OWASP Top Ten
 Amit Sangwan
Amit Sangwan
Current project status as of September 2024: Planning to announce the release of the OWASP Top 10:2025 in the first half of 2025.
Top 10 Web Application Security Risks
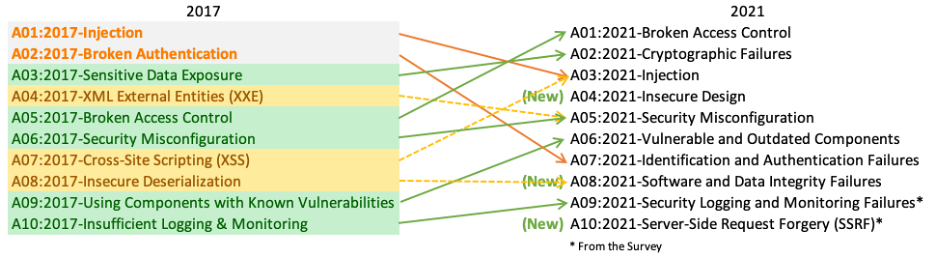
There are three new categories, four categories with naming and scoping changes, and some consolidation in the Top 10 for 2021.
1. A01:2021 – Broken Access Control
Description:
Access control ensures users cannot act outside their intended permissions. Failures lead to unauthorized data access, modification, or execution of unauthorized functions.
Common Vulnerabilities:
Violation of the principle of least privilege or "deny by default".
URL manipulation (parameter tampering, force browsing).
Bypassing access checks via API tools, HTML/JS manipulation.
Prevention Tips:
Implement access control in trusted server-side code.
Deny access by default except for public resources.
Rate-limit access to sensitive endpoints.
Log access control failures and alert on repeated issues.
Example Scenario:
An attacker force-browses to:
arduinoCopyEdithttps://example.com/app/getappInfo
https://example.com/app/admin_getappInfo
If a non-admin or unauthenticated user can access admin pages, it's a critical access control flaw.
2. A02:2021 – Cryptographic Failures
Description:
Inadequate protection of sensitive data in transit or at rest—like passwords, credit cards, health records—can lead to severe consequences.
Key Questions:
Is any sensitive data transmitted in clear text?
Are deprecated or weak cryptographic protocols used?
Prevention Tips:
Classify and identify sensitive data per legal/regulatory needs.
Encrypt all sensitive data at rest and in transit.
Avoid unnecessary data storage.
Example Scenario:
Credit card numbers are encrypted in the DB but auto-decrypted on retrieval. A SQL Injection flaw can then extract them in clear text.
3. A03:2021 – Injection
Description:
Occurs when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a query or command. Common types include SQL, NoSQL, OS commands, and LDAP.
Prevention Tips:
Validate and sanitise all user input.
Prefer parameterised queries and ORM layers.
Implement security testing (SAST, DAST, IAST) in CI/CD pipelines.
Recommended Testing Areas:
- Parameters, headers, cookies, URLs, JSON/XML payloads.
4. A04:2021 – Insecure Design
Description:
Refers to missing or ineffective security controls due to poor design, not just implementation errors. Cannot be fixed by code alone.
Root Cause:
Lack of threat modeling or business risk profiling.
Prevention Tips:
Adopt a secure SDLC.
Conduct threat modeling early in development.
Use secure design patterns and define security-focused user stories.
Design for tenancy isolation, rate-limiting, and fault tolerance.
Example Scenarios:
Weak password reset via security questions.
Logic flaw in cinema seat booking allows abuse.
Bots purchasing goods faster than humans.
5. A05:2021 – Security Misconfiguration
Description:
Happens due to improper security settings, exposed features, verbose errors, or missing headers.
Common Scenarios:
Default credentials in production.
Directory listing enabled, exposing internal files.
Stack traces revealing backend details.
Misconfigured cloud storage exposing data.
Prevention Tips:
Harden security configurations before deployment.
Disable unnecessary features and services.
Use automated configuration scanners.
6. A06:2021 – Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Description:
Use of outdated libraries, frameworks, or dependencies introduces vulnerabilities, especially when not tracked or updated regularly.
Risk Factors:
No component inventory.
Infrequent patching or rigid change management.
Insecure default component configurations.
Prevention Tips:
Maintain an inventory of all components and their versions.
Use SCA tools like OWASP Dependency-Check, Retire.js.
Subscribe to vulnerability advisories.
7. A07:2021 – Identification and Authentication Failures
Description:
Weak authentication or session management leads to account compromise and unauthorized access.
Vulnerable Behaviours:
Credential stuffing or brute force allowed.
Weak/default/common passwords accepted.
Passwords stored in plain text.
Sessions not invalidated on logout.
Prevention Tips:
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Enforce strong password policies.
Block default credentials and limit login attempts.
Monitor and log authentication failures.
8. A08:2021 – Software and Data Integrity Failures
Description:
Occurs when apps trust unverified components, such as plugins, libraries, or updates, without checking integrity.
Common Risks:
Using untrusted CDNs or third-party scripts.
Auto-updates without digital signature verification.
Prevention Tips:
Use signed packages and libraries.
Validate integrity of third-party components.
Implement Subresource Integrity (SRI) for scripts.
9. A09:2021 – Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
Description:
Without proper logging and monitoring, attackers can act undetected, leading to delayed response to breaches.
Typical Issues:
Missing logs for login attempts, access to sensitive data.
Logs stored locally or poorly formatted.
No alerting mechanism.
Prevention Tips:
Log key events: login, account changes, errors, and high-risk transactions.
Use centralised logging solutions (e.g., ELK stack).
Sanitise logs to prevent injection.
Correlate logs with intrusion detection systems.
Examples:
Indian Airline Leak: Cloud misconfig undetected due to lack of monitoring.
European Airline Breach: GDPR violation from poor logging led to £20M fine.
10. A10:2021 – Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Description:
SSRF happens when the server fetches a remote resource specified by user input without validating the URL, allowing attackers to target internal systems.
Risks:
Bypass firewalls, internal networks, or metadata services (e.g., AWS IMDS).
Exfiltration of sensitive internal data.
Prevention Tips:
Validate and sanitize user-provided URLs.
Allow only safe destinations via a positive allow list.
Block raw responses and HTTP redirections.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Amit Sangwan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Amit Sangwan
Amit Sangwan
Software Engineer | AI Enthusiast | Tech Blogger Passionate about tech, automation, AI agents, and Security. Exploring innovations in tech while sharing insights on technology and career growth. Always learning, always evolving.