Quality Assurance Testing: Everything You Need to Know
 Ayush Gupta
Ayush Gupta
In a technologically dominated world, producing top-notch software isn't merely a competitive edge - it's a must. Whether creating a mobile application, a website, or a large-scale enterprise system, consumers anticipate that your software be secure, responsive, and flawless.
That's where Quality Assurance (QA) Testing comes in. It doesn't just make your software work - it work well, do what users need it to do, and meet world-class standards of excellence. QA testing is no longer a luxury. It's an SDLC mandate.
Quality Assurance in Software
Software development QA is not testing - it's ensuring and improving quality at every step of the development life cycle. It's ensuring quality standards, training your team members, establishing CI/CD pipelines, and tracking metrics to keep getting better.
What Quality Assurance in software projects involves:
Requirement Validation: Are we building the right thing?
Design Reviews: Are we building it right?
Code Reviews and Static Analysis: Is the code clean, secure, and maintainable?
Process Optimization: Are we doing it the best way to prevent risks?
QA is omnipresent. Testers are only half of QA, but also developers, product owners, project managers, and users.
What is Quality Assurance Testing?
Quality Assurance (QA) Testing is one type of testing for software such that it meets the standards required and behaves as expected under live situations. QA Testing provides a guarantee for the discovery of bugs, usability issues, performance inefficiencies, and security vulnerabilities prior to software being released for end users.
In reality, QA testing is a combination of a little manual work and a little automated work to test an application thoroughly to assess its quality. Let's break that up a bit more:

Major QA Testing Objectives:
Functionally Complete
Everything about functionality and features should function as documented in the requirements. It therefore recommends testing for user flows, edge cases, and integration to guarantee that everything is working as described. InnovativeRobust
It should not crash or fail when it is given unexpected input, network loss, or faulty user input. That's where QA testing comes in where an application continues to function under stress or even when it hits an error.Secure
Secure QA testers help reveal weaknesses like SQL injection, XSS attack, violation of access control, etc., mostly in security test cycles. Leaking confidential data or facilitating intrusions in systems is not what is aimed at.Performant
Performant It must also be properly backed in terms of loading time, responsiveness, and heavy loads. Performance testing, load testing, and stress testing are used to measure this.User-Friendly
User-Friendly Along with performing as required, the app must also be usable, simple to use, and responsive. Usability testing assures that the app provides a good experience to real users.
Types of Quality Assurance Testing

Manual Testing
Manually, the testers interact with the app - clicking buttons, entering forms, or navigating flows - to identify bugs that tools cannot catch. It is most suitable for exploratory testing, UI checks, and usability or visual mismatch detection.
Key Features:
Ideal for exploratory, UI/UX, and visual testing
Easy to use and flexible
No code
Slower and less scalable
Automated Testing
Test scripts (usually created in programming languages like JavaScript, Python, or Java) are executed by agents like Keploy, Selenium, or Cypress. The scripts imitate user or API interaction and check UI controls, inputs, or outcomes - executing more rapidly than rerunning the same tests.
Key Features:
Ran fast, iteratively, and in bulk
Less susceptible to human error
Ideal used for regression and integration testing
Needs to be installed and supported
Unit Testing
Independent methods or functions are tested separately by developers with tools like Pytest, Jest, or JUnit. Mock objects are often used instead of real dependencies (databases or APIs) to test units under required behavior without interference from outside.
Key Features:
Grants immediate feedback to developers
Usage of mocks/stubs to isolate code
Heart of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Catch bugs early during development
Integration Testing
Trains modules to communicate with one another when used together. For instance, it ensures a sign-up process for a user correctly ties together the frontend form, backend route, database layer, and email service. Postman or pytest + Flask typically help that way.
Key Features:
Ensures data passing between systems
Guarantees services and APIs are well-integrated
Usually automated by software like Postman, Pytest, or Karate
Has detection of logic inconsistency between modules
System Testing
Deploy the entire system after integration. It includes functional testing on every module, verifying from end-to-end workflows, e.g., a user logs in, purchases something, and gets confirmation - all in a single flow.
Key Features:
Simulates real usage patterns
Preserves end-to-end business processes
Validate app behavior in production environment-like configuration
Executes prior to user acceptance testing (UAT)
Acceptance Testing (UAT)
End users or product owners make the system business need compliant. Test cases like "Can I successfully add an item to the cart and pay?" are here ensured. It makes the product production -ready before it goes live.
Key Features:
Customer - or stakeholder-run
With business logic in mind, not technicalities
Shuts down prior to production
Test cases like "Can I buy successfully?"
Regression Testing
After each code change (new feature, patch, or config refresh), regression tests re-verifies core functionality in order not to break anything by mistake. Tests tend to be automated and executed relatively frequently in CI/CD pipelines.
