Web -3 Cryto
 LIKHITHA N
LIKHITHA NThe content covers foundational concepts of Blockchain and Web3, highlighting their significance in the evolution of the internet and financial systems. Here are the key points:
Blockchain & Web3 Overview
Social Network were the Key pillar of the evolution from web 1 to web 2
Web 1 was marked by static websites — publishers created content, and internet users consumed the content.
Web 2 was marked by dynamism and interactivity — web pages were on longer static but become dynamic and interactive,though they were still controlled by centralized platform entities.
Web 3 : Enables open,permissionless,and user-governed social networking protocols that solve many of the problems with web 2 social.
Represents a new internet infrastructure that leverages blockchain technology, decentralized applications, and tokenized assets .
Problems of Web 2 : Centralization and data contol , issues Monitization and Exploitation , Limited interoperability and innovation , Algorithmic Manipulation and misinformation , Lack of financial inclusion.

BLOCKCHAIN
Definition :A decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers without a centralized authority. It is an evolution of traditional financial ledgers .
Blockchain : Distributed Ledger Technology
Ledger : record transactions
Distributed : many copies of

BLOCKCHAINS
Purpose: To securely and transparently record transactions on a distributed ledger without the need for a centralized authority.
Key Elements : Decentralization ,Financial Incentives ,Consensus Mechanisms.
Key Features of Blockchain
1. Decentralization: No single entity controls the data; it is distributed across multiple nodes .
2. Transparency: Transactions are visible and verifiable by all participants.
3. Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
Why join a blockchain network?
Money , Blockchains have financial incentivies baked into their software , People earn money for securing the network and processing transactions as validators.
Paying people through codes allowed Bitcoin to become a permissionless, globally distributed network of nodes.
Think of bitcoin distributing financial rewards like a company distributing shared. People running network to earn crypto makes them part Owners. No one entity owns or runs the blockchain.

Builiding a Decentralized Future : Connecting People Through Blockchain
#What is Web3?
Web3 is a new internet infrastructure underpinned by a shared,distributed ledger that records peer — to — peer transactions.
Is an ecosystem of :
Blockchain based protocols
Decentralized applications
Tokens:fungible and Non fungible
Networks
Web3 Characteristics
1.**Ownership Economy: Users have control over their data and digital assets, contrasting with Web2, where data is controlled by a few corporations.
2.**Decentralized Applications (dApps): Applications that run on a blockchain, allowing for peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries.
3. Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies that serve as a medium of exchange and store of value, native to their respective blockchains.
4. Tokens: Units of value created on top of blockchain protocols, which can represent various assets and rights.
Fungible Tokens (e.g., ERC-20): Identical and interchangeable .5.**Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs, e.g., ERC-721): Unique and not interchangeable.
6.Consensus Mechanisms**Proof of Work (PoW):** Requires computational power to validate transactions, used by Bitcoin.
**Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators lock up capital to secure the network and validate transactions, promoting energy efficiency.
Importance of Web3
* Financial Sovereignty: Empowers individuals to manage their assets without intermediaries.
* New Economic Models: Enables users to participate in governance and decision-making through token ownership.
### Wallets in Web3
- Crypto Wallets: Essential for managing cryptocurrencies, tokens, and NFTs. They can be software-based or hardware devices.
- User Control: Unlike traditional banking, users have full control over their private keys and assets.

Imagination of the Web3 World
CRYPTOCURRENCIES
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies that serve as a medium of exchange and store of value, native to their respective blockchains.
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that are cryptographic technology for secure transactions and decentralized control.
Digital money : It is the medium of exchange and store of value.
Native to a Blockchain: Decentralized and run on peer to peer networks.
Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat money) ,cryptocurrencies operate on Blockchain Technology.
Use (blockchains and cryptography) : Secure and Verify peer to peer transactions.
#What are altcoins?
