GFG Day 1: Java Basics and First Program
 sri parthu
sri parthu
Introduction to Java
- Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language. It was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in 1995. Now it is owned by Oracle Corporation. It was designed to be platform independent, which means it can run on any device or OS where the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is installed. This platform independence follows the write once, run anywhere approach.
Key feature of Java
There are 10 important Java features. They are:
Object-Oriented:
Java is an Object-Oriented Programming Language (OOPL). It follows:
Abstraction
Encapsulation
Inheritance
Polymorphism
Simple:
- Java is very easy to learn, and its syntax is simple, clean, and easy to understand.
Platform Independent:
- Java programs will run on any OS, which means our Java code will compile into bytecode and run in the JVM.
Secure:
- Java provides a secure environment with features like bytecode verification, no pointer access, a security manager, and access control.
Robust:
Java checks for errors at both compile time and runtime.
Storage memory management using garbage collection.
Exception handling helps to build reliable applications.
Architecture Neutral:
- Java is architecture neutral because the size of the primitive data types is fixed for 32 & 64-bit OS.
Portable:
- Java is platform independent because it can carry or move Java bytecode from one place to another on any platform.
High Performance:
- Java enables high performance. It uses JIT (Just-In-Time) compilers, garbage collection, and code execution speed.
Multi-threaded:
- Java supports multithreading, allowing multiple tasks to be executed.
Distributed:
- Java is designed for the distributed environment of the internet to develop applications.
Writing Hello world Program in Java
- When we are learning any programming language, the first program we write is "Hello World." Below is a simple Java program that displays "Hello World" on the screen.
Java Hello World Program
// This is simple Java program that print Hello World
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
/* Note: File name
and class name
should be same... */
Output:
Hello World
How does program work (Java architecture)
- Flowchart of Java Architecture and its Information

Source code: Source code is a set of instructions written by the programmer in a human-readable language. We use the .java extension for our file to write the program.
- Compiler: A compiler is a program that translates our source code written in a high-level programming language into a low-level programming language like bytecode.
Bytecode: Bytecode is the program code that has been compiled from the source code into low code. It is designed for a software interpreter. It automatically uses .class for the file.
- Interpreter: An interpreter is a computer program that directly executes machine code instructions and runs the Java program.
Machine code: Machine code consists of machine language, which is a low-level programming language used to be directly controlled by the CPU.
Comments in Java
The comments are notes written inside the code to explain what the code is doing. These comments are not executed in the program. There are 2 types:
Single-line comments: Single-line comments are written to the right side of the double slash (
//).// This is simple Java program that print Hello World (Single-Line Comment)Multi-line comments: Multi-line comments are written inside the slash and asterisk (
/*.....*/)./* Note: File name and class name should be same... */
Naming Conventions in Java
Java uses some standard naming rules, which make code easier to read and improve readability.
In Java, class names always start with capital letters, like
HelloWorld, and method and variable names start with lowercase letters and use camel case, likeprintingMessage.
Note:- Most of the programmers are use camel case naming convention
Applications of Java and Use Case
In Java, we can build many applications like the following:
Web applications using Servlets, JSP (Java Server Pages), Spring Boot, Hibernate, and JSF (Java Server Faces). Ex: Online banking portals, e-commerce websites, etc.
Mobile applications (Android) using Android SDK. Ex: WhatsApp, Uber, Instagram, etc.
Enterprise applications using Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) and Spring Framework. Ex: CRM tools, HR management systems, etc.
Desktop applications using Swing and JavaFX. Ex: media players, editors, etc.
Cloud-based applications using AWS, Google, Azure
Gaming applications using jMonkeyEngine, JavaFX, and LibGDX. Ex: Super Mario, puzzle games, etc.
Download and Install JDK on Windows
- JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. It is the most important tool for developers to build, compile, and run Java applications. It acts as a crucial part of the Java platform because it is platform-independent. JVM translates byte code to machine code to execute the program. It manages memory, handles garbage collection, and supports multithreading.
Key Feature of JDK
Compiler (javac): Convert Java code into byte code to machine code for JVM to execute the program.
JVM + JRE: It includes a runtime environment to execute Java programs.
Rich libraries: Pre-built class like I/O, networking, database and more
Debugging Tools: KDK provides JDB (Java Debugger) to troubleshoot the code
Mulit-platform support: JDK support Write Once and Run Anywhere ( WORA ) like Windows, Linux, MacOS
Why Install JDK ?
To develop and run Java applications
Compile Java source code (javac)
Includes runtime environment like JRE (Java Runtime Environment) and JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
Required for Android app development (Java/Kotlin/AndriodSDK)
Java JDK Download
- We need to download the JDK first; follow the steps below to get started:
Step 1: Visit the Official Website
- Go to the official JDK website to download the file.
Oracle Official Website
- Since JDK is open-source, you can get it from OpenJDK in a few clicks.
Step 2: Select the Appropriate Version
- As of 2025, the latest stable versions are JDK 23 (SE) and JDK 21 (LTS). Select the compatible version according to your operating system (Windows, Mac, or Linux).
Step 3: License and Agreement
- Go through all the licenses and agreements before downloading (from the Oracle website); it will not ask if you download it from the OpenJDK website.
Install JDK on Windows
- Follow the steps below to install JDK in a Windows environment, i.e. Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.
Step 1: Run the Java Development Kit (JDK) Installer
- Locate the downloaded .exe file (e.g. jdk-23-windows-x64_bin.exe) and double-click to begin the installation process. Follow the installation wizard prompts to complete the installation.
Step 2: Set Up the Environment Variables
Once the installation is completed, you need to configure environment variables to notify the system about the directory where the JDK files are located.
Proceed to C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-{YOUR_JDK_VERSION}\bin (replace {YOUR_JDK_VERSION} with your JDK version)
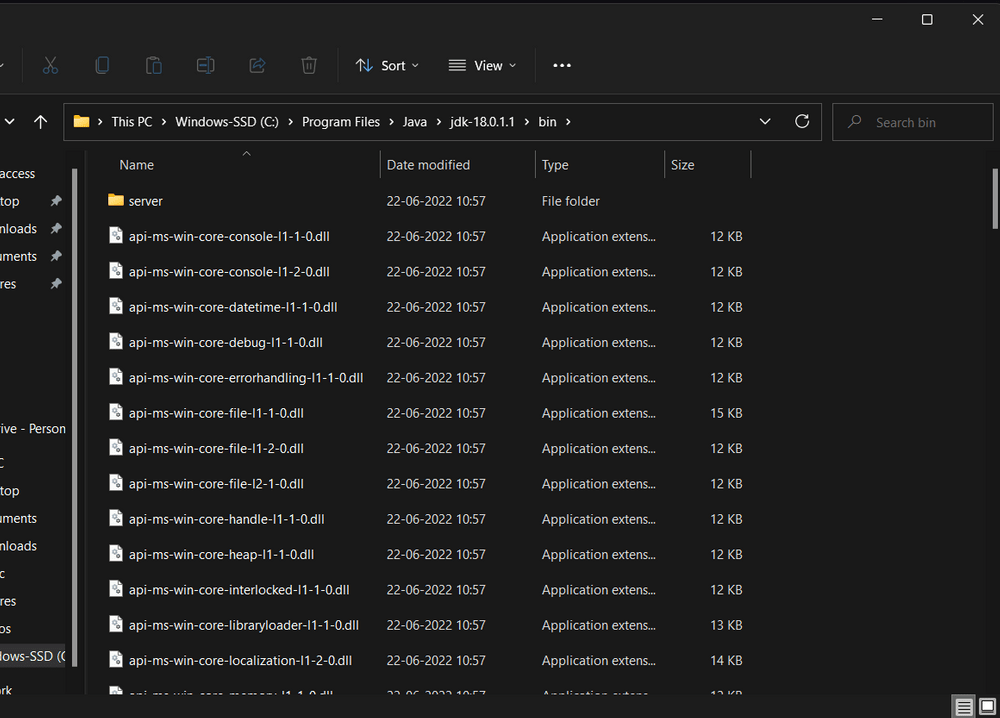
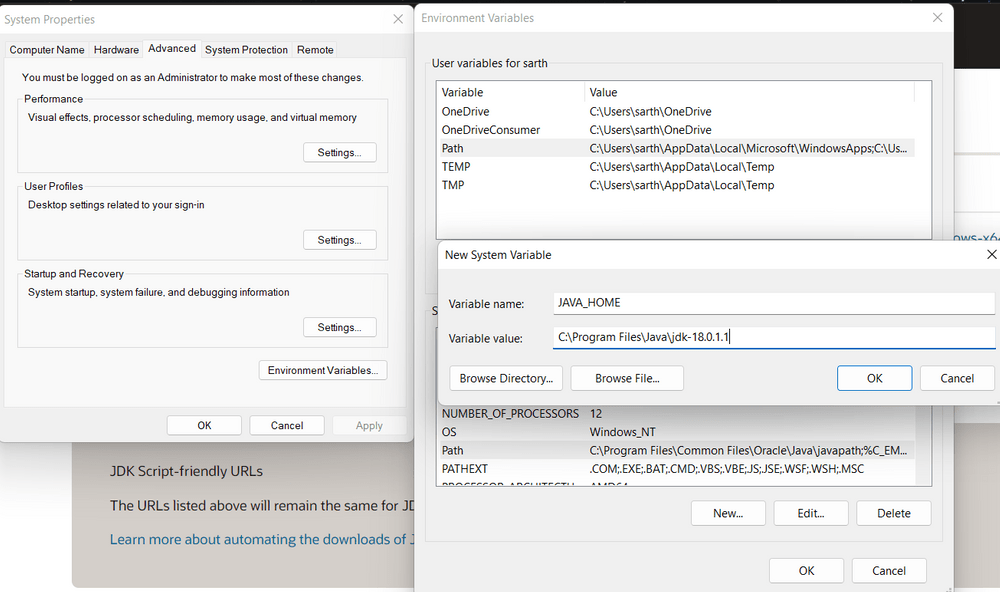
- Step 2.1: To set the Environment Variables, you need to search Environment Variables in the Task Bar and click on “Edit the system environment variables”.
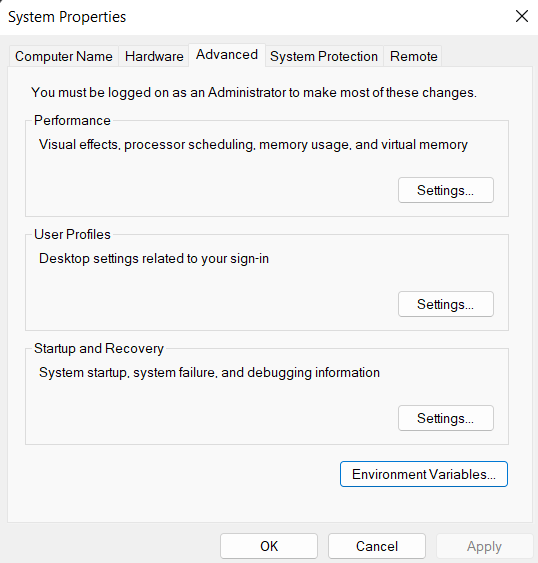
- Step 2.2: Under the Advanced section, Click on "Environment Variables".
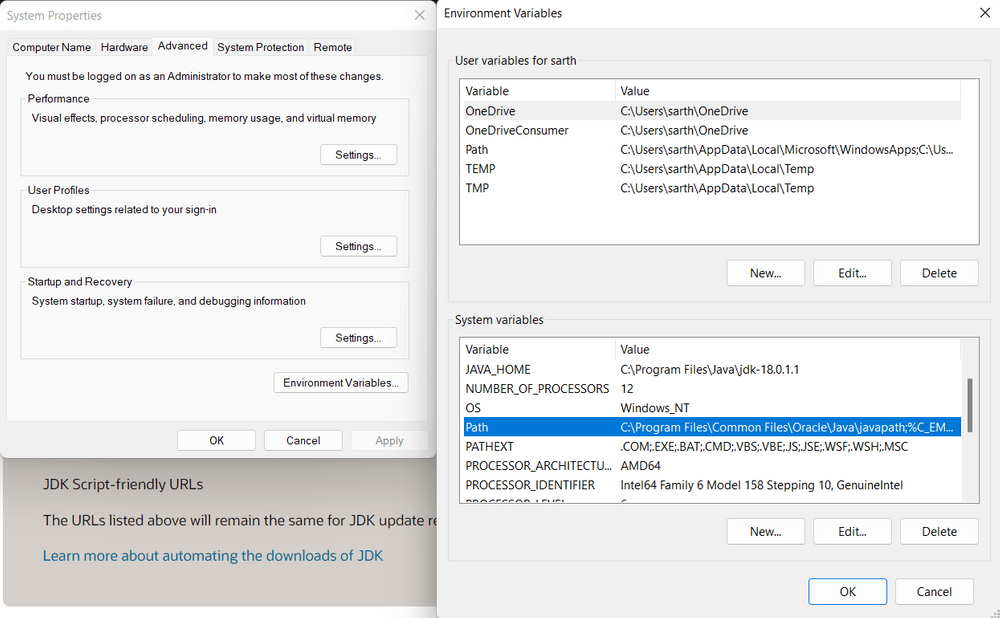
- Step 2.3: Under System variables, select the "Path" variable and click on "Edit". Click on "New" then paste the Path Address i.e. C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-{YOUR_JDK_VERSION}\bin. Click on "OK".
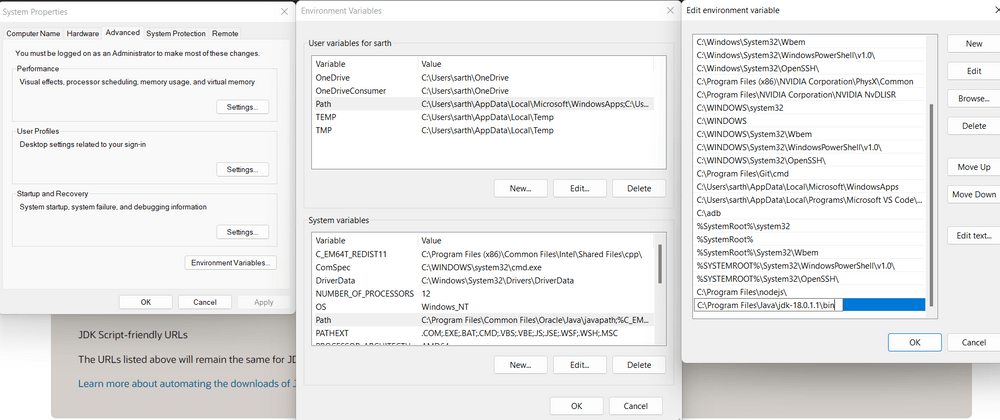
- Step 2.4: Now, in the Environment Variables dialogue, under System variables, click on "New" and then under Variable name: JAVA_HOME and Variable value: paste address i.e.
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-{YOUR_JDK_VERSION}. Click on OK => OK => OK.
Step 3: Check the Java Version
- Open Command Prompt and enter the following commands:
java -version
javac -version

Java Hello World Program
- Java is most popular widly used programming language and platform. we will learn how to write a simple Java Program, how to compile and run java code, Understanding the Hello World program structure. With the help of Java, we can develop web and mobile applications.
Implementation of Java Hello World
- Writing simple program of Java and printing “Hello World” on the screen and userstand the code step by step
// FileName: HelloWorld.java
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
Output
Hello World
Understanding the Java Hello World Program
- class definition:
- class is the keyword. Every program must have at least one class. If the class is public, then the filename and class name should be the same.
// FileName: Hello World.java
public class HelloWorld{
// Statement goes here
}
- main method:
- In java programing language in every application containes main method as it is the entry point of the java application
public static void main(String[] args){
// Execution done here
}
public: allow JVM to acces method from any where
static: method can run without creating any object
void: It doesn’t return any value
String[ ] args: Accepts command line arguments
- System.out.println( )
- This print output to the console
System.out.println("Hello World");
System: It is the built-in class from java.lang package.
out: Static member (PrintStream object) of System.
println(): The method that prints to the console and moves to the next line.
Steps to Implement a Java Program
- Flowchart of Java Architecture and its Information

Source code: Source code is a set of instructions written by the programmer in a human-readable language. We use the .java extension for our file to write the program.
- Compiler: A compiler is a program that translates our source code written in a high-level programming language into a low-level programming language like bytecode.
Bytecode: Bytecode is the program code that has been compiled from the source code into low code. It is designed for a software interpreter. It automatically uses .class for the file.
- Interpreter: An interpreter is a computer program that directly executes machine code instructions and runs the Java program.
Machine code: Machine code consists of machine language, which is a low-level programming language used to be directly controlled by the CPU.
Happy Learning
Thanks For Reading! :)
SriParthu 💝💥
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from sri parthu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

sri parthu
sri parthu
Hello! I'm Sri Parthu! 🌟 I'm aiming to be a DevOps & Cloud enthusiast 🚀 Currently, I'm studying for a BA at Dr. Ambedkar Open University 📚 I really love changing how IT works to make it better 💡 Let's connect and learn together! 🌈👋