Inside the Mind of Agentic AI: From Generative to Autonomous Intelligence
 Parth Sohaney
Parth Sohaney
“Remember Avengers? When Jarvis took over Veronica to deploy Hulk-Buster Armor? That’s Agentic AI in action—autonomous, powerful, and mission-ready.”
Why is everyone talking about Agentic AI ?
src: https://www.gsdcouncil.org/blogs/line-graph-reveals-agentic-ai-market-penetration
Market Analysis : Agentic AI adoption is rapidly rising, with 80% of Indian firms exploring autonomous agents by 2025 and 86% of global companies projected to run agentic AI by 2027. Over 70% of generative AI users are already leveraging agentic systems, showing a strong link between generative and autonomous AI evolution.
Till now we use AI Chatbots to provide responses based on a single interaction. A person makes a query and the chatbot uses natural language processing to reply .
But what if we had a personal assistant that not only does everything AI chatbots can do, but also plans and executes tasks based on a specific goal? That would be amazing, right?
Now imagine the amount of work a company could take off its employees’ shoulders and the time it could save—simply by automating everything using Agentic AI.
This is why the market is so excited about it. Honestly, who wouldn't want free assistance?
From Prompts to Purpose : The Evolution of AI models -

You'll get a general idea from the image above, but let me clarify where the confusion starts—
Difference between Workflows , AI Agents and Agentic AI —
WORKFLOWS - it is a neutral term , which can exist in both Tool Augmented AI and Agentic AI .It is a pipeline containing a series of steps you follow to complete a goal usually in specific order .These steps can be done by humans , Ai tools or both - Let me give you an example -
1- You have a PDF containing all Holiday /Leave related policies of the company and the company has made a Workflow , which will provide the answer written in PDF based on the type of question
2- Even ChatGPT can be a part of human-driven workflow , until it is done autonomously.
Answering normal questions or coding related problem are termed as Workflows (in Anthropic Paper) but AI Agents are different.
TOOL AUGMENTED AI (AI Agents) - Lets us understand this with an example of [lovable.dev] for those who don’t know it is a famous AI tool used to build frontends -
Now if I want to build a website with Auth and DB connection -
1- First I will go to Lovable and ask it to create a frontend for me , will also provide it the UI idea and theme — it will use LLM for this
2- Then if I want to use Clerk service , I will manually go and add it to my website or ask GPT for steps .
3- For DB connection I will again have to manually connect AWS or any other service to it .
So you get the idea what I wanted to say - here you have to tell each step manually , and then LLM generates the code of give me the steps to for it .
If we are using a tool (like lovable or anything else ) , it will perform a function based on my input but will not plan any steps further .
Its like input —>LLM —> output .You are yourself a planner and a controller.
AGENTIC AI - this has autonomy and memory , this can reason , plan , decide and act over multiple steps -
Understanding due to same example - Now if there was an Agentic AI here , I just have to give command “Make a SAAS webapp for me with Auth and DB (AWS) and payments ” , it will automatically create a frontend , then plans and execute the Clerk Auth , and yes if clerk auth requires the changes in frontend , it will also manage it automatically and then connects the DB , will also add env variable . At last it will integrate RAZOR pay payment gateway.
And finally will generate you a completely running SAAS webapp.
Now I think you all would have gained a clear understanding , but if not I have made a table for you - below
Example of Agentic AI use cases -
1- Booking a trip , with flight booking , cab booking , hotel booking etc.
2 - Automating food ordering , or cold emailing .
The most famous agentic AI tools is n8n ,and Zapier
Here is the table for better understanding -
| Aspect | Tool-Augmented AI | Agentic AI | Workflow |
| Initiation | You prompt: "Build my frontend" | You say: "Make me a full-stack SaaS app" | You use multiple tools in a pipeline |
| LLM Usage | Single-shot per action (e.g., generate HTML) | Multiple times at each decision point (e.g., "Should I use Clerk?") | Human coordinates LLM tools per step |
| Frontend (Lovable.dev) | You run Lovable manually | Agent runs Lovable itself | You manually run it in workflow |
| Auth (Clerk) | You ask ChatGPT, then add Clerk | Agent decides to add Clerk automatically | You manually add Clerk |
| DB (AWS) | You ask ChatGPT to integrate it | Agent chooses AWS, sets up DB, handles credentials | You run a script or tool to do it |
| Reasoning & Planning | You decide each step | AI plans all steps with subgoals | You plan each step and tools execute |
| Error Handling | You retry manually | Agent retries or changes tools on its own | You intervene and rerun |
| Goal-Oriented? | No — task-based | Yes — understands final goal | Partially — human defines and manages |
| Autonomy | None | High | Low to moderate |
| Who’s in Control? | You | The Agent | You |
Why ‘Just Talking’ Isn’t Enough Anymore: Enter Agentic AI —
“Sure, ChatGPT can write your essay. But can it file your tax return end-to-end?”
I know we’re too good at explaining things to AI, but AI is not just meant for chit-chat. One of the main goals of evolving AI was to increase productivity and reduce time spent on work that can easily be done by us humans.
So now, we need a solution that not only talks, but also plans, executes, updates, and stores. Let me draw a clear line between the old Generative AI and the new Agentic AI —
Generative AI :
Trained on huge datasets to generate content (text, images, code)
Has no persistent memory (can only remember within the same session, and forgets everything once the chat ends)
No planning. No execution.
Reactive in nature.
Example: “Write a blog about Japan.”
Agentic AI :
Built on LLMs but empowered with tools, persistent memory, goal-setting, and multi-step orchestration.
Learns from feedback and adapts.
Executes actions across systems.
Example: “Plan a Japan trip, check visa rules, create my itinerary, and book hotels.”
Think: ChatGPT vs. AutoGPT.
A good resource to read about this topic : Link
Comparison Table (from Sapkota et al., 2025 and Publicis Sapient)
| Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Input | Prompt | Goal / Intent |
| Output | Single response | Multi-step plans and actions |
| Memory | Stateless or session-limited | Persistent, contextual memory |
| Autonomy | None | Autonomous and proactive |
| Tool Use | Plugins or external tools (limited) | Deep integration with APIs and tools |
| Planning | None | Task decomposition and stepwise planning |
| Learning | Static (pretrained) | Continuous via feedback loops and environment signals |
| Collaboration | None | Can coordinate with other agents |
| Use Case | Content creation, summarization, Q&A | Decision support, workflow execution, research agents |
| Examples | ChatGPT, DALL·E, Bard | AutoGen, LangGraph agents, TaskMatrix.AI |
Why the Difference Matters :
Generative AI is transformative for creativity, content, and conversational UX.
But it doesn’t solve for goal completion, task orchestration, or agent-level cognition.
As Publicis Sapient puts it:
“Generative AI helps create... Agentic AI helps get things done.”
In Summary :
Agentic AI builds on the foundation of generative models.
But it pushes beyond: it’s intelligent, tool-integrated, memory-augmented, and autonomous.
This marks a shift from prompt engineering to autonomous agent design.
This shift is at the heart of the paradigm explored by Sapkota et al. in their paper: AI Agents vs. Agentic AI (arXiv:2505.10468).
Agents, But Not Intelligent: The Limitations of Old-School AI —
Before we talk about the revolution of Agentic AI, we need to understand what we’re moving away from—and why traditional AI agents weren’t enough.
What Were "AI Agents" Before?
The term “AI Agent” has been around for decades. It typically referred to:
A standalone software module that could sense its environment, make decisions, and take action.
Often used in:
Expert systems
Robotic controllers
Chatbots
Rule-based assistants (think: Clippy)
In the modern LLM era, these became tool-augmented AI agents: LLMs with access to:
Search APIs
Function calls
External data sources
Examples include:
LangChain agents calling web APIs
AutoGPT following instructions across tools
ChatGPT with plugins
These systems simulate goal-seeking, but they suffer from major limitations.
The Problem With Traditional AI Agents :
Based on the research paper : Sapkota et al. (2025), old-school agents even those powered by LLMs—fail to achieve true autonomy, reasoning, and coordination .
Let’s break down the core limitations:
1. Stateless or Short-Term Memory Only
Most traditional agents forget everything once the task ends.
No cross-task memory, learning from mistakes, or long-term personalization.
Example: A tool-augmented bot can't recall how it solved a similar problem last week.
2. No True Collaboration or Coordination
They don’t work with other agents or humans in a coordinated way.
No shared goals, no role awareness, no distributed decision-making.
Anthropic notes: "Traditional agents are often locked in fixed workflows and can’t delegate or collaborate."
3. Rigid or Shallow Planning
Most rely on prompt chains or static instructions.
They can't self-reflect, re-plan, or simulate alternatives.
Agent planning is hard-coded, not emergent or adaptive.
4. Limited Causality or Intent Modeling
They don’t understand why they're doing something.
There’s no causal reasoning or long-term impact estimation.
Sapkota: “They lack models of environment dynamics and can't predict how actions will unfold over time.”
5. High Fragility and Brittleness
One tool-call failure breaks the flow.
Agents often hallucinate tool names, pass wrong formats, or retry incorrectly.
Anthropic: “Agents can fail catastrophically if error-handling isn't explicitly designed.”
6. Lack of Evaluator and Feedback Loops
There's no mechanism to assess success or revise strategies.
Agents don’t learn from their outputs unless wrapped in complex external loops.
📉 Performance often degrades with task complexity or iteration depth.
Inside the Brain: How Agentic AI Makes Autonomous Decisions :

Agentic AI isn’t just about making large language models smarter , it’s about engineering entire systems that think, plan, act, and adapt.
As described by both Anthropic and Markovate, an agentic architecture is a symphony of modular, intercommunicating layers, combining LLMs with tool-use, orchestration logic, and long-term memory to solve dynamic, real-world tasks autonomously.
Core components of an Agentic AI System :

1. Perception Layer
Role: Ingests raw input from users, sensors, APIs, or systems.
-
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Context extraction
Realization: Often the first LLM prompt, or a specialized classifier module.
2. Planning and Reasoning Engine
Role: Converts input into a sequence of actionable steps.
Inspired by: ReAct, Tree of Thoughts, and Anthropic’s “transparent planner” principle.
Key Behaviors:
Goal decomposition
Step validation
Error recovery and replanning
How it works: Uses LLMs to simulate multiple plans and select the optimal path.
Anthropic Prompt Chaining :

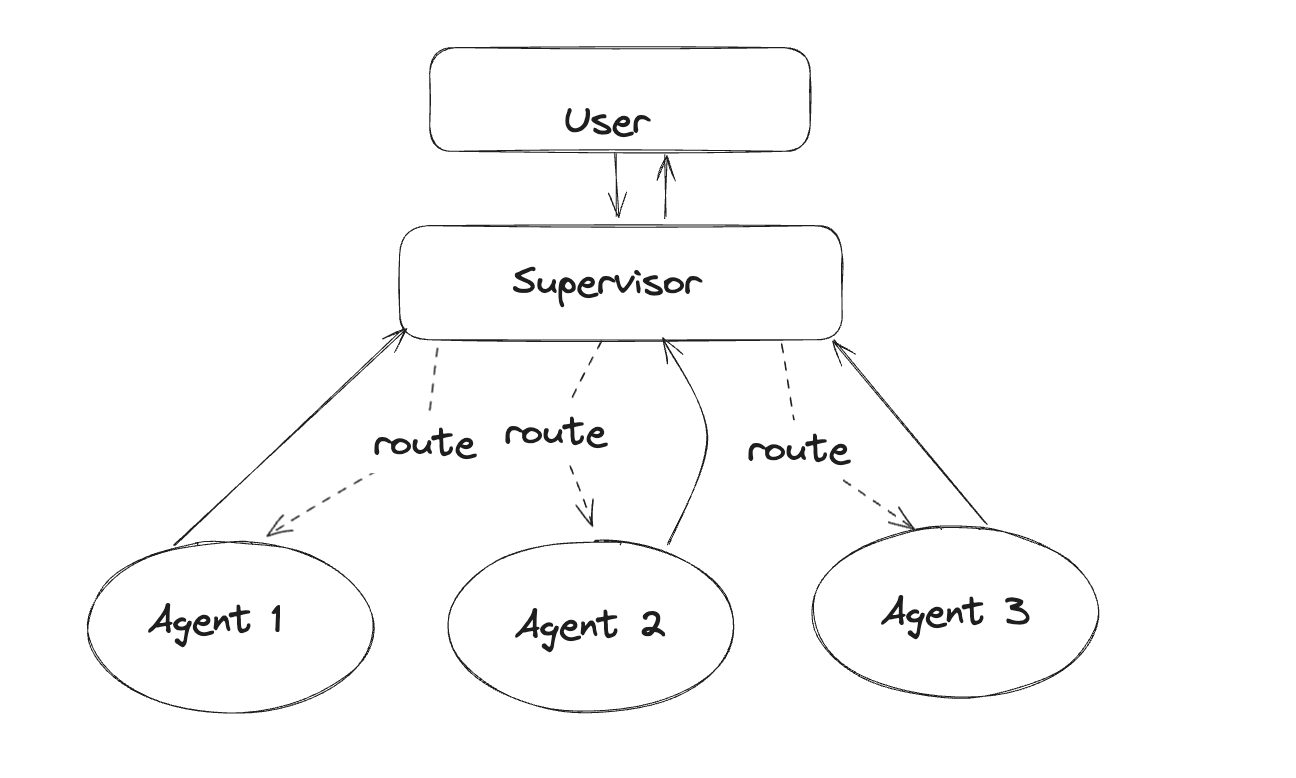
3. Routing and Specialization -
Anthropic Workflow: Routing
“The planner selects the most appropriate specialized sub-agent for each step.”

Example:
Travel planner agent
Budget checker agent
HR policy enforcer agent
4. Tool Use Interface
Role: Executes actions by interacting with external tools, APIs, or databases.
Anthropic Note: Tools should have “clean, well-documented interfaces” to reduce reasoning errors.
Anthropic Workflow : Parallelization

Examples:
Web search API
Notion/GDocs editor
Database query engine
Code executor
5. Memory Stack
Role: Tracks past actions, task state, and long-term user preferences.
Markovate Categorization:
Episodic Memory (task-specific)
Semantic Memory (domain knowledge)
Procedural Memory (how-to knowledge)
Technologies Used:
Vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate)
Contextual retrievers
LangChain Memory modules
6. Orchestrator / Control Flow
Role: Oversees task lifecycle and coordinates between components.
Architectures Used:
LangGraph (graph-based flow control)
CrewAI (role-based agent teams)
AutoGen (hierarchical orchestration)
Responsibilities:
Looping over steps until task is done
Managing retries, role-switches, or collaboration
Executing evaluator-optimizer feedback cycles

7. Feedback and Evaluation Layer
Role: Ensures quality, monitors progress, and improves agent behavior over time.
Pattern: Anthropic’s Evaluator-Optimizer loop

Includes:
Output scoring
Self-reflection modules
External human-in-the-loop review
Logging and observability

Full Flow Example :
Command : “Plan a company offsite for 10 people within budget.”
Perception Layer: Understands the task, attendees, and constraints
Planner (Prompt Chaining): Breaks into venue search, travel options, food preferences, and cost checking
Router: Assigns HR agent, travel agent, and finance agent
Tool Layer (Parallelization): Queries APIs and books multiple services
Memory: Stores past location preferences and budgets
Orchestrator-Worker: Supervises team agents, resolves failures
Evaluator-Optimizer: Reviews final plan, cost, and satisfaction score; learns from failure modes
Key Design Principles (Anthropic and Markovate Papers ) :
Start simple: Use as few modules as needed to deliver value.
Expose planning logic: Let agents narrate their decisions.
Design clean interfaces: Better tools = better tool use.
Use workflows first, agents second: Not all tasks need full autonomy.
Test in sandbox mode: Always validate before deploying agents in production.
The Power of Many: When AI Agents Team Up
If traditional agents were lone freelancers, Agentic AI is the enterprise team—collaborating, sharing knowledge, and aligning toward a single mission.
This shift—from single-agent workflows to multi-agent systems (MAS)—is central to the rise of truly autonomous intelligence.
As Sapkota et al. (2025) point out:
“Agentic AI is not merely an enhanced AI Agent—it is a coordinated collective of agents, each with distinct capabilities, operating under a unified goal.”
Q-Why Single Agents Aren’t Enough
Single agents—even if powerful—struggle with:
Task breadth: One agent can't specialize in all domains.
Scalability: Bottlenecks emerge when a single LLM handles all decisions.
Modularity: Maintenance and debugging become difficult without role separation.
Thus, modern systems are evolving into agent collectives, where:
Agents act as specialists (planner, executor, memory retriever, evaluator)
Each agent can have its own prompt, tools, and memory
Orchestration logic governs communication and conflict resolution
Architecture: Multi-Agent Systems in Practice
Agentic AI systems can be configured using multiple collaborating agents with:
| Role | Description |
| Planner Agent | Decomposes the high-level goal into tasks |
| Worker Agents | Execute individual subtasks (e.g., call APIs, summarize docs) |
| Retriever Agent | Fetches external knowledge or memory documents |
| Evaluator Agent | Reviews results and gives feedback |
| Coordinator Agent | Maintains order, resolves conflicts, tracks goal status |
Frameworks That Enable Multi-Agent Systems
Several modern tools support multi-agent orchestration:
LangGraph: Flow-based multi-agent graph execution
AutoGen: Hierarchical agent design with task delegation
CrewAI: Define teams with roles and workflows
TaskMatrix.AI: Scalable, plugin-based agent collaboration system
Challenges of Multi-Agent System :
| Challenge | Impact |
| Misalignment | Agents may pursue conflicting subgoals |
| Looping / Deadlock | Poor control flow can cause infinite loops or stalling |
| Error Propagation | Faulty data from one agent may affect others |
| Latency & Cost | More agents = more API calls = slower & expensive inference |
Building One Yourself? Here’s What You’ll Need
| Layer | Tools / Frameworks |
| LLM | OpenAI GPT, Claude, Mistral, Llama |
| Planning / Logic | LangGraph, AutoGen, CrewAI |
| Tool Integration | LangChain Tools, REST APIs, Node-based wrappers |
| Memory | Pinecone, Weaviate, Redis, Supabase |
| UI / Interface | Next.js, React, Tauri (for agents with GUI) |
| Orchestration | CrewAI, LangGraph, Node-based agents |
Here is the best video to get started : What are AI agents.Let’s build one
Hallucinations, Conflicts & Chaos: Challenges of Agentic AI :
1. Hallucinations at Scale
While LLMs hallucinating facts is well-known, agentic systems amplify the risk:
Agents may invent:
API endpoints
Tool names
Output formats
Entire subtasks that were never requested
Hallucinated decisions propagate through memory and planner loops.
Anthropic warns: “Agents that use tools without constraints can hallucinate commands that break downstream logic.”
2. Error Propagation
One wrong decision doesn’t stay isolated—it spreads:
Faulty memory → Misleading retrieval
Incorrect tool output → Bad planning
Inconsistent state → Wasted loops or retries
And the worst part? It’s hard to debug due to:
Asynchronous planning
Multiple tool interactions
Autonomous reasoning layers
3. Inter-Agent Conflict
In multi-agent setups:
Agents might disagree on facts
Retry each other's failed tasks
Override or ignore outputs from peer agents
Without a strong orchestrator, agents may enter deadlocks, infinite loops, or regressions.
4. Inconsistent Memory Handling
Agentic systems depend on memory for:
Task tracking
Preference retention
State transitions
But poorly managed memory can cause:
Feedback loops of misinformation
Contradictory context from past interactions
Slow degradation of task quality
Sapkota: “Memory consistency and lifecycle management remain under-researched and high-risk.”
5. Lack of Ground Truth or Evaluation
How do you know if the agent did the job well?
There’s often no clear success metric
LLMs may claim success even when failing
Auto-evaluation is hard, especially in dynamic tasks
Anthropic’s Evaluator-Optimizer loop tries to fix this, but most systems still lack robust agent-level QA.
6. Latency, Cost, and Compute Explosion
Multi-agent systems can get expensive:
5 agents calling GPT-4 → 💸💸💸
Dozens of tool calls per iteration
Retry loops and memory fetches
Without optimization, your “smart agent” may be:
Slow
Expensive
Unscalable
7. Security, Trust & Abuse Risk
Agentic AI that controls:
File systems
Browsers
Payment tools
Critical operations
…can be a huge security liability if not properly sandboxed.
Key risks:
Prompt injection → Unauthorized tool use
Memory poisoning → Long-term behavioral shifts
Model exploits → Bypassing intended safeguards
Anthropic and OpenAI both recommend extensive sandbox testing, strong permissions, and audit logging.
Vaults of Resources for Agentic AI Builders :
Credits and References :
Articles:
Videos:
Repos:
Final Words :
Agentic AI is not the future—it’s the now. Build it. Break it. Blog about it.
Project Ideas I got from here :
I will build one stop solutions from many long tasks such as —
1- Building End_to_End_Trip_Planner (Booking tickets + booking hotels + Marking destinations on map + Planning the entire trip + option to extend the trip to visit nearby city + etc)
2-Building Event_Planner (Taking details of event from you (kind+date+venue) to setting up the menu + sending the request or message to all the nearby caterers/Home chefs for quotation + Deciding the best offer based on rating and price + etc)
3- Building SaaS through a single command from building frontend from lovable and adding auth from Supabase and connecting DB to directly deploying it on either vercel or anything .
Let’s see which is more challenging and excites me…
💬 Got questions or want help building your first agent? Drop a comment below or DM me!-
LinkedIn - http://www.linkedin.com/in/parthsohaney
Gmail - parthsohaney04@gmail.com
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Parth Sohaney directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