Altcoins: an alternative to Bitcoin = “alternative”+”coin”
e.g : Dogecoin is on the Dogecoin Blockchain , Ethereum is on the ethereum Blockchain.
#What are Tokens?
Tokens: Units of value created on top of blockchain protocols, which can represent various assets and rights.
— Fungible Tokens (e.g., ERC-20): Identical and interchangeable.
— Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs, e.g., ERC-721): Unique and not interchangeable.Unit of value : Like cryptocurrencies created by protocols that build on top of blockchains.
Tokens are a broader unit of value and have more use cases than digital money. Types : Fungible and Non Fungible Tokens
How transaction validated?
- \> consensus mechanism
Blockchain nodes must agree to a single source of truth about what transactions happened on the blockchain
Because there is no middle man or bank ,they must follow a set of rules.
A Consensus Mechanism is the set of rules that determine how a distributed network of nodes agrees on a single source of truth.
All of the nodes on the blockchain must have the same consensus mechanism or rules to come to agreement
To Participate :
To participate in consensus,a person must commit capital resources.
e.g : In Bitcoin : Miners use hardware and computing power to process new blocks of transactions and secure the networking
Capital resource:Hardware,Electricity
e.g : In Ethereum : Validators use money-not computing power to process new block of transactions and secure the network
Capital resource:Ehereum/protocol tokens
Two different consensus mechanism are:
Proof of work(POW)
Proof of stakes(POS)
#How it works?
Every computer in the network uses the same rules to check transactions. These rules help ensure everyone agrees on what transactions happened

Consensus Mechanism
#Why we need?
Since blockchains work across many computers (or nodes) worldwide,they need a fair and secure way to agree on transactions without needing a central boss.
PROOF OF STAKE
Requires computation power to validate transactions , used by BITCOIN
Staking is act of looking up or depositing crypto into a protocol
Consists of a Network validator nodes that lock up crypto to:
Validate blocks of transactions,Secure the network.
To become a validator , a user must pay their crypto “at stake” first
To stake = to lock up or deposit in the network.
Validators receive financial rewards in return for staking their crypto in the network .By staking crypto ,they get to validate blocks of transactions and earn rewards
Benefits:
Accesibity :- via staking crypto ,more people can secure the network, Process trasactions than those that had access to hardware and electricity. Rewards are issued in relation to how much ETH is locked up and what rewards the network is offering over a time period.
PROOF OF STAKE
Validators lock up capital to secure the network and validate transactions,promoting energy efficiency.

Crypto Currencies Like Bitcoin and Ethereum
WALLET
A wallet is a software program or physical device
It serves two functions :
Sending and receiving crypto funds.
A single login to all web3 application
Crypto wallets allow users to manage , send and receive money .
e.g : venmo → a digital wallet on your phone where you can send money to your friends phone number. Chase bans online*-> a digital wallet on your computer.*
Curently on the web2 internet , you need a different login for every single application. e.g : 50 apps = 50 logins. E.g : facebook,instagram,whatsapp all need new login to every apps.
Web3 — login once,no matter how many are there
#Why do Web3 wallets matters?
Web3 wallets store, protect and manage cryptocurrencies , Tokens and NFTs without a middleman.
A wallet also tells the blockchain a user is the legitimate owner of the funds and able to move them.
A wallet is how users navigate web3 and use applications
Activities include : swapping,lending,minting and buying NFTs,voting ,taking quizzes,etc
## Wallet Key Features
- Secret Recovery Phrase (Seed Phrase):
- Public and Private Keys:
- PIN and Accounts:
Secrete Recovery Phase(SEED PHRASE)
secret phrase : A mnemonic phrase of 12,18 or 24 words in a specific order
It create wallet and all of the accounts in it.
This is your recovery phrase if something happens to your wallet
You need it to restore or import your wallet
If you forgot password you need this
NEVER SHARE IT
— Essential for creating and restoring wallets; it must be kept secure.
