{scrapeless_base_url}?{urlencode(query_params)}"
config = BrowserConfig(cdp_url=browser_ws_endpoint)
browser = Browser(config)
return browser
async def setup_agent(browser: Browser) -> Agent:
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o", # Or choose the model you want to use
api_key=SecretStr(OPENAI_API_KEY),
)
return Agent(
task=task,
llm=llm,
browser=browser,
)
Step 4. Create the Main Function
Here’s the main function that puts everything together:
async def main():
load_dotenv()
browser = await setup_browser()
agent = await setup_agent(browser)
result = await agent.run()
print(result)
await browser.close()
asyncio.run(main())
Step 5. Run your script
Run your script:
python run main.py
You should see your Scrapeless session start in the Scrapeless Dashboard.
In addition, Scrapeless supports session replay, which enables program visualization. Before running the program, make sure you have enabled the Web Recording function. When the session is completed, you can see the record directly on the Dashboard to help you quickly troubleshoot problems.
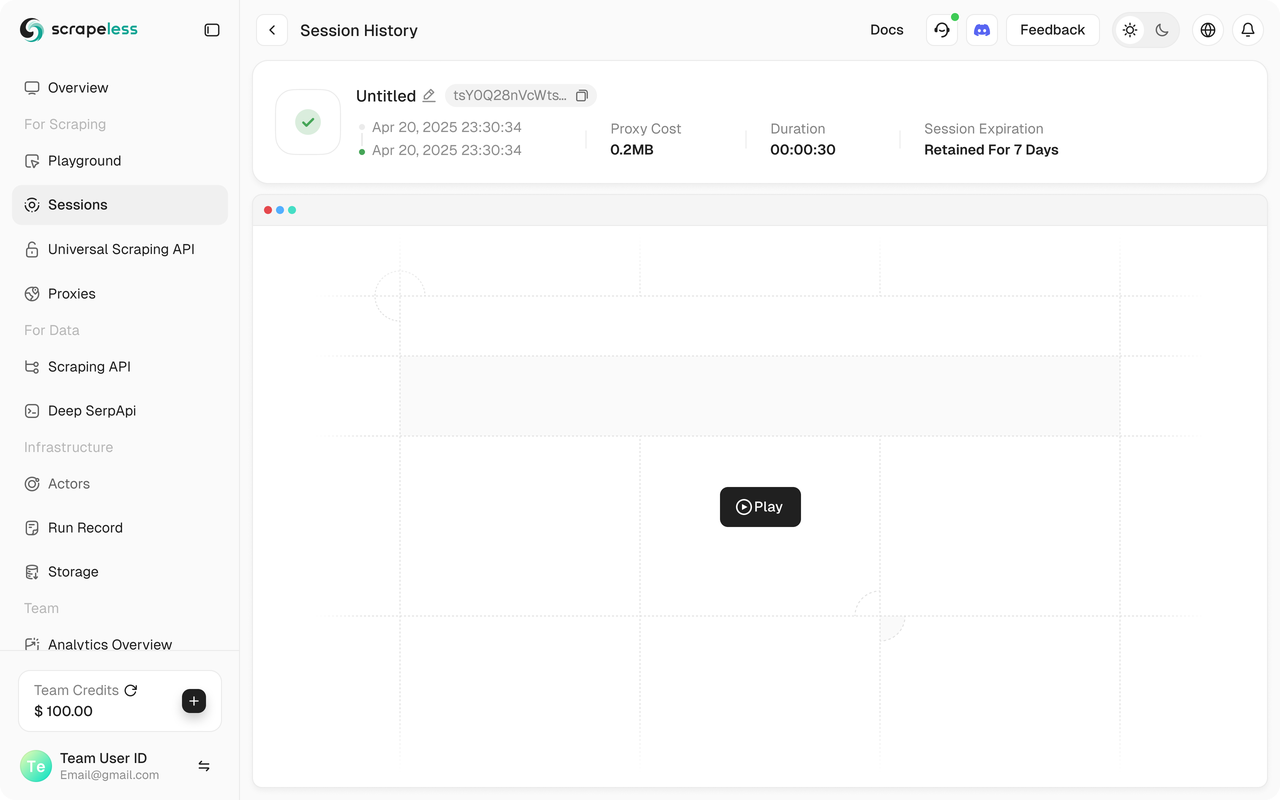
Full Code
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
import asyncio
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from browser_use import Agent, Browser, BrowserConfig
from pydantic import SecretStr
task = "Go to Google, search for 'Scrapeless', click on the first post and return to the title"
SCRAPELESS_API_KEY = os.environ.get("SCRAPELESS_API_KEY")
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
async def setup_browser() -> Browser:
scrapeless_base_url = "wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser"
query_params = {
"token": SCRAPELESS_API_KEY,
"session_ttl": 1800,
"proxy_country": "ANY"
}
browser_ws_endpoint = f"{scrapeless_base_url}?{urlencode(query_params)}"
config = BrowserConfig(cdp_url=browser_ws_endpoint)
browser = Browser(config)
return browser
async def setup_agent(browser: Browser) -> Agent:
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o", # Or choose the model you want to use
api_key=SecretStr(OPENAI_API_KEY),
)
return Agent(
task=task,
llm=llm,
browser=browser,
)
async def main():
load_dotenv()
browser = await setup_browser()
agent = await setup_agent(browser)
result = await agent.run()
print(result)
await browser.close()
asyncio.run(main())
💡Browser Use currently only supports Python.
