Letting AI Narrate My Past: A Telegram Bot with Google Drive and GenAI Magic
 Atharva Sharma
Atharva SharmaOverview
In the age of cloud storage and AI, our digital memories often remain buried in folders, rarely revisited or shared meaningfully. This project bridges that gap by combining the capabilities of the Google Drive API, Generative AI, and Telegram Bot API to create a personal assistant that not only surfaces photos from your Google Drive but also generates thoughtful, human-like captions for them.
The assistant is designed to automatically pull a random image from a specified Google Drive folder every 24 hours (with modifiable frequency) and send it to a Telegram group. Each photo is accompanied by an AI-generated caption that attempts to interpret or narrate the memory behind the image in a relatable and engaging way.
Architecture
We make use of the following AWS services to implement this assistant:
Lambda: AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your function, and Lambda automatically scales and executes it in response to events such as HTTP requests, file uploads, or scheduled triggers. You only pay for the compute time your code consumes, making it a cost-effective and scalable way to build backend logic or automation tasks.
AWS Lambda is the preferred compute choice for this project because the assistant doesn’t need to run continuously. It only needs to execute once every 24 hours (or at a defined frequency). With Lambda’s serverless model, we can trigger the function on a schedule without worrying about server uptime or manual scaling. This makes it highly efficient and cost-effective, as we only pay when the code runs.Event Bridge: Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that makes it easy to connect and trigger actions based on time-based schedules or events from AWS services. In this project, EventBridge is used to invoke the Lambda function every 24 hours, acting like a cloud-based cron scheduler. It’s reliable, scalable, and requires no infrastructure management—perfect for automating periodic tasks.
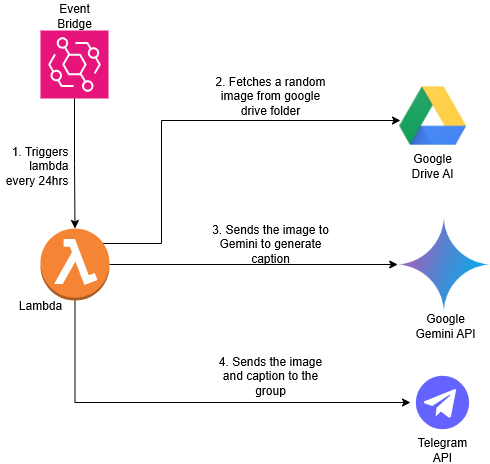
Setting Up AWS Lambda and EventBridge
Step 1: Create the Lambda Function
Go to the AWS Lambda Console.
Click “Create function”.
Choose:
Author from scratch
Function name:
MemoryBotFunction(or your preferred name)Runtime: Choose your language (e.g., Python 3.x or Node.js)
Click Create Function.
Step 2: Create a Scheduled Rule in EventBridge
Go to the Amazon EventBridge Console.
Click "Create rule".
Enter:
Name:
DailyMemoryBotTriggerDescription: “Triggers Lambda every 24 hours”
Event bus: Leave as
defaultRule type: Choose “Schedule”
Under Schedule pattern:
Select “Rate expression”
Example:
rate(1 day)for once every 24 hours
(You can modify this torate(6 hours),cron(0 8 * * ? *), etc.)
In Target:
Choose Lambda function
Select your Lambda (
MemoryBotFunction)
Click Next, then Create Rule.
Integrating with Google Drive
Step 1: Create a Google Cloud Project and Enable Drive API
Go to the Google Cloud Console.
Click Select a project → New Project.
Enter a project name (e.g.,
MemoryBotProject) and click Create.Navigate to APIs & Services → Library.
Search for Google Drive API and click Enable.
Step 2: Set Up OAuth 2.0 Credentials
In the Cloud Console, go to APIs & Services → Credentials.
Click Create Credentials → OAuth client ID.
Configure the OAuth consent screen if prompted.
Choose Application type:
- For a backend app, select Web application.
Add authorized redirect URIs if needed (for OAuth flow).
Click Create and download the
credentials.jsonfile.
Intregrating with Gemini API
Step 1: Get Access to Gemini API
Sign up or log in to the [Google AI studio] (https://aistudio.google.com) .
Create a new API key or obtain your access credentials (API key, client ID, secret, etc.).
Make sure to securely store these credentials.
Intregrating with Telegram API
Step 1: Create a Telegram Bot
Open Telegram and search for BotFather.
Start a chat with BotFather and send the command
/newbot.Follow the prompts to:
Name your bot.
Choose a unique username ending with
bot(e.g.,MemoryBot).
After creation, BotFather will provide a bot token. Save this token securely — you will need it to access the Telegram Bot API.
Step 2: Get your group ChatId
Add your bot to the group or start a private chat with it.
Send any message in that chat (or group).
Open this URL in your browser (replace
<YOUR_BOT_TOKEN>with your bot token):https://api.telegram.org/bot<YOUR_BOT_TOKEN>/getUpdatesLook for the
"chat":{"id":...}field in the JSON response — that number is your chat ID.
###It's time to write code!
Add the following code to the lambda by navigating to the code tab in lambda console. Make sure to replace the systemPrompt with context for your bot.
const { GoogleGenerativeAI } = require('@google/generative-ai');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const { google } = require('googleapis');
const TelegramBot = require('node-telegram-bot-api');
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const botToken = process.env.TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN;
const chatId = process.env.CHAT_ID;
const geminiApiKey = process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY;
const bot = new TelegramBot(botToken, { polling: false });
const SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly'];
const credentialsPath = '/tmp/credentials.json';
const rootFolderId = process.env.GOOGLE_DRIVE_FOLDER_ID;
const credentials = JSON.parse(process.env.GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS_JSON);
fs.writeFileSync(credentialsPath, JSON.stringify(credentials));
async function authenticateGoogleDrive() {
const auth = new google.auth.GoogleAuth({
keyFile: credentialsPath,
scopes: SCOPES,
});
return google.drive({ version: 'v3', auth });
}
async function getSubfolders(drive, parentFolderId) {
const res = await drive.files.list({
q: `'${parentFolderId}' in parents and mimeType = 'application/vnd.google-apps.folder' and name != 'videos' and name != 'Bannerghatta'`,
fields: 'files(id, name)',
});
return res.data.files;
}
async function getImagesFromFolder(drive, folderId) {
const res = await drive.files.list({
q: `'${folderId}' in parents and mimeType contains 'image/'`,
fields: 'files(id, name, mimeType)',
});
return res.data.files;
}
async function downloadFile(drive, fileId, filePath) {
const dest = fs.createWriteStream(filePath);
await drive.files.get({ fileId, alt: 'media' }, { responseType: 'stream' })
.then(res => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
res.data
.on('end', () => resolve())
.on('error', err => reject(err))
.pipe(dest);
});
});
}
async function generateCaptionWithGemini(imagePath) {
const genAI = new GoogleGenerativeAI(geminiApiKey);
const model = genAI.getGenerativeModel({ model: "gemini-1.5-flash" });
const imageBuffer = fs.readFileSync(imagePath);
const imageData = {
inlineData: {
data: imageBuffer.toString('base64'),
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
}
};
// Add your prompt here
const systemPrompt = ""
const result = await model.generateContent([
{ text: systemPrompt},
imageData,
{ text: "Give a short and warm caption for this photo."},
]);
const response = await result.response;
const caption = response.text();
return caption;
}
async function sendRandomImage() {
try {
const drive = await authenticateGoogleDrive();
const folders = await getSubfolders(drive, rootFolderId);
if (folders.length === 0) {
console.log('No folders found.');
return;
}
let selectedImage = null;
while (!selectedImage) {
const randomFolder = folders[Math.floor(Math.random() * folders.length)];
console.log(`Selected folder: ${randomFolder.name}`);
const images = await getImagesFromFolder(drive, randomFolder.id);
if (images.length === 0) {
console.log(`No images found in folder: ${randomFolder.name}`);
continue;
}
selectedImage = images[Math.floor(Math.random() * images.length)];
if (selectedImage.mimeType.startsWith('video/')) {
console.log(`Skipping video: ${selectedImage.name}`);
selectedImage = null;
}
}
const filePath = path.join('/tmp', selectedImage.name);
await downloadFile(drive, selectedImage.id, filePath);
const caption = await generateCaptionWithGemini(filePath);
await bot.sendPhoto(chatId, filePath, { caption });
console.log(`Sent image with caption: ${caption}`);
fs.unlinkSync(filePath);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending image:', error);
}
}
await sendRandomImage();
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify('Image sent successfully!'),
};
};
Add the following code to package.json:
{
"name": "your-project-name",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"@google/generative-ai": "^0.24.1",
"dotenv": "^16.4.5",
"googleapis": "^140.0.1",
"node-telegram-bot-api": "^0.66.0"
}
}
Add envrionment variables
This is the final step where we add all the environment variables required for our app to function.
Navigate to: Configuration -> Environment Variables from the AWS console and add the following environment variables:
CHAT_ID- Chat Id received in this stepGEMINI_API_KEY- Gemini API key generated in this stepGOOGLE_CREDENTIALS_JSON- Content of the JSON file downloaded in this stepGOOGLE_DRIVE_FOLDER_ID- Open the google drive folder you want to fetch memories from. The part after/folders/in the URL is the folder IDTELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN- Telegram BOT token generated in this step
Conclusion
Building a Telegram bot that seamlessly integrates Google Drive and Gemini AI to share personalized memories is a powerful way to combine cloud storage, AI, and messaging platforms. By leveraging AWS Lambda and EventBridge, you can automate the process efficiently without keeping the bot running 24/7.
This project not only showcases how APIs can work together to create unique user experiences but also provides a solid foundation to explore more advanced AI-powered automation.
Feel free to customize the bot’s frequency, add more AI capabilities, or expand it to other platforms. The possibilities are endless!
Happy coding and memory sharing! 🚀
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Atharva Sharma directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