— Best practices include never sharing it, storing it offline, and using a password manager if necessary.
Every wallet has a Public address and Private key pair
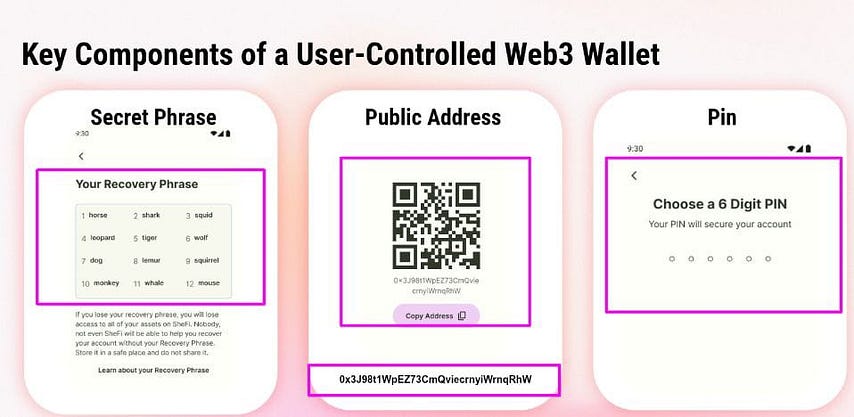
Public Key address
-> your shareable address to receive funds.
It can be a QR code , a string of text or named.e.g:0x34cb8711eeo0983jsjd
Its your unique identifier on the blockchain.
Its like an email address can recieve email from anyone
You need to share your public address to receive funds
— Each wallet has a public address for receiving funds and a private key for accessing them.
— Users must never share their private key or seed phrase to maintain security.
Private Key
“You never shares this with anyone” , “NEVER EVER”
A private key is a sophisticated form of cryptography
Each individual address/account has a unique private key
This is what allows you to access and move crypto
Your seed phrase generate private keys
PIN
In addition to your private key and secrete phrase, your wallet may also require a pin.
A pin is a number combinations you set when you create your wallet
Just like pin of credit card ,It is private should not be shared
— A unique PIN is required for wallet access, and some wallets allow multiple accounts.
Some wallets can contain multiple accounts or multiple wallet addresses
accounts = wallet addresses
You may want to create different accounts for different purposes
One to collect NFTs,one for multi signature wallets, one for Defi
Each account has its own public address
#Seed phrase, Private key and Password Best Practices
Print it out on a piece of paper or save in USB srive
Store this paper or USB in different physical locations
Do not store your private keys in Dropbox , Google Drive , or other cloud storage
Types of wallets
Custodial
Non Custodial
Hot Storage
Cold Storage
1.CUSTODIAL
A third party stores your crypto for you . Like a bank, you deposit your crypto and they control . You both access crypto ,but
They can close your account*,*lock you out and restrict activities . Have no longer withdrawal periods . “ you can recover your crypto if something happens”*. eg: coinbase , phone pay*
2.NON CUSTODIAL
A user contolled wallet and funds . No one can access but you . You manage your own crypto .
Only you have contol in your wallet . No one can restrict when you use your crypto ,No waiting periods . “If you lose your private key or secret phrase , there is no way to regain access” . Eg: Shefi
\Custodial* \= Trust the company
\Non custodial* = Trust the code and yourself
3.HOT STORAGE
Hot storages wallet are software wallets
Hot storage wallets are Online . means always connected to the internet
Digital assests in a hot storage wallet are also always online
Web based/Browser wallet: Online wallets , that run in your browser like any other website. Ex : Zerion,metaMask
Mobile wallets : Wallets that run on your mobile phone . Ex : Shefi Wallet ,family
Keywords : hot,online,software ,connected
Pros: 1. usually free, user- friendly. 2. immediately available to use .3. easy to connect to apps and interact with web3
Cons : Easier to hack since private keys are online. Beware of airdrops with malware
4. COLD STORAGE
A physical device that keeps your cryptocurrency completely offline.Many look like USB drives
Cold storage wallets are offline means not connected to the Internet
Your assets in a hardware wallet are offline
A physical wallet : looks like USB.Paper/steel wallets.a secondary offline computer
Key words: cold,offline,hardware,physical
Pros : More secure/ nearly impossible to hack. Storing crypto offline , funds cannot stolen , as the transactions has to be signed by the device itself .
