GFG Day 6: Basic Input and Output in Java
 sri parthu
sri parthu4 min read

- Java provides various streams with its I/O package that help the user perform input and output operations. This supports reading and writing data from the keyboard, files, devices, etc., to fully execute the I/O operation.

Standard or Default Streams in Java
- To explore various input and output streams, we have 3 standard or default streams in Java that provide and are commonly used: System.in, System.out, & System.err.
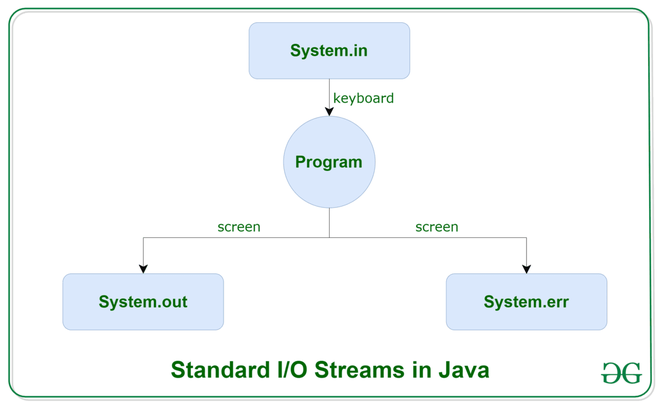
System.in
- This is the standard input stream (System.in) that is used to read characters from the keyboard or any other standard input devices.
Example using Scanner:
// file name: InputExample.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class InputExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // wraps System.in
System.out.print("Enter your name: ");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Hello, " + name);
}
}
Output
Enter your name: Core Advn ance Java
Hello, Advance Java
System.out
- This is the standard output stream (System.out) that is used to produce the result of a program on an output device like the computer screen. They are print( ), println( ), printf( ).
Java Print Functions Used with System.out
- print( )
- This method in Java is used to display a text on the console. This text is passed as the parameter to this method in the form of String. Prints text on same line, cursor stays at end.
Example: print()
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Java ");
System.out.print("is ");
System.out.print("fun!");
}
}
Output
Java is fun!
- println( )
- This method in Java is also used to display a text on the console. It prints text and moves cursor to next line.
Example: println()
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Line 1");
System.out.println("Line 2");
}
}
Output
Line 1
Line 2
- printf( )
- This is the easiest of all methods as this is similar to printf in C. Note that System.out.print() and System.out.println() take a single argument, but printf() may take multiple arguments. This is used to format the output in Java.
Example: printf()
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 25;
double pi = 3.14159;
System.out.printf("Age: %d years, PI: %.2f", age, pi);
}
}
Output
Age: 25 years, PI: 3.14
System.err
- It is used to display the error messages. It works similarly to System.out with print(), println(), and printf() methods.
Example
// Java Program demonstrating System.err
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Using print()
System.err.print("This is an error message using print().\n");
// Using println()
System.err.println("This is another error message using println().");
//Using printf()
System.err.printf("Error code: %d, Message: %s%n", 404, "Not Found");
}
}
Output
This is an error message using print().
This is another error message using println().
Error code: 404, Message: Not Found
Types of Streams
- The Types of Streams can be divided into two primary classes
- input Stream: These streams are used to read data that must be taken as an input from a source array or file or any other device. For eg., FileInputStream, BufferedInputStream, ByteArrayInputStream etc.
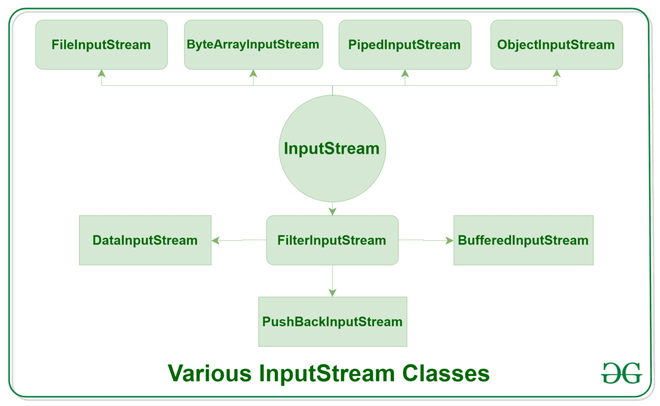
- Output Stream: These streams are used to write data as outputs into an array or file or any output peripheral device. For eg., FileOutputStream, BufferedOutputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream etc.

Types of Streams Depending on the Types of File
- Depending on the types of file, Streams can be divided into two primary classes which can be further divided into other classes you can see the below diagram.

- ByteStream: This is used to process data byte by byte (8 bits). Though it has many classes, the FileInputStream and the FileOutputStream are the most popular ones. The FileInputStream is used to read from the source, and FileOutputStream is used to write to the destination.
Here is the list of various ByteStream Classes:

- CharacterStream: In Java, characters are stored using Unicode conventions. The character stream automatically allows us to read/write data character by character. Though it has many classes, the FileReader and the FileWriter are the most popular ones. FileReader and FileWriter are character streams used to read from the source and write to the destination, respectively.
Here is the list of various CharacterStream Classes:

Note: Later, we will dive deeper into this topic in a more understandable way.
Happy Learning
Thanks For Reading! :)
SriParthu 💝💥
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from sri parthu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Core JavaJavaScriptjava full stack developmentJava Full Stack Developer Traininggeeksforgeeks#skillupwithgfg#nationskillup.input output
Written by

sri parthu
sri parthu
Hello! I'm Sri Parthu! 🌟 I'm aiming to be a DevOps & Cloud enthusiast 🚀 Currently, I'm studying for a BA at Dr. Ambedkar Open University 📚 I really love changing how IT works to make it better 💡 Let's connect and learn together! 🌈👋