The Importance of AI and Data Science
 Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Science are two of the most influential fields shaping our digital world. They power everything from the recommendations we see online to the way doctors diagnose diseases, how banks detect fraud, and how cities become smarter. Despite their close relationship, AI and Data Science have distinct roles, methods, and goals. This blog will help you understand what each field means, how they work together, and why they matter in our daily lives.
What Is Data Science?

Data Science is a field that uses scientific methods, programming, and statistics to extract meaningful information from data. This data can come in many forms: numbers in spreadsheets, text from social media, images, videos, and more. The main aim is to turn raw data into useful knowledge that supports decision-making in business, healthcare, government, and beyond.
Key Steps in Data Science
Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources such as databases, sensors, websites, or manual entry.
Data Cleaning: Removing errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies to ensure the data is accurate and reliable.
Data Analysis: Using statistical methods and algorithms to find patterns, trends, and relationships.
Data Visualization: Presenting findings through charts, graphs, and dashboards to make insights easy to understand.
Predictive Modeling: Building models that can forecast future events or behaviors based on past data.
Data scientists use tools like Python, R, SQL, and visualization software to carry out these tasks. Their work often involves collaboration with experts from other fields to ensure the insights are relevant and actionable.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is about creating computer systems that can perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. These tasks include recognizing speech, understanding language, making decisions, and even driving cars. AI systems learn from data, adapt to new information, and improve over time.
Types of AI
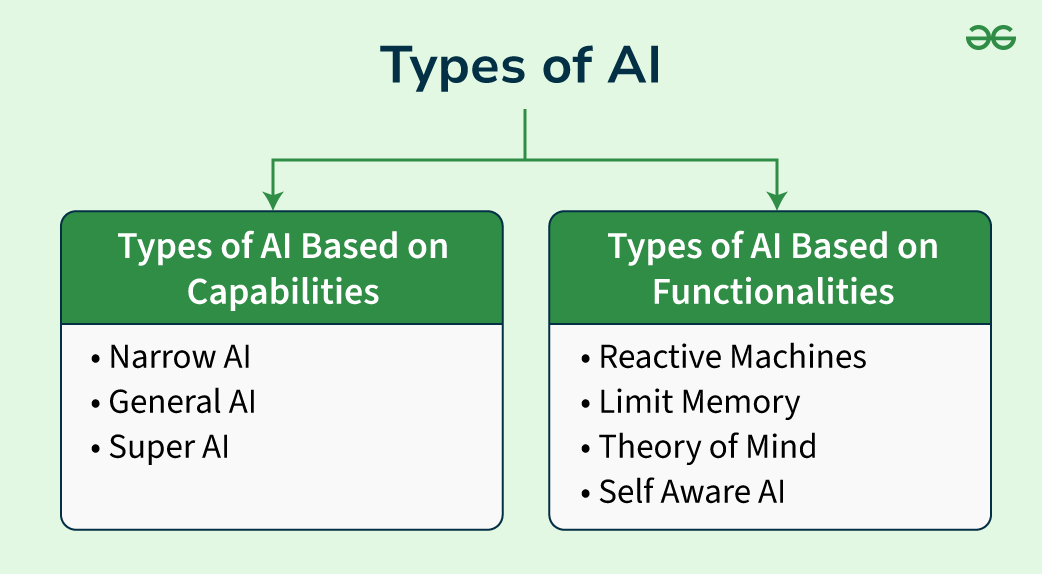
Types of AI Based on Capabilities
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Definition: AI systems designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks.
Examples: Voice assistants (like Siri, Alexa), recommendation systems, image recognition software.
Characteristics: Cannot perform tasks outside their programmed domain.
General AI (Strong AI)
Definition: AI systems that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks at a human-like level.
Examples: Currently theoretical; no real-world examples yet.
Characteristics: Can reason, solve problems, and adapt to new situations like a human.
Super AI
Definition: AI that surpasses human intelligence and capabilities in all aspects—creativity, problem-solving, decision-making, and emotional intelligence.
Examples: Entirely hypothetical at present.
Characteristics: Would be able to outperform humans in every field.
Key Concepts in AI
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where computers learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML models can recognize patterns and make predictions.
Deep Learning: A branch of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers to process complex data like images and speech.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables computers to understand and respond to human language.
Types of AI Based on Functionalities
Reactive Machines
Definition: The most basic type of AI that reacts to current inputs but doesn’t store memories or past experiences.
Examples: IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer.
Characteristics: No learning from past actions, only responds to specific situations.
Limited Memory
Definition: AI systems that can use past experiences or data for a short period to make decisions.
Examples: Self-driving cars (using recent sensor data to make driving decisions).
Characteristics: Can learn from historical data but has limited memory.
Theory of Mind
Definition: Advanced AI that can understand emotions, beliefs, intentions, and interact socially like humans.
Examples: Still in research; not yet achieved.
Characteristics: Would be able to understand and predict human behavior.