Cons: If you lose the physical device,you lose the crypto forever.less convinient and user friendly : you must powe it on, type in pin and 24 words,then connect to internet.
## Navigating Web3 Applications
- Wallets are essential for interacting with blockchain applications, allowing users to send and receive assets.
- Users must connect their wallets to applications carefully to avoid risks, such as granting unauthorized access.
#Wallet Safety and Best Practices
Use of Hot wallets,Cold wallets
Use strong passwords and enable two factor authentication
Keep software updated and backup wallets regularly
Enable withdrawal allowlist
Use dedicated devices for crypto transactions.
- Scams and Phishing:
— Users should be cautious of phishing scams that impersonate legitimate services.
— Best practices include avoiding unsolicited messages and verifying sources before downloading software.
- Protecting Against Hacks:
— Recommendations include logging out of applications after use, regularly reviewing connected apps, and being wary of direct messages.

Wallets World
ETHEREUM
Ethereum aims to be a Global platform where anyone can build and use decentralized applications cheaply , quickly and easily.
Ethereum transactions: 1) Sending ETH or a token to someone. 2) Swapping 3) Minting NFTs 4) Buying NFTs 4) Yield Farming 5) Staking 6) Depositing
When a user sends a transaction , she must pay a trasaction fee.
Every network has transaction fees
Its fees are measured in gas
Gas — The fuel that allows it to operate , in the same that a car needs gasoline to run
Gas = The cost of performing a transaction on Ethereum
Gas fees are paid in Ethereum native currency ,Ether(ETH)
Fees depens on : Blocks Capacity , paying higher gas fees for a faster transactions.more complex transactions cost more,gas fees increases with high network activity.
Purpose : pays validators on the Ethereum network to validate and secure the network. attaching cost to every transactions prevent spamming by nefarious actors.
## Overview of Blockchain Layers
- Layer 1 (L1) : The base layer of a blockchain network responsible for core functionality and security. Transactions can take up to 10 minutes to finalize.
Layer 1
Native blockchain that processes and finalizes all transactions
Provides Decentralization and security
Underpins all applications and scaling solutions
- Layer 2 (L2) : A scaling solution that operates on top of Layer 1, enabling transactions to occur within seconds and with nearly zero fees.
Layer 2
Scaling solutions that sits on top of the native blockchain
They anchor into the Layer 1 chain
Derive part of their security from Layer 1
SCALING
#Why we need to scale ethereum?
During periods of High Network congestion,Ethereum Transactions fee prices can spike very high that is $25
The future and commerce cannot have $25 fees
Therefore, scaling aims to:
Increase transcation throughput speed and reduce the transaction fees paid by end users.
- Scalability trilemma : we cannot have scalability , security , and decentralization.
- Importance of Layer 2: Enhances transaction speed and reduces costs, addressing scalability issues of Layer 1.
- Types of Layer 2 Solutions:
— zk-Rollups: Bundles multiple transactions into one.
— Optimistic Rollups: Similar to zk-Rollups but with different verification methods.
— State Channels: Allows transactions to occur off-chain.
— Sidechains: Independent blockchains that run in parallel to the main chain.
— Plasma: A framework for building scalable applications.
SOLUTION :
We dont want to give up ethereum security and decentralization
So build up New Layer 2 blockchains on top of Ethereum
Layer 2 blockchains for scalability and privacy that anchor into Ethereum
Layer 2 = Scalability and privacy
Ethereum Layer 1 = Decentralization and Security.
All scaling solutions aim to Increase transaction throughput speed and reduce the transaction fees paid by end users.
Whereas a L1 (Ethereum) transaction might require a painful amount of ETH of gas fees and process slowly, L2 transactions happen instantly with nearly — free fees.
#Why Layer 2s?
Transactions happen instantly with nearly free fees.
Near $0 dollar fees instant finality of transcations suitable for a large user- base of millions of people.
## Functionality of Layer 2 Solutions
- Transaction Processing: Layer 2 solutions process transactions off-chain and periodically settle them on the main chain, reducing congestion and costs.
- Benefits:
1. Scalability\:* Increases the number of transactions per second.
2. Cost Efficiency*: Lowers transaction fees.
3. Interoperability*: Connects with other blockchains.
How Do Layer 2 Solutions Works?
Layers 2s are built on top of Ethereum L1
They execute transactions on their L2 chain
Then,they package many transactions into a one rollup block
Then submit the one bundle of transactions to Ethereum L1
This bundle is inclined in an Ethereum L1 block , ensuring its accounted for
Everything that happens on a Layer 2 must be accounted for on Ethereum Layer 1
#Why do Layer 2 s Submit Transaction Info to Ethereum?
Layer 2s are built “ on top of” Ethereum L1
They alleviate congestion for Ethereum,but they are not separate from the Ethereum ecosystem
Ethereum must remain informed of the L2 transactions and keep record of them
What are Blockchain Rollups?
Rollups are helpers for Ethereum , making it faster and cheaper by processing transactions off Ethereum
They help Ethereum handle more transactions quickly and at lower costs while keeping them secure.
Rollups are a crucial innovation for improving the usability of blockckain networks like Ethereum

Futuristic digital illustration representing Web3 scaling solutions! It showcases interconnected blockchain nodes, Layer 2 rollups, sidechains, and high-speed transaction flows in a high-tech, cybernetic setting🚀
CELO

Celo Makes Easy
Celo will be the Layer 1 blockchain to transition to a Layer 2,ensuring transactions are both scalable and secure.
Layer 2s (Ethereum based)
Rollups : Optimistic and ZK snaks / Starks
Optimistic Rollup : celo
Celo is an emerging ethereum layer 2 focused on mobile users. it connects mobile numbers to blockchain accounts,making it easy to use
Use Proof of Stake Blockchains
The Celo Whitepaper was released in 2018.Celo launched on Earth Day 2020 as an energy- efficient and low cost Layer 1 blockchain.
Clabs is a leading contributor to the Celo technical stack.
Why Ethereum needs Celo’s help?
Ethereum is decentralized and secure,but it struggles on the scalability.Celo address this by extending the functionality of Ethereum with a mobile- first approach.Transaction faster,reducing network congestion and lowering fees.
Layer 2 Blockchain. But it technically is a rollup. Celo will be optimistic roll up . It can process transactions off Ethereum using a technology called a sequencer ehich creates blocks and submits the blocks to the Ethereum L1 for validation.
BRIDGES
Each blockchain is an individual piece of technology with incompatible protocols,tokens,algorithms and records of data and wallets
Blockchain bridges enable interoperability
Therefore,digital assets and data hosted on one blockchain can interact with another different chain.
Bridges allow for assets to move between different chains and exist on new chains that are not their native chain.
What happens?
First , she deposits her tokens into a bridge
Once her tokens are deposited,the exact amount tokens is issued on a Layer 2
This is clled token wrapping
Depositing a token in a bridge to mint a representation of it on a new chain
When Ethereum is bridged to a new chain it become Wrapped Ethereum WETH.
The tokens the user locked on the Ethereum stay locked
This newly newly minted tokens are issued 1:1 of what she locked in the bridge
Trusted bridges depend upon a central entity or system for their operations.
Trustless bridges operate using smart contracts and algorithms
#When a user bridges her tokens to a Layer 2 ,What happens?
- \> She deposit her tokens into a bridge contract and new tokens to the same type and quantity are issued on a Layer.
## Bridging Between Layers
- Bridges Overview: Facilitate the transfer of assets between Layer 1 and Layer 2.
— Token Bridges: Transfer tokens between different chains.
— Data Bridges: Enable the transfer of data and smart contracts.
- Bridging Process:
— Assets are locked on Layer 1 during the transfer.
— Equivalent assets are received on Layer 2.
Centralized Finance (CeFi):
Operated by centralized entities, requiring KYC and holding user assets.
Centralized Finance(cefi): crypto products,platforms and applications
operated and managed by a centralized organization.
not built on a blockchain even if it they offer access to crypto assets
Require know your constomer
Custodies holdes your assets for you
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
Built on blockchain, non-custodial, and permissionless.
Run by code
Built on a blockchain
Know your customer not required
Non-custodial do not hold your assets for you
Decentralized governance of the platform
Regenerative Finance (ReFi):
Integrates financial systems with ecological and social goals.The intersection of finance and sustainability
Refi is a financial system that aims to create a more sustainable future by :
Promoting environmental and social stability
Incentivizing communities to solve systemic issues
Leveraging innovative financial tools and technologies
Creating a more inclusive financial system
Refi projects realize these principles using smart contracts and Defi applications
DECENTRALIZED FINANCE(Defi)
One of the Largest Ecosystem in Blockchain
- Definition: Reimagines traditional financial services in a peer-to-peer framework, allowing users to become their own banks.
Traditional and not so traditional financial tools and services reimaged in a peer to peer framework.
Global,permissionless,financial rails that anyone anywhere can access with an internet connection.
Key Properties:
— Decentralization: No single entity controls the network.
— Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger.
— Security: Ensured through cryptographic techniques.
## Popular DeFi Use Cases
Popular Use Cases*:
— Stablecoins, *Lending & Borrowing, Decentralized Exchanges, Insurance, Staking, and Governance*.Advanced : Derivatives,Options,Yield farming that is Liquidity Providing,Governance ,DAOs
### Stablecoins: Solving for Volatility
- Cryptocurrency volatility poses challenges for using digital currencies as everyday money, necessitating stable alternatives like stablecoins.
- Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged 1:1 to stable assets, aiming to maintain a value close to $1.Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable price by linking their price to some external asset or reference.Just like the traditional economy, the digital / crypto economy also needs stable money for everyday payments and more.
- Examples include USDT, USDC, and DAI, which are designed to provide stability in the digital economy.
#Why we need stable cryptocurriencies?
Cryptocurrency vision : replace fiat money globally as everyday currency
fiat money is money accepted by a government but not backed by gold or other valuables . that is US dollar
Problem: cryptocurrency prices are volatile.
volatility : the fluctuation in the price or value of an asset over a specific period of time.
Ethereum price swings occur frequently.
These swings can be upward and downward in price.
### Lending & Borrowing: Utilizing Idle Crypto
- Lending platforms allow users to earn interest on their crypto by lending it out, creating a decentralized market.
- This system opens access to financial services for those without traditional bank accounts and offers better rates than conventional banks.
### Exchanges: Centralized vs. Decentralized
- Centralized exchanges (e.g., Binance, Coinbase) operate under a single entity, providing ease of use but less transparency.
- Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) allow users to trade without a central authority, prioritizing privacy and security.
- DEXs are seen as the future of trading, promoting decentralization in the crypto space.
Key components of Exchange
Parties : Sellers and Buyers
Medium : Money,Cryptocurrency , Goods
Platforms : Physical venue or digital / selling
Liquidity : Supply and demand
Settlement : Delivery and Payment mechanisms
Fees : Costs for using the exchange
### Index Tokens: Diversified Investment
- Index tokens track a collection of assets, allowing users to invest in a diversified portfolio without managing individual tokens.
- The All-inclusive Market Token (AMT) tracks the top 25 digital assets, providing exposure to the broader crypto market.
### Staking: Earning Through Participation
- Staking involves locking up crypto to earn rewards, contributing to network security through Proof-of-Stake consensus.
- Users should consider factors like lockup periods and fees before staking.
### Derivatives: Advanced Financial Instruments
- Derivatives derive their value from underlying assets and include futures, options, and swaps.
- They serve purposes such as hedging, speculation, and leveraging investments.
- Options provide the right to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price, similar to making a restaurant reservation.
### Central Bank Digital Currencies vs. Stablecoins
- CBDCs are digital currencies issued by central banks, considered legal tender, while stablecoins are often privately issued to minimize volatility.
- CBDCs face concerns regarding privacy and financial stability due to their centralized nature.
## Mobile Privacy Settings
The document discusses mobile privacy settings, emphasizing the rights of property owners and the potential future use of data collected through these settings.
## Crypto-Collaborative Strategies
- Understand*: Collaboration is crucial in the crypto space, enhancing knowledge sharing and resource distribution.
- **Engage: Active participation in discussions and projects is encouraged to foster community growth.
- Network: Building connections with other crypto enthusiasts is vital for collaborative efforts.
- Contribute: Offering skills and expertise to projects can enhance the overall quality of work.
- Innovation:* Encouraging creative solutions through collaboration can lead to significant advancements in the field.
## Types of Crypto Exchanges
- Centralized Exchanges (CEX): These are managed by a central authority, requiring users to trust the organization with their funds. Examples include Binance and Coinbase.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): Operate without a central authority, allowing users to trade directly without KYC requirements, though they may be less user-friendly.
## Order Book vs. Automated Market Maker (AMM)
- Order Book Exchange: Users place orders that the system matches, facilitating trades.
- Automated Market Maker (AMM): Users provide liquidity, and algorithms set prices, allowing for decentralized trading.A financial institution who is always placing limit orders to buy or sell an asst on an order book based exchange
A class of decentralized exchange that : depoly smart contracts to act as a market maker in an exchange transactions. 24/7
AMMs rely on Mathematical formula to set the price of token and to quote prices ffor a trade
## Liquidity Pools
- Definition: A liquidity pool is a collection of funds locked in a smart contract, enabling trading without a traditional order book.
- Benefits: They provide liquidity for trading, allow users to earn fees, and enable yield farming.
- Accessibility: Anyone can contribute to liquidity pools, promoting decentralization and efficiency in trading.
## Liquidity Providers
- Liquidity Definition: The ability to buy or sell an asset without causing a significant impact on its price .
- Role of Crypto: Crypto enables permissionlessness by replacing humans with code .
- Advantages of Liquidity Providers: They help reduce slippage and improve trade execution .
## Best Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) for DeFi
- Carbon Deli: A hybrid order book exchange and automated market maker (AMM) .
- Uniswap V3: An automated market maker (AMM) .
- Ubeswap: Another automated market maker (AMM) .
## Proof of Stake (PoS) Overview
- Definition of Token: A digital asset created on a blockchain .
- Blockchain Basics: A blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across many computers .
- PoS Mechanism: Validators create new blocks based on the number of tokens they hold, making it more energy-efficient than Proof of Work (PoW) .

Consesus Mechanism
## Staking
- Staking Definition: The locking up of cryptocurrency to earn a reward .
- Reasons for Staking: To earn passive income and secure the network .
- Experience as a Staker: Participants receive staking rewards and have learning potential .
## Pooled and Liquid Staking
- Pooled Staking: Allows multiple participants to combine their stakes to increase chances of earning rewards .
- Liquid Staking: Users stake their tokens while retaining liquidity, receiving a tokenized representation of their staked assets .
- Benefits of Liquid Staking: Users can stake without a minimum requirement, increase security, and earn rewards while maintaining liquidity .
## Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs)
- Definition: LSTs represent shares of staked tokens in a liquid format, allowing trading and use in DeFi applications .