Key Features:
Generally automated within CI/CD pipelines
Needs to be run after patches, new feature, or config changes
Saves time by executing existing test suites one additional time
Performance Testing
It examines for speed, responsiveness, and stability under load. Load testing simulates many users (e.g., 1,000 all at once slamming the server), whereas stress testing goes beyond boundaries to locate points of failure or memory leaks.
Key Features:
Load Testing, Stress Testing, Soak Testing.
Bottlenecks (CPU, memory, DB) discovered
Guarantees smooth experience at scale
Tools: JMeter, Gatling, Locust
Security Testing
Scans for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, CSRF, or insecure APIs. They use testing tools such as OWASP ZAP or Burp Suite to mimic attacks and check whether the system correctly handles authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
Key Features:
Reveals vulnerabilities and misconfigurations
Simulates attacks by exploiting using tools like OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite
Guarantees secure handling of sensitive information
Complies (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
Smoke and Sanity Testing
Smoke tests are shallow tests (e.g., does the app begin, are there major endpoints?). Sanity tests are performed to make sure one bug fix or minor feature modification won't make related functionality useless. They are often executed after each build or deploy.
Key Features:
Smoke: Does the app open and react?
Sanity: Does the new feature/fix function without murdering the rest?
Quick, lightweight, and often automated
Saves time by not spending it on garbage builds
Quality Assurance vs Testing — What’s the Difference?
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they’re not the same:
| Aspect | Quality Assurance | Testing |
| Objective | Prevent defects | Find defects |
| Timing | Throughout development process | After development or during sprints |
| Responsibility | Everyone involved | Dedicated QA/Testers |
| Focus | Process-oriented | Product-oriented |
QA is the umbrella under which testing lives.
Why Quality Assurance Testing Matters?
Still not quite understanding why Quality Assurance (QA) Testing really matters? Let's run through the whys - and why skimping on QA might cost you more than a few extra bugs.

1. Fewer Bugs and Costly Post-Launch Problems
Wild bugs will cost 10 times as much to debug as they would if they were still in development. QA testing keeps problems away that arise in early lifecycle, and your team will not need to perform crisis patching, handle customer complaints, or endure terrible reviews.
2. Enhances User Experience
Even if all the magic behind the scenes of your app is harmoniously in concert, kludgey interfaces, delayed response, or clumsy workflow will push customers through the door. QA ensures your app isn't just working - but silky smooth, beautiful, and sheer bliss to use.
3. Builds Customer Trust
Nothing subverts faster than a buggy or intermittently functioning app. Test software on a frequent basis to show that you care about quality, gain the trust of your users, and enable you to reap a loyal customer base.
4. Saves Development Time in the Long Run
QA can seem to retard the development process in the beginning but then speeds up the entire process. Automated feedback loops and testing catch issues early, and hence the development process becomes less tense and sophisticated.
5. Ensures Standards Compliance
Be it data privacy legislation (such as GDPR), accessibility (WCAG), or compliance with industry standards (such as HIPAA in healthcare), QA gets your application compliant and secure to roll out.
Without proper QA, you’re essentially releasing your product into the wild untested - a risky move that could lead to user churn, data loss, brand damage, and high support costs.
Quality Assurance Tools in Software Testing

The right tools make QA testing more efficient, reliable, and scalable. Here are some of the most popular ones:
1. Keploy
Keploy is a cutting-edge, open-source QA tool that auto-generates test cases and API mocks directly from real user traffic. It’s perfect for developers and teams who want to increase test coverage without writing scripts manually.

Why Keploy Stands Out:
Zero-effort testing: Just run your app, and Keploy records test cases automatically in the background.
Mocks & Replays: Reproduce production behavior locally with precision, making bug replication and resolution faster.
CI/CD Friendly: Seamlessly integrates with tools like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and more.
Boosts coverage: Great for teams without dedicated QA testers - Keploy ensures nothing slips through the cracks.
If you're looking for smarter, faster, and effortless testing, Keploy is an absolute must-try.
Keploy Product:
-
Captures actual API calls
Produces YAML-based test cases and mocks
Automates running tests
-
Interoperates with Python, Go, Java, and others
Easy API to record and play back test cases
-
Central dashboard for test and mock management
Real-time insights into coverage, failures, and CI runs
Collaboration tools for devs and QA teams
Keploy Chrome Extension
Tracks API calls made by your browser when active.
Single-click setup for test and mock.
Exports to Keploy Cloud for easy centralization of tests.
Keploy VS Code Extension
Execute unit and API tests from your IDE automatically.
Making use of code context and AI to deliver right and correct test cases.
Best fit for scaling test coverage with least effort.
Keploy GitHub PR Agent
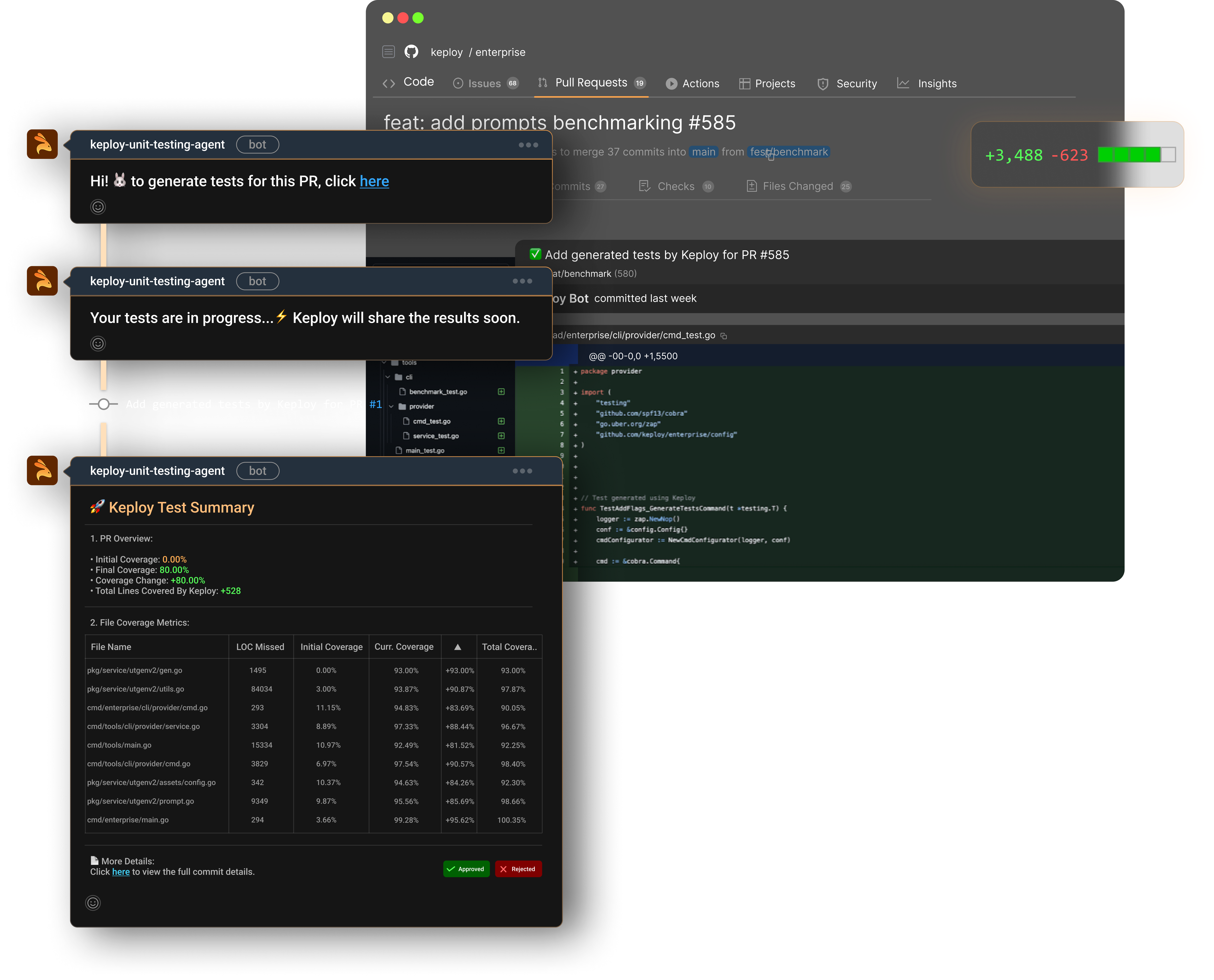
Automatically attempts pull requests and creates associated test cases out of it.
Reports test coverage in-line within the PR discussion.
Makes teams able to review code changes confidently and never think about skipping testing.
Automated API Testing
Records live traffic well and replays it as tests in CI runs.
Less manual test writings and coverage automation.
Best for teams that must test at scale without decreasing development speed.
Keploy Use Cases
1.Non-Documented or Legacy API Testing
Keploy records and tests actual traffic, even for non-documented - ideal for legacy or high-speed services.
2.Fast CI/CD Pipelines Where Tests Are Often Skipped
Auto test cases so nothing breaks - even when manual tests aren't written by teams.
3.Production Issue Debugging with Traffic Replay
Replay actual production requests to give feedback and correct issues in real time without the need to guess.
4.Support Small Teams Without QA Engineers
Developers can simply write, execute, and retain tests about - team-based quality assurance and efficient.
2. Selenium – Web Automation Champion
Selenium is one of the most popular open-source tools for automating web browsers. It supports multiple programming languages (Java, Python, C#, etc.) and works across all major browsers.
Ideal for: End-to-end UI testing of web applications
Supports parallel test execution
Works with Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and more
3. Jest – JavaScript Testing Made Simple
Created by Facebook, Jest is a delightful JavaScript testing framework, mainly used with React and Node.js apps.
Ideal for: Unit testing in modern JavaScript projects
Fast and reliable test execution
Built-in code coverage reports
4. Postman – API Testing & Monitoring
Postman is a powerful platform for testing, documenting, and monitoring APIs.
Send HTTP requests, inspect responses, and validate outputs
Organize requests into collections for better testing workflows
Monitor APIs in real-time
5. JUnit – Java Developer’s Testing Toolkit
JUnit is a widely-used unit testing framework for Java that simplifies writing and running repeatable tests.
Ideal for: Java applications (unit and integration tests)
Easily integrated with build tools like Maven and Gradle
Supports test automation in CI pipelines
6. TestRail – Test Management Master
TestRail is a comprehensive test case management tool that helps QA teams track, organize, and analyze their testing efforts.
Centralized platform for managing test cases
Analytics dashboards to monitor progress
Integrates with JIRA, Selenium, Jenkins, and others
7. JMeter – Load & Performance Powerhouse
Apache JMeter is used to test the performance and scalability of web applications.
Simulates heavy user loads to find performance bottlenecks
Generates detailed performance graphs and stats
Supports API and database load testing
8. Cypress – Modern Frontend E2E Testing
Cypress is a fast, modern testing framework for building robust end-to-end tests for web apps.
Blazing fast and highly interactive
Built-in time travel and DOM snapshots
Developer-friendly for frontend engineers
9. BrowserStack – Real Device Cloud Testing
BrowserStack allows you to test your web or mobile app across real browsers and devices, ensuring cross-browser compatibility.
Access real iOS and Android devices
Test on 3000+ browser/OS combinations
No need for local infrastructure
10. Appium – Mobile Test Automation Expert
Appium is an open-source tool that lets you automate native, hybrid, and mobile web apps on both Android and iOS platforms.
Supports all major mobile platforms
Write tests using common programming languages
Reuse tests across different platforms
Recommended Blogs on APIs
1. What Is Component Testing?
Discover how to test individual components of your application individually. Component testing ensures every component works as expected before merging it into the whole system.
2. Cross Browser Testing: A Complete Guide
Discover how to have your application up and running with multiple browsers and devices. Cross-browser testing detects layout and functional bugs early on, improving user experience on all fronts.
3. Automating Test Case Generation for Quick API Testing
Automatic test case generation techniques and tools for reducing the overhead of manual testing are covered in this article. It explains how AI and dynamic analysis can generate more effective tests for REST APIs.
4. Ad Hoc Testing: A Quick Guide To Finding Hidden Bugs
Watch how impromptu, ad hoc testing reveals latent defects. Ad hoc testing is fast, flexible, and perfect for revealing sneak-up-on-you bugs and edge conditions.
Conclusion
Quality Assurance (QA) isn't something that gets checked off in the development process - it's a way of thinking that prioritizes product quality from day one. With the speed of development today, it can all come down to the right tools. That's where Keploy is here to help - by automatically generating test cases and mocks from actual user traffic, it lets teams catch problems early, test quicker, and ship with confidence.
Whether you're a small new company releasing your initial product or a big company with intricate systems, a good QA process can be what gets you through. It saves time and money, and best of all, it guarantees your users a smooth and trustworthy experience. Ultimately, good QA is not really about fewer bugs - it's about establishing trust, release by release.
FAQs
1. Why is Keploy revolutionary?
Because it creates test and mocks automatically from live user traffic, which reduces manual work considerably. QA becomes a cakewalk even for high-speed development teams.
2. What is the ultimate goal of QA Testing?
To make the final product defect-free and meet functional as well as business requirements. It puts high standards of quality throughout the software cycle.
3. Is QA different from software testing?
Yes! QA is everything about process, standard, and methodology improvement in development. Testing is everything about defect detection in the live software product.
4. Can QA testing automatable?
Absolutely. Tools like Keploy, Selenium, and Cypress allow you to automate many QA tasks efficiently.Yes. Using Keploy, Selenium, and Cypress tools, the teams can automate repetitive test cases. It saves time and gives consistent results with reproducible test coverage.
5. What are the most prominent tools for QA in 2025?
Keploy, Postman, Cypress, and JMeter lead the 2025 list because they provide high performance, support for automation, and ease of integration. They are friendly with existing development and CI/CD practices.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ayush Gupta directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ayush Gupta
Ayush Gupta
Open Source enthusiast with knowledge of DevOps tools.