What is Prompt Engineering? — Part 3: Elementary Prompting Techniques
 NonStop io Technologies
NonStop io Technologies
In the previous stories, we went through The Basics and Properties of Effective Prompts. In this story, we dive deeper to understand the different prompting techniques.
Prompting techniques refer to the guiding strategies devised to create and optimize language prompts in order to generate effective, relevant, and desirable outputs from language models or other AI systems that align with the user’s preferences, goals, or intents. A few common prevalent prompting techniques are:
1. Zero-shot Prompting

In zero-shot prompting the language model is not provided with any sample expected output as an example. Essentially, the model has to generate a response without any previous knowledge or experience with similar circumstances. Zero-shot prompting is beneficial when one wants to assess or exploit the model’s capacity for creativity, problem-solving prowess, and overall versatility under unexpected situations.
For example
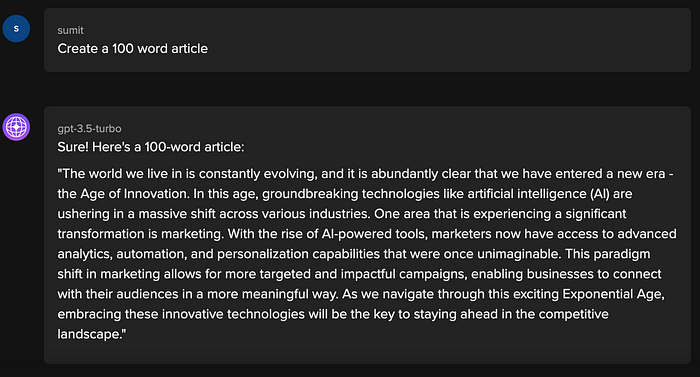
In the examples above, the model is given clear instructions without any demonstrations or examples. The zero-shot capability of the model allows it to understand the task and generate appropriate outputs.
Potential risks while employing zero-shot prompting: Amplified biases, misinformation, and anomalous behavior. Zero-shot prompting should also be avoided when tasks are complex
2. One-shot Prompting

In this prompting technique, the model is given one example, template, hint, or instruction as part of the input data, in order to guide it to a desirable output.
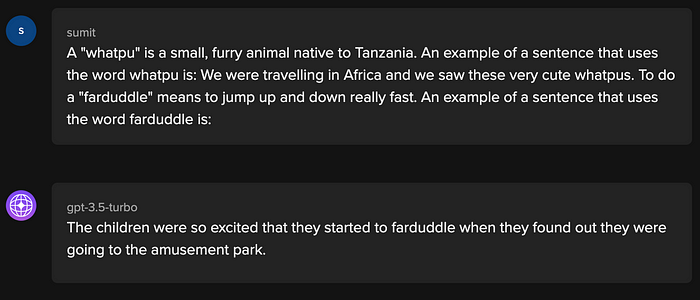
In the above example, the model has learned to use a new word by understanding its context with just one example (1-shot).
3. Few-shot Prompting

In this prompting technique, the model is given a small number of examples, and the model adapts to the new examples of previously seen objects in order to generate the desired output.
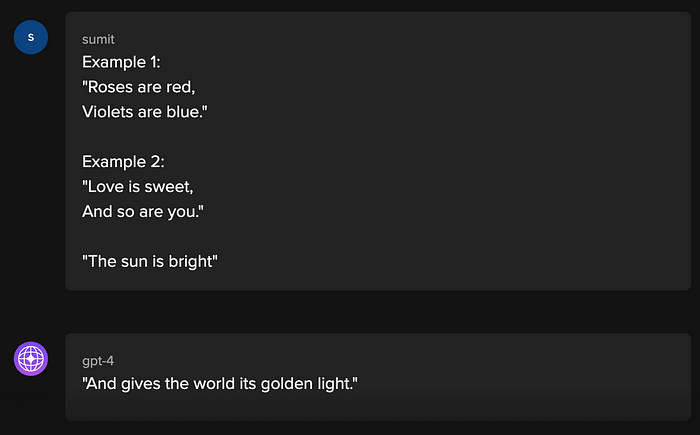
Example: Few-shot prompting
In the above example, the prompt was given a couple of examples of rhyming couplets, and when presented with the first half of the third couplet, the model generated a response that completed the third couplet.
4. Chain-of-thought (CoT)

The chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting technique involves describing intermediate reasoning steps while dealing with a rather complex question.
As highlighted in the below samples, an approach where a step-by-step explanation of the logic built to arrive at a certain conclusion/solution, provides better accuracy, as compared to not providing the intermediate steps to arrive at a certain answer.
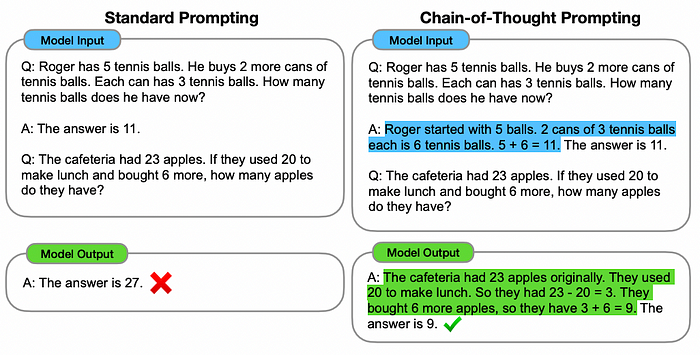
Chain-of-thought prompting enables large language models (eg: PaLM 540B) to tackle complex arithmetic, commonsense, and symbolic reasoning tasks. Ref: Wei et al. (2022)
References
Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models — Wei et al. (2022)
Envato Elements — For images/creatives
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from NonStop io Technologies directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

NonStop io Technologies
NonStop io Technologies
Product Development as an Expertise Since 2015 Founded in August 2015, we are a USA-based Bespoke Engineering Studio providing Product Development as an Expertise. With 80+ satisfied clients worldwide, we serve startups and enterprises across San Francisco, Seattle, New York, London, Pune, Bangalore, Tokyo and other prominent technology hubs.