- Examples of LSTs: Rocket Pool (RPL), Lido (LDO), and Frax Ether (Frax ETH) .
- Price Variability: The price of LSTs can vary based on market demand and the price of the underlying staked assets .

Web3 DeFi illustration featuring liquidity pools, decentralized exchanges (DEX), and staking tokens. It showcases interconnected financial elements, staking rewards, and a cyberpunk-style trading network.🚀
## The Creator Economy
- Definition and Components
— The creator economy is built on tools and platforms that support creators, including influencers, content creators, artists, musicians, and writers .
- Monetization Opportunities
— Emerging opportunities for creators include direct monetization through platforms, brand partnerships, subscription models, and crowdfunding .
## Problems with Current Social Media Platforms
- Exploitation of User Data
— Social media tools exploit the monetization of user data, compromising users’ data privacy and failing to adequately compensate them for their contributions .
- Earnings of Creators
— As a result, 94% of creators earn less than $100/year, highlighting significant challenges in monetizing content .
## Web3 and Its Promise
— Web3 leverages blockchains, smart contracts, and tokens to reinvent power and control back to creators and users, allowing for ownership and direct monetization without intermediaries .
- Web3 Social Experience
— It offers a decentralized and user-centric approach, enabling creators to connect with fans and communities while maintaining control over their data .
## Protocols vs. Platforms
- Definitions:
— Protocols govern the exchange of data ensuring interoperability, while platforms provide tools and services for application development .
- Importance of Protocols
— Protocols ensure security and privacy, fostering a more equitable ecosystem for creators and consumers .
## The Mission
- The mission is to create an open and fair social network for all, promoting digital inclusion to drive enhanced market adoption .
## Getting Started with SocialConnect
— SocialConnect is a digital platform that integrates multiple social media accounts into one interface, streamlining social media management and enhancing user engagement .
## Fanactor Ecosystem
- Key Features
— Fanactor provides a platform for building multiple applications, enhancing user engagement and interaction through customizable interfaces and real-time analytics .
## Introduction to DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are defined as organizations governed by rules encoded as computer programs, ensuring transparency and autonomy without central authority. They are designed to operate through smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements written in code.
## Key Features of DAOs
DAOs possess several key features that distinguish them from traditional organizations:
- Transparency: All operations and rules are visible to members, promoting trust.
- Autonomy: DAOs function independently of centralized control, allowing members to self-organize.
- Decentralization: Governance is distributed among members who hold tokens that represent voting power.
## Governance in DAOs
Governance in DAOs is facilitated through token-based systems, where tokens incentivize participation, represent ownership, and enable governance. Members can create a DAO by writing and deploying smart contracts on a blockchain. This structure allows for innovative funding and collaboration alternatives to traditional organizational frameworks.
## Evolution of DAOs
The concept of DAOs has evolved, with the term encompassing a variety of structures that share the principles of decentralization and autonomy. DAOs are increasingly recognized as Decentralized Experimental Organizations (DEOs), emphasizing their role in experimentation and innovation.
## Challenges and Considerations
While DAOs offer new organizational possibilities, they also present challenges. The decentralized nature means that control and management can be complex, as human organization around common goals can lead to difficulties in governance. Understanding these challenges is crucial for effective participation in DAOs.
## Conclusion
DAOs represent a significant shift in how organizations can be structured and governed, leveraging technology to create decentralized, transparent, and autonomous systems. Their development continues to evolve, offering new opportunities for community coordination and value creation in a decentralized era.

DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) Web3 illustration, showcasing interconnected nodes, smart contracts, governance tokens, and a digital voting system in a cyberpunk-style blockchain network🚀
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from LIKHITHA N directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

LIKHITHA N
LIKHITHA N
Tech enthusiast with a passion for learning and sharing. Blogging my journey through electronics, AI, and innovation. #LearningInPublic