GFG Day 8: Classes, Objects, and Methods
 sri parthu
sri parthu
- In Java, classes and objects are basic concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP).
Java Classes
- A class is like a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines properties (variables) and behaviors (methods) that an object will have. A class does not allocate memory until an object is created from it.
Syntax
class ClassName {
// Fields or Variables
dataType variableName;
// Methods
returnType methodName() {
// code
}
}
A class in Java is a template with the help of which we create real-world entities known as objects that share common characteristics and properties.
Here, the below Java code demonstrates the basic use of class in Java. It defines a
Studentclass with two instance variables (idandn), creates an objects1 and prints values of s1.
// File: Student.java
class Student {
int id;
String n;
// Added constructor to initialize both fields
public Student(int id, String n) {
this.id = id;
this.n = n;
}
}
// File: Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Student object using the new constructor
Student s1 = new Student(10, "Advance Java");
System.out.println(s1.id);
System.out.println(s1.n);
}
}
Output
10
Advance Java
Java Object
An object is an actual instance of a class it's like a real house built from the plan. When you create an object, you're allocating memory and accessing the class's fields and methods.
State: It is represented by attributes of an object. It also reflects the properties of an object.
Behavior: It is represented by the methods of an object. It also reflects the response of an object to other objects.
Identity: It gives a unique name to an object and enables one object to interact with other objects.

Note: Objects (non-primitive types) are always allocated on the heap, while their reference variables are stored on the stack.
Syntax to create object
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();
Initializing a Java Object
- The new operator instantiates a class by allocating memory for a new object and returning a reference to that memory. The new operator also invokes the class constructor.
// Java Program to Demonstrate the
// use of a class with instance variable
// Class Declaration
public class Dog {
// Instance Variables
String name;
String breed;
int age;
String color;
// Constructor Declaration of Class
public Dog(String name, String breed, int age,
String color)
{
this.name = name;
this.breed = breed;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
// method 1
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// method 2
public String getBreed() {
return breed;
}
// method 3
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
// method 4
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
@Override public String toString()
{
return ("Name is: " + this.getName()
+ "\nBreed, age, and color are: "
+ this.getBreed() + "," + this.getAge()
+ "," + this.getColor());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Dog tuffy
= new Dog("tuffy", "papillon", 5, "white");
System.out.println(tuffy.toString());
}
}
Output
Name is: tuffy
Breed, age, and color are: papillon,5,white
Explanation:
The Dog class has instance variables for name, breed, age, and color.
A constructor initializes these variables using passed arguments.
Constructors have no return type and share the class name.
Object tuffy is created with: new Dog("tuffy", "papillon", 5, "white").
toString() returns a string representation of the object.

Java Methods
A method is a block of code that performs a specific task. It helps in:
Code reusability (write once, use many times)
Organizing logic
Reducing code duplication
All methods in Java must belong to a class. Methods are similar to functions and expose the behavior of objects.
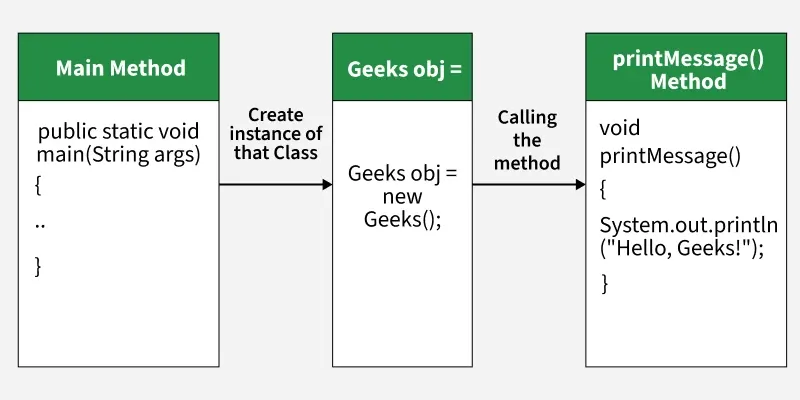
Java program to demonstrate how to create and use a method
// Creating a method
public class Geeks
{
public void printMessage() {
System.out.println("Hello, Advance Java!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of the Method class
Geeks obj = new Geeks();
// Calling the method
obj.printMessage();
}
}
Output
Hello, Advance Java!
Explanation:
printMessage() is a simple method that prints a message.
It has no parameters and does not return anything.
Here, first we create a method that prints Hello, Advance Java!
Types of Methods in Java
Predefined Method
- Predefined methods are the method that is already defined in the Java class libraries. It is also known as the standard library method or built-in method.
Math.random() // returns random value
Math.PI() // return pi value
User-defined Method
- The method written by the user or programmer is known as a user-defined method. These methods are modified according to the requirement.
sayHello // user define method created above in the article
Greet()
setName()
Happy Learning
Thanks For Reading! :)
SriParthu 💝💥
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from sri parthu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

sri parthu
sri parthu
Hello! I'm Sri Parthu! 🌟 I'm aiming to be a DevOps & Cloud enthusiast 🚀 Currently, I'm studying for a BA at Dr. Ambedkar Open University 📚 I really love changing how IT works to make it better 💡 Let's connect and learn together! 🌈👋