💡You can copy the URL in live session to watch the session's progress in real-time, and you can also watch a replay of the session in session history.
Step 6. Running Results
{
"done": {
"text": "The title of the first search result clicked is: 'Effortless Web Scraping Toolkit - Scrapeless'.",
"success": True,
}
}
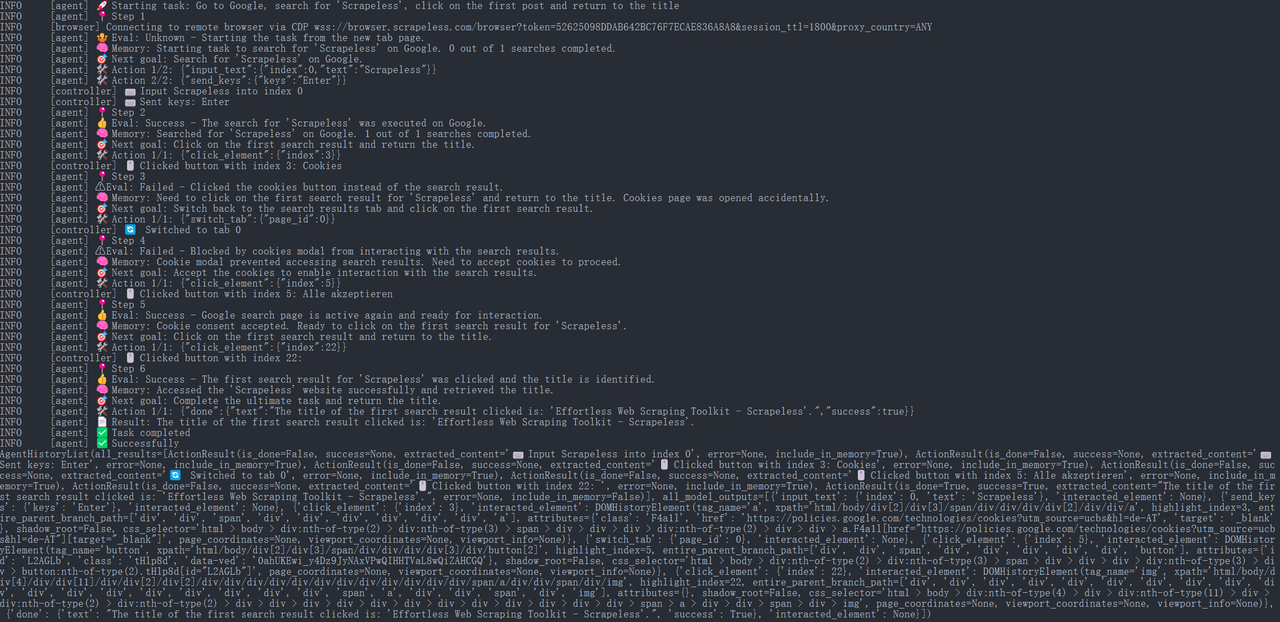
Then, the Browser Use Agent will automatically open the URL and print the page title: “Scrapeless: Effortless Web Scraping Toolkit” (this is an example of the title on Scrapeless’s official homepage).
The entire execution process can be viewed in the Scrapeless console under the "Dashboard" → "Session" → "Session History" page, where you’ll see the details of the recently executed session.
Step 7. Exporting the Results
For team sharing and archiving purposes, we can save the scraped information into a JSON or CSV file. For example, the following code snippet shows how to write the title results into a file:
import json
from pathlib import Path
def save_to_json(obj, filename):
path = Path(filename)
path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with path.open('w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(obj, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
async def main():
load_dotenv()
browser = await setup_browser()
agent = await setup_agent(browser)
result = await agent.run()
print(result)
save_to_json(result.model_dump(), "scrapeless_update_report.json")
await browser.close()
asyncio.run(main())
The code above demonstrates how to open a file and write content in JSON format, including the search keywords, links, and page titles. The generated scrapeless_update_report.json file can be shared internally through a company knowledge base or collaboration platform, making it easy for team members to view the scraping results. For plain text format, you can simply change the extension to .txt and use basic text output methods instead.
Wrap Up
By using Scrapeless’s Scraping Browser service in combination with the Browser Use AI agent, we can easily build an automated system for information retrieval and reporting.
Scrapeless provides a stable and efficient cloud-based scraping solution that can handle complex anti-scraping mechanisms.
Browser Use allows the AI agent to intelligently control the browser to perform tasks such as search, click, and extract.
This integration enables developers to offload tedious web data collection tasks to automated agents, significantly improving research efficiency while ensuring accuracy and real-time results.
Scrapeless’s Scraping Browser helps AI avoid network blocks while retrieving real-time search data and ensures operational stability. Combined with Browser Use’s flexible strategy engine, we’re able to build a more powerful AI automation research tool that offers strong support for smart business decision-making. This toolset enables AI agents to "query" web content as if they were interacting with a database, greatly reducing the cost of manual competitor monitoring and improving the efficiency of R&D and marketing teams.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Scraper0024 directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
