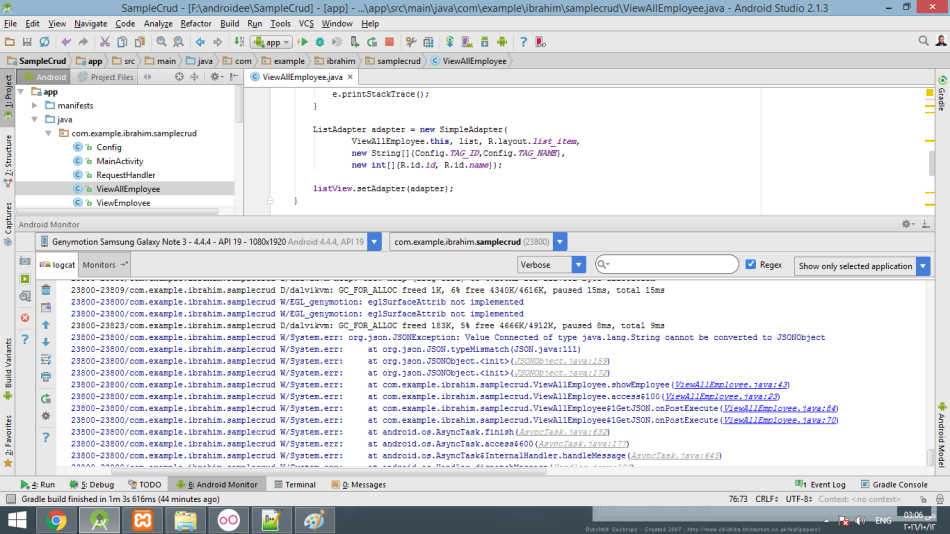
Why ‘String Cannot Be Converted to JSONObject’ Occurs and How to Fix It
 Tuanhdotnet
Tuanhdotnet5 min read
1. Understanding the Error: What Does It Mean?
When Java processes JSON data using libraries like org.json or Gson, it requires the input to follow strict JSON formatting. The error String cannot be converted to JSONObject indicates that the application attempted to parse a string as a JSON object, but the string failed to meet the JSON structure requirements.
1.1 Basic Definition of JSONObject
A JSONObject in Java represents a JSON object. For example:
{
"key": "value",
"anotherKey": 42
}
This structure contains key-value pairs, which JSONObject can easily process. If the input string is missing required syntax, such as braces {} or is malformed, Java throws this error.
1.2 Common Causes
- The string is not in valid JSON format (e.g., a plain string instead of JSON).
- The string contains additional characters, such as a newline or whitespace, that prevent parsing.
- The API response is unexpected, such as returning XML or plain text instead of JSON.
- Improper encoding or decoding during transmission.
2. Resolving the Issue with Practical Examples
Let's address how to debug and fix this issue in Java. Each method below includes an example and a detailed explanation.
2.1 Validate the Input String
Before attempting to parse, ensure the string is valid JSON. Using a validation library or method helps avoid unnecessary exceptions.
Code Example:
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class JsonValidator {
public static boolean isValidJson(String json) {
try {
new JSONObject(json);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "{ "name": "Tuan Anh", "age": 30 }";
if (isValidJson(input)) {
System.out.println("Valid JSON: " + input);
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid JSON");
}
}
}
Explanation:
- This code checks whether a given string is valid JSON.
- If the string is invalid, you can handle it gracefully instead of letting the application crash.
2.2 Handle Unexpected API Responses
Sometimes, the error occurs because the string comes from an API that doesn’t consistently return JSON. For example, an error response might be plain text.
Code Example:
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class ApiResponseHandler {
public static void processResponse(String response) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(response);
System.out.println("Parsed JSON: " + jsonObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Invalid response format: " + response);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String apiResponse = "<html>Error 404: Not Found</html>"; // Simulated API response
processResponse(apiResponse);
}
}
Explanation:
- This code demonstrates how to safeguard against non-JSON responses from APIs.
- By wrapping the parsing operation in a try-catch block, it catches exceptions and logs invalid data.
2.3 Strip Unnecessary Characters
Sometimes, strings contain unwanted characters such as whitespace or escape sequences. Stripping these can help.
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class JsonCleaner {
public static String cleanJsonString(String input) {
return input.trim(); // Removes leading and trailing whitespace
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String rawInput = " {"key":"value"} ";
String cleanedInput = cleanJsonString(rawInput);
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(cleanedInput);
System.out.println("Cleaned and Parsed JSON: " + jsonObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error parsing JSON");
}
}
}
Explanation:
- This solution trims unnecessary spaces or characters from the string before parsing.
- It’s particularly useful when dealing with inconsistent input formats.
3. Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Always Validate API Responses
Use libraries such as Jackson or org.json to handle JSON, but always validate the response to ensure it adheres to expected formats.
Monitor Encoding Issues
Encoding problems, especially when transferring data between systems, often cause malformed JSON. Double-check encoding standards (e.g., UTF-8).
Use a Robust JSON Library
For better error handling and more advanced features, consider using Gson or Jackson. These libraries provide better utilities for working with JSON.
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParser;
public class GsonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonString = "{ "name": "Tuan Anh", "role": "Developer" }";
try {
JsonObject jsonObject = JsonParser.parseString(jsonString).getAsJsonObject();
System.out.println("Parsed with Gson: " + jsonObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Failed to parse JSON");
}
}
}
4. Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Relying on Assumptