Automate GitHub Repo Analytics to Google Sheets Using n8n (No-Code Guide)
 Gaurav Kulkarni
Gaurav Kulkarni
🌎 Introduction
In the world of software development and data-driven decisions, staying on top of your GitHub repository statistics like stars, forks, watchers, and programming languages used is essential. Manually collecting and logging this data into a Google Sheet every day is repetitive and inefficient.
That’s where n8n comes in. n8n is a powerful workflow automation tool that allows you to connect different services like GitHub and Google Sheets without writing a single line of backend code.
In this blog, we will walk through building a fully automated n8n workflow that fetches data from GitHub and appends it to a Google Sheet.
🚀 Why This Workflow?
It automates daily tracking of repository performance.
Makes reporting and monitoring efficient.
Perfect for developers, open-source contributors, and teams who want to log GitHub stats.
Enables integration with Google Sheets for easy sharing and visualization.
🔄 Tools & Services Used
n8n (https://n8n.io/): Workflow automation tool
GitHub API: To fetch repository data
Google Sheets: To store and review the data
🏠 Workflow Overview
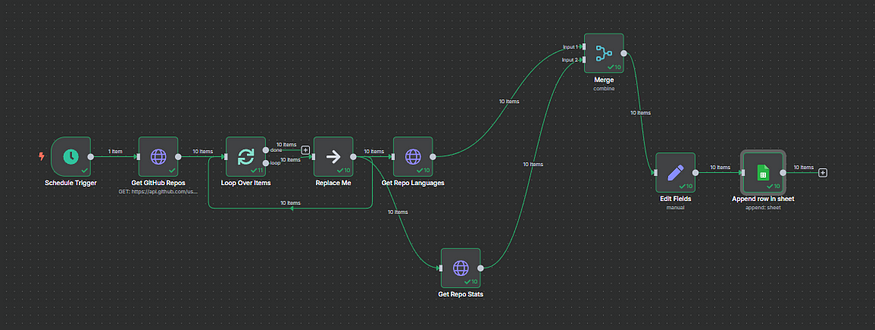
✅ Node-by-Node Detailed Explanation
1. Schedule Trigger Node
Purpose: Automatically runs the workflow at a specified time.
Settings: You can set this to run daily, weekly, or at any interval. In our case, we run it after every 7 days of gap at 10 a.m.
Why we use it: This helps us to automate the GitHub data collection without manually triggering it.
2. HTTP Request (Get GitHub Repos)
Purpose: To get a list of all public repositories for a GitHub user.
Method: GET
URL:
https://api.github.com/users/repos
Headers:
Authorization:
Bearer <your_github_token>GitHub requires this token to authenticate the user and authorize access.
User-Agent: Custom value like your GitHub username.
Why this URL?: This endpoint returns all public repositories of a given user. It includes repo name, description, stars, forks, language, etc.
3. Item Lists (Loop over Items)
Purpose: The GitHub API returns an array of repositories. We use this node to split the array so that each repo can be processed individually in the workflow.
4. Set Node (Replace Me)
Purpose: To prepare and rename important data fields for further use, such as:
{
“name”: “repo-name”,
“owner”: {
“login”: “username”
}
}
We extract repo name and owner.login as these will be used in subsequent API calls.
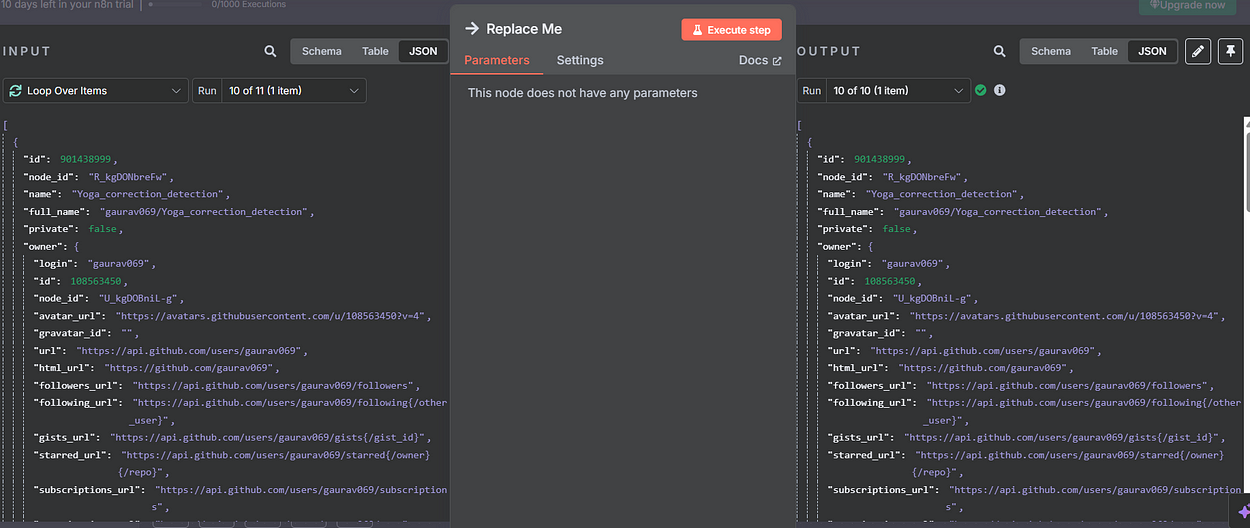
5. HTTP Request (Get Languages)
Purpose: To retrieve programming languages used in a specific repo.
Method: GET
URL (with expressions):
https://api.github.com/repos/{{$json["owner"]["login"]}}/{{$json["name"]}}/languages
Why this URL?: This GitHub endpoint returns a JSON object with languages and number of bytes written in each.
Authentication: Same as before using Bearer token.
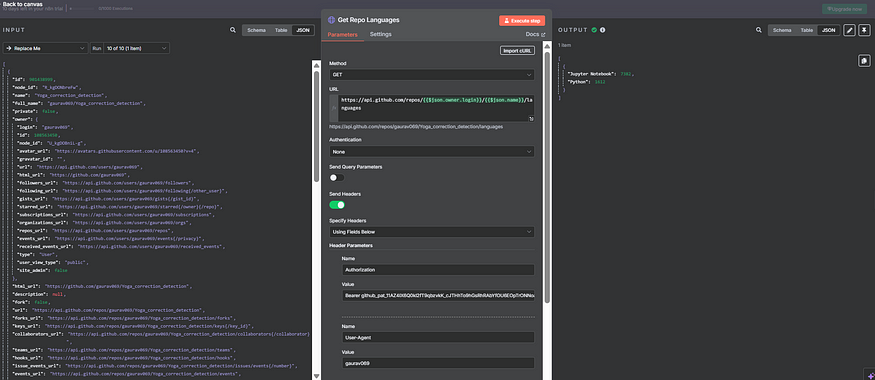
6. HTTP Request (Get Repo Stats)
Purpose: To retrieve metadata about the repo like:
stargazers_countforks_countwatchers_count
URL: https://api.github.com/repos/{{$json["owner"]["login"]}}/{{$json["name"]}}
This data gives us a snapshot of repo popularity.
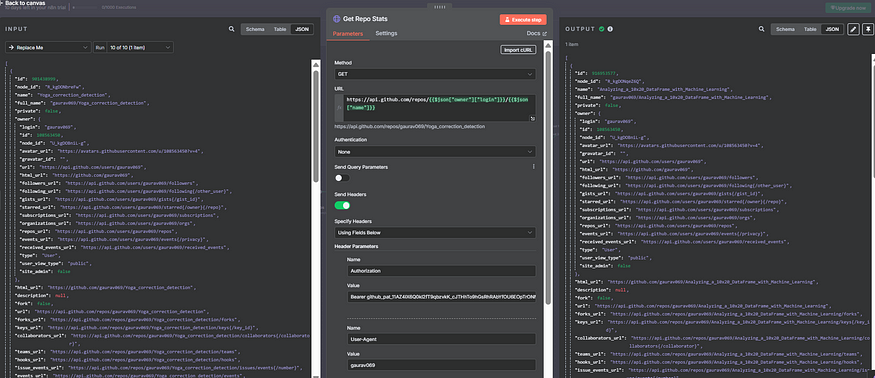
7. Merge Node
Purpose: Combine the output of two nodes:
Repo languages
Repo stats
Mode: Combine
Combine By: Position
Number of inputs: 2
This merges the data from both branches into a single JSON object for each repository.
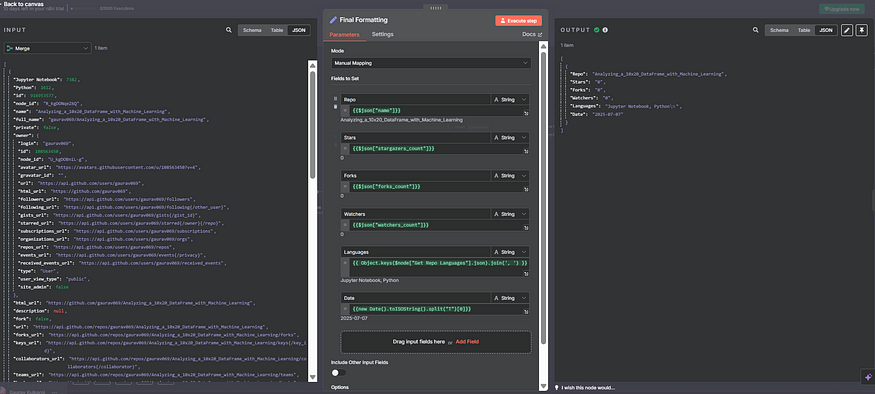
8. Set Node (Final Formatting)
Purpose: To format the data before inserting into Google Sheets.
Fields Set:
Repo: {{ $json["name"] }}Stars: {{ $json["stargazers_count"] }}Forks: {{ $json["forks_count"] }}Watchers: {{ $json["watchers_count"] }}Languages: {{ Object.keys($node[“Get Repo Languages”].json).join(‘, ‘) }}Date: {{new Date().toISOString().split(“T”)[0]}}
This node makes sure only the needed values are passed to the Google Sheet.
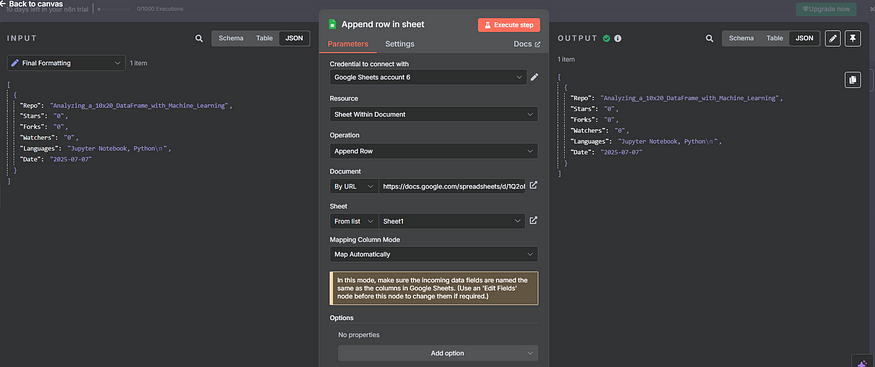
9. Google Sheets Node (Append Row)
Purpose: Append the final JSON data as a new row in your spreadsheet.
Configuration:
Operation: Append Row
Resource: Sheet Within Document
Authentication: Use Google Sheets OAuth2 credentials
Document: By URL
Sheet: From List
Mapping Column Mode: Map Automatically
Note: Make sure your sheet has the following columns:
Repo | Stars | Forks | Watchers | Languages | Date
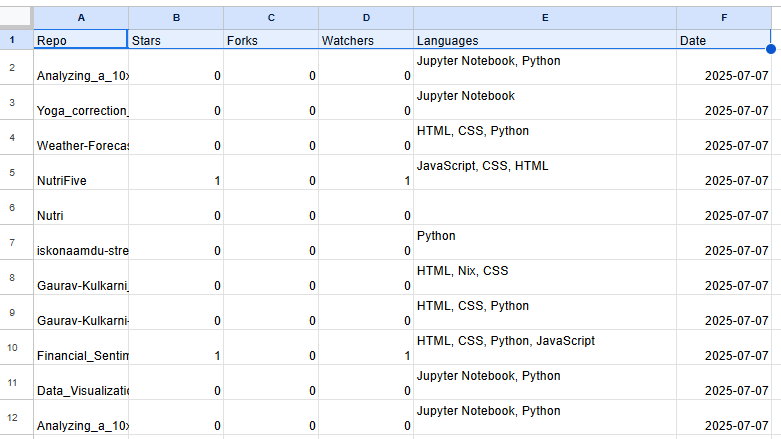
🎉 Final Output
At the end of the workflow, your Google Sheet will have a daily entry of:
GitHub repo name
Star count
Fork count
Watcher count
Languages used
Date of entry
Example:
🚧 Common Errors & Debug Tips
403 Forbidden: Check your GitHub token and scopes.
No Output from Merge: Ensure repo names match from both branches.
Google Sheet Quota Exceeded: Limit execution frequency.
Headers Error in HTTP Node: Ensure
AuthorizationandContent-Typeare correctly set.
✨ Conclusion
This workflow demonstrates how simple it is to use n8n for GitHub analytics automation. With zero backend coding, you can track repo metrics and log them into a live Google Sheet.
This is just the beginning! You can extend this project by:
Adding email alerts
Creating visual dashboards
Tracking only specific repositories
Logging changes over time
✅ Share your feedback in comments!
Stay tuned for the next workflows where we automate skill extraction from resumes and personalized career recommendations!
📚 Connect With Me:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gaurav Kulkarni directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Gaurav Kulkarni
Gaurav Kulkarni
🚀 I'm Gaurav Kulkarni, an AI/ML Developer & Data Scientist passionate about automating real-world workflows. Currently building intelligent systems like automated GitHub analytics and resume skill extractors using AI, n8n, and OpenAI APIs. I bridge data, code, and automation to solve everyday challenges smarter.