Self-aware AI
Definition: The most advanced form of AI, with its own consciousness, self-awareness, and emotions.
Examples: Entirely theoretical at this stage.
Characteristics: Would have self-driven thoughts, emotions, and awareness.
How Are Data Science and AI Connected?
The relationship between Data Science and AI is strong and complementary. Data Science provides the tools and methods to collect, clean, and analyze data, which is essential for training AI systems. In turn, AI enhances Data Science by automating analysis, finding complex patterns, and making predictions.
How They Work Together
Data as the Foundation: AI systems need large amounts of data to learn and make decisions. Data Science ensures this data is accurate and well-prepared.
Improving Accuracy: Data Science techniques help select the best features and clean the data, which boosts the performance of AI models.
Automating Analysis: AI can automate routine data analysis tasks, freeing up time for data scientists to focus on more complex problems.
Handling Unstructured Data: AI, especially deep learning, can process unstructured data like text, images, and video, expanding what Data Science can achieve.
Continuous Learning: AI systems can keep learning from new data, creating a feedback loop that makes both AI and Data Science more powerful.
Real-World Applications
Healthcare
Data Science: Analyzes patient records to find trends in disease outbreaks or treatment outcomes.
AI: Assists in diagnosing diseases from medical images, personalizing treatment plans, and powering virtual health assistants.
Finance
Data Science: Studies transaction data to spot spending trends and customer segments.
AI: Detects fraudulent transactions, automates trading, and provides personalized financial advice.
Retail and E-Commerce
Data Science: Examines customer behavior to optimize marketing campaigns and product placement.
AI: Powers recommendation engines, chatbots for customer service, and demand forecasting.
Manufacturing
Data Science: Monitors production data to improve quality and efficiency.
AI: Predicts equipment failures, automates quality control, and optimizes supply chains.
Smart Cities
Data Science: Analyzes traffic and energy usage data to improve urban planning.
AI: Controls traffic lights, manages energy grids, and supports public safety systems.
The Data Science Life Cycle
Understanding how data moves through a project is key to both Data Science and AI. Here’s a simplified version of the typical life cycle:
Data Capture: Collecting raw data from various sources.
Data Maintenance: Storing and organizing data securely.
Data Processing: Cleaning, transforming, and preparing data for analysis.
Data Analysis: Applying statistical and machine learning methods to extract insights.
Result Communication: Sharing findings through reports, dashboards, or automated alerts.
This cycle is not strictly linear; it often involves going back and forth between steps as new questions arise or more data becomes available.
Skills Needed for Data Science and AI
To work in these fields, certain skills are essential:
Programming: Knowledge of languages like Python or R is crucial for data manipulation and modeling.
Mathematics and Statistics: Understanding concepts like probability, regression, and hypothesis testing helps in building and evaluating models.
Data Handling: Skills in cleaning, transforming, and managing large datasets.
Machine Learning: Knowing how to select, train, and evaluate algorithms.
Data Visualization: Ability to present data clearly using charts, graphs, and dashboards.
Domain Knowledge: Understanding the industry you work in (e.g., healthcare, finance) to ensure solutions are practical and relevant.
Challenges and Limitations
While Data Science and AI offer many benefits, they also come with challenges:
Data Quality: Poor or biased data can lead to incorrect conclusions or unfair AI systems.
Computational Resources: Training advanced AI models requires powerful hardware and can be expensive.
Interpretability: Some AI models, especially deep learning, act as "black boxes" and are hard to interpret.
Privacy and Ethics: Handling personal data responsibly and ensuring AI systems are fair and transparent is a growing concern.
Skill Gap: There is a high demand for skilled professionals, making it challenging for organizations to find the right talent.
The Future of AI and Data Science
The influence of AI and Data Science is only expected to grow. As more devices and systems generate data, the need for advanced analysis and smart automation will increase. Here are some trends to watch:
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML): Tools that automate the process of building and tuning machine learning models, making AI more accessible.
Explainable AI: Techniques that help make AI decisions more transparent and understandable.
Edge Computing: Running AI models on devices like smartphones and sensors, enabling faster decisions without sending data to the cloud.
Integration Across Industries: From agriculture to education, more sectors are adopting AI and Data Science to solve unique challenges.
AI and Data Science are transforming the way we live and work. Data Science turns raw data into valuable insights, while AI uses those insights to automate tasks and solve complex problems. Their partnership is at the heart of modern innovation, powering advances in healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and beyond.
As technology continues to advance, the opportunities in these fields will only expand. Whether you’re a student, a professional looking to switch careers, or simply curious about the future, understanding AI and Data Science is a smart investment in today’s data-driven world.
By building the right skills and staying curious, anyone can be part of this exciting journey. The future belongs to those who can understand data, build smart systems, and use them to make the world a better place.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aakashi Jaiswal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Coder | Winter of Blockchain 2024❄️ | Web-Developer | App-Developer | UI/UX | DSA | GSSoc 2024| Freelancer | Building a Startup | Helping People learn Technology | Dancer | MERN stack developer