What is Port Forwarding | Beginner's Guide
 BrowserScan
BrowserScanAre you an e-commerce seller struggling with remote inventory management? Or a tech enthusiast eager to optimize home networks for smooth device connectivity?
Port forwarding could be the powerful solution you've been searching for.
This article explains the essentials of port forwarding and helps you enhance your network's functionality in minutes. Read it to manage remote operations and improve connectivity more easily.
What is Port Forwarding?
The Basics of Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a networking technique that directs Internet traffic to specific devices on your local network.
Imagine your router as a sophisticated post office: when packages (data) arrive, port forwarding acts as an efficient sorting system. It ensures each package is delivered to the correct recipient (device) in your home.
Key Terms and Definition
Key Term | Definition |
Router | Connects your local network (LAN) to the Internet |
Port | A “door number” for network services or applications |
LAN (Local Area Network) | Your private network within your home or office |
WAN (Wide Area Network) | The broader public Internet |
Public IP | Your router’s unique Internet address visible to the outside world |
Private IP | Each device’s unique address within your local network |
NAT (Network Address Translation) | Allows multiple devices on your LAN to share a single public IP address |
Port Forwarding Process
- Incoming Traffic
Traffic from the Internet (WAN) arrives at your router using its Public IP.
Incoming Traffic refers to data or requests that arrive at your network or device from an external source, such as the Internet.
- Router’s Role
The router checks the destination port of incoming traffic.
- Port Specification
The specified Port determines which service or application the traffic is intended for (e.g., port 80 for HTTP, port 21 for FTP).
- NAT in Action
NAT maps the incoming traffic to a specific Private IP address within your LAN.
- Final Destination
The traffic is forwarded to the device with the corresponding Private IP, allowing the device to receive and respond to the incoming request.
Why does Port Forwarding Matter?
Accessing Internal Devices from Outside
Suppose you're on vacation and want to check if everything is okay at your home. You have a security camera installed and connected to your home network.
Without port forwarding, you can only view the camera feed at home. But with port forwarding, you can open an app on your smartphone and see live footage from your camera no matter where you are.
The port forwarding tells your router to send the camera's video data to your phone over the Internet.
Boosting Network Efficiency
Consider your network as a busy highway; without proper organization, traffic can get congested and slow. Port forwarding acts like dedicated lanes for specific types of traffic, ensuring they reach their destination quickly.
For instance, if you're a gamer, how can you reduce latency and enhance your gaming experience? Yes, by setting up port forwarding for your gaming console. This is because the router knows exactly where to send the game data quickly. It won't get stuck in a traffic jam of other data packets. Your game then soon runs smoother, and your in-game actions are more responsive.
Similarly, if you use a smart home system with multiple devices like lights, thermostats, and locks, port forwarding can prioritize the traffic for these devices. This means your smart home commands (like turning off the lights or adjusting the temperature) are executed faster.
How to Use Port Forwarding?
Remote Access to Home Devices
Port forwarding enables secure access to devices like NAS drives, IP cameras, or home automation systems from anywhere in the world. You can stream videos from your NAS or monitor security cameras even while away.
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a dedicated storage device connected to a network that allows centralized data storage and sharing across multiple users and devices.
Follow these steps:
Assign a static IP to the device on your local network.
Open the necessary ports (e.g., 80/443 for a web interface, 5000 for Plex) on your router.
Use your public IP address or a dynamic DNS service (e.g., No-IP) to access the device remotely.
Security Tips:
Change default passwords and enable two-factor authentication (if supported).
Restrict access to specific IP ranges or use a VPN to avoid exposing your network directly to the Internet.
Home Server Hosting
Hosting a personal server, such as a website or game server, requires port forwarding to make it reachable externally. Examples include running a Minecraft server or hosting a personal blog:
Assign a static IP to the server and forward ports like 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), or 25565 (Minecraft).
Configure your router’s firewall to allow inbound traffic on these ports.
Use a DDNS service to avoid issues if your ISP assigns a dynamic public IP.
DDNS, or Dynamic Domain Name System, allows your network device to be accessible via a fixed domain name, even with a dynamic public IP address. When your ISP assigns a new IP address, the DDNS service automatically updates the domain to point to the new IP, preventing connection issues due to IP changes.
Considerations:
Ensure your ISP allows port forwarding (some block specific ports).
Regularly update the server’s OS and software to patch vulnerabilities.
Enhancing Online Gaming
Port forwarding can reduce latency and improve multiplayer gaming experiences by allowing direct connections between players. To host a game server or to reduce NAT restrictions, you can:
Forward ports recommended by the game (e.g., 27015-27030 for Steam).
Set your gaming PC as the DMZ (demilitarized zone) on your router for unfiltered traffic (use cautiously).
A DMZ can bypass a router's firewall to allow full access to a target device, but it also raises the risk of network attacks as the device is directly exposed to the Internet.
Optimization Tips:
Use a wired connection to your router for stability.
Adjust your router’s QoS (Quality of Service) settings to prioritize gaming traffic.
General Best Practices
Always back up your router settings before making changes.
Test connectivity using advanced tools like https://www.browserscan.net/port-scanner
to verify open ports.
- Consult your router’s manual for specific forwarding instructions.
Is Port Forwarding Safe?
Every coin has two sides. Port forwarding does come with potential security risks as well. You need to carefully consider and manage them.
Potential Security Risks
Port forwarding can expose your home devices to the Internet, making them more vulnerable to attacks. Cybercriminals could potentially exploit weaknesses in your devices or network to gain unauthorized access. This could result in data breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents. For example, an unsecured port 21 (FTP) could allow hackers to access and manipulate your files.
Additionally, some applications or devices may not be designed to handle direct Internet exposure, which could introduce further security risks.
It's crucial to be aware of these potential threats and take steps to mitigate them.
Using BrowserScan for Security Checks
To help safeguard your port forwarding setup, you can try the scanning tool BrowserScan to conduct security checks.
The free online tool can analyze your network and identify open ports, allowing you to assess your security posture. It helps you determine if your port forwarding configuration is adequately protected.
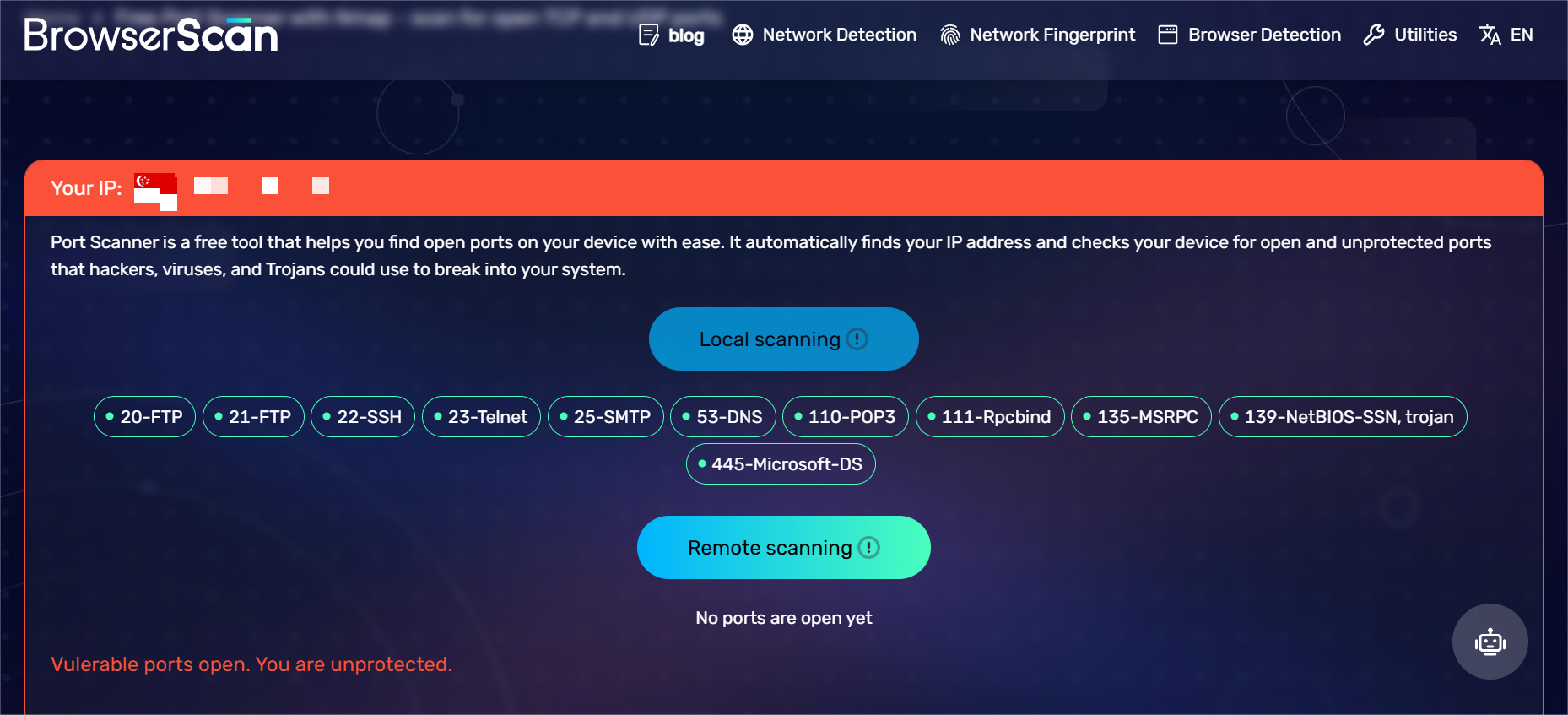
By regularly using BrowserScan, you can stay informed about your network's security status and take corrective actions if necessary. It's a simple yet effective way to monitor your network's safety.
Extra Security Tips
First, always use strong and unique passwords for your devices and accounts. Consider enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added layer of security.
Second, use a VPN for remote access instead of relying solely on port forwarding.
Third, keep your devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This can help fix known risks in time and improve overall security.
Lastly, consider implementing a firewall on your router or devices to help block unauthorized access and filter incoming and outgoing traffic.
Start Optimizing Your Network Today!
Port forwarding enhances network capabilities, balancing connectivity and security.
By implementing it thoughtfully with the best practices discussed in this article and using detected tools like BrowserScan, you can unlock your network’s full potential while staying protected.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from BrowserScan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

BrowserScan
BrowserScan
Am I 100% anonymous? Check your browser fingerprints and IP address to find how your online identity looks👉www.browserscan.net