Email Scams: Why Small Businesses are Targets for Hackers
 John Richard
John RichardThe AI-based system that stands guard protecting your business from cyber threats
Introduction
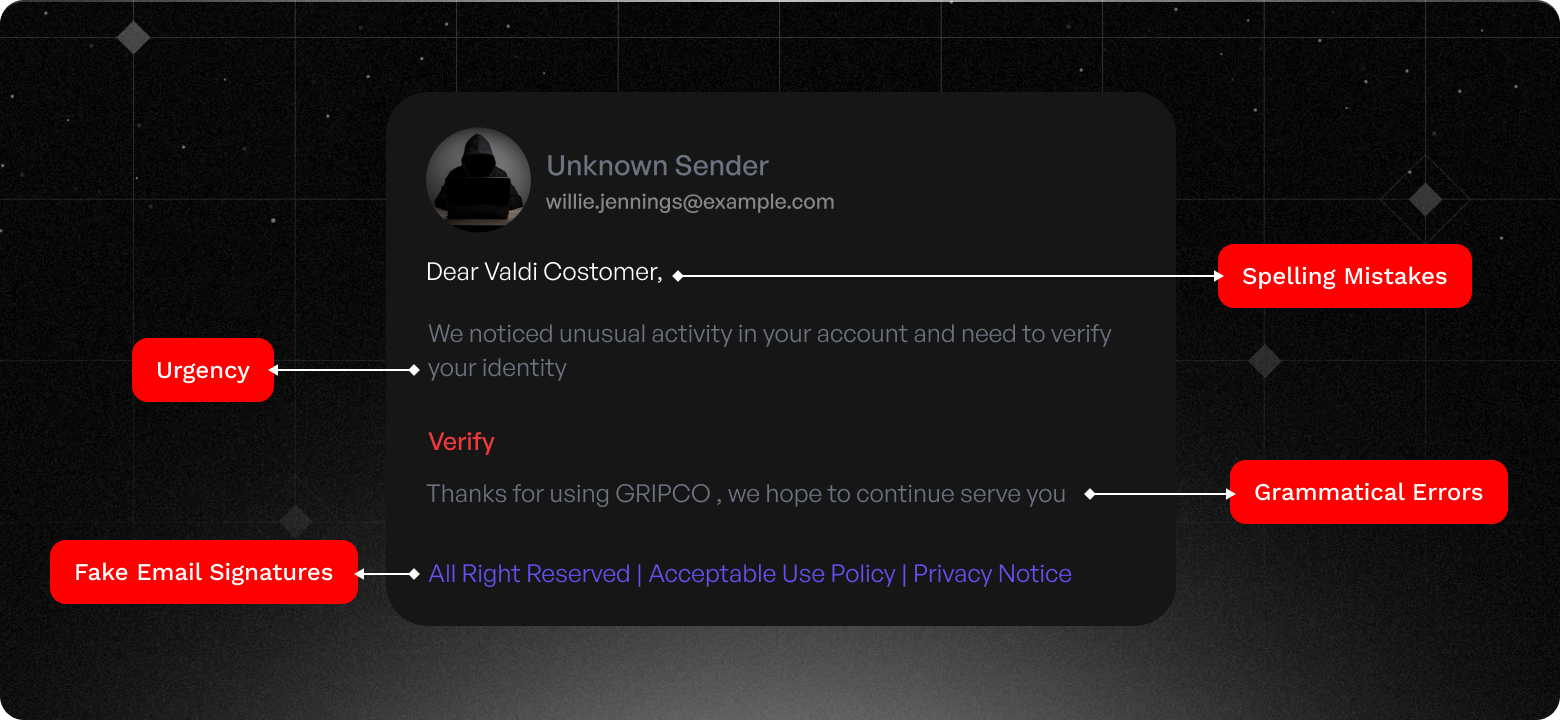
Phishing emails are hard to spot when hackers disguise themselves as trusted vendors
Over 20% of spam emails originate from Russia, with scammers impersonating government agencies to threaten small businesses with license suspension. Email scams, especially Business Email Compromise (BECs) are becoming increasingly sophisticated, posing threats to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Hackers disguise themselves as trusted vendors in deceptive emails, tricking employees into revealing sensitive information or transferring funds to fraudulent accounts.
From October 2013 to July 2019, the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) received reports of 166,349 online scam incidents, leading to losses of over $26 billion globally.
In 2023 and 2024, many SMBs fell victim to online scams. For instance, in 2023, a small manufacturing company in Ohio received a phishing email pretending to be from a trusted vendor. The email contained an urgent payment request, complete with fake invoices and detailed instructions. Believing the email to be legitimate, the company's accounting department transferred $50,000 to the hackers' account. The fraud was only discovered after the money was irretrievably lost.
A notable evolution of BEC scams is payroll diversion, where scammers spoof emails from employees to change direct deposit information, redirecting salaries to prepaid card accounts. Between January 2018 and June 2019, over 1,000 complaints of this nature were reported, with a total loss of $8.3 million.
In another case, a digital marketing agency in California encountered a scheme where attackers impersonated a major client. They sent an email during a busy workday, urging the agency to click a link for critical project updates. Clicking the link installed malware on the agency's network, enabling the attackers to steal confidential client data and demand a ransom for its return. The agency ended up paying $30,000 to regain access to their data and avoid further damage.

5 Tips to Protect Your Business from Online Scams
1. Verify email authenticity of invoices
Always check the sender's email address and look for inconsistencies or suspicious details. If an email seems out of the ordinary, verify its authenticity by directly contacting the sender through a trusted communication method.
2. Avoid Suspicious Links
Refrain from clicking links or downloading attachments from unknown sources, especially if the email id is misspelled.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Use MFA for all critical accounts and systems to add an extra layer of security. This makes it difficult for attackers to gain access, even if they acquire login credentials.
4. Regularly Update Software
Keep all software, including antivirus programs and operating systems, up to date. This is crucial, especially for remote teams working with diverse systems.
5. Educate employees
Conduct regular training sessions to inform employees about fake invoices, fake online listings, and other phishing tactics. Teach them how to recognize suspicious emails.
Phishing can have devastating consequences on SMBs. Unlike larger enterprises, SMBs lack the resources and cybersecurity infrastructure to quickly recover from a breach.
Small business owners can learn about tech and business, but failing to prioritize cybersecurity can potentially disrupt your entire business chain. If attackers get into your system once, they can potentially steal sensitive data, even after you've implemented basic security measures.
SMBs receive the highest rate of targeted malicious emails, with one in every 323 emails containing threats like phishing, spam, or malware. Therefore, safeguarding your business against advanced email scams is essential.
Get a Free Cyber security Audit
How Cube Can Help
Cube's advanced threat detection capabilities safeguard against phishing attacks. Using behavioral analysis and machine learning, Cube detects suspicious activities in real time, flagging potential threats before they can cause harm. It integrates with your existing email platforms and other communication tools.
When Cube detects a phishing email, it analyzes the content and context, identifying anomalies, hidden characters, and patterns typical of phishing attempts. Cube then immediately alerts the user with clear warnings and guides on appropriate actions. Moreover, its automated response features can block malicious links and attachments, preventing them from reaching employees' inboxes.
By implementing Cube, SMBs can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing scams.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from John Richard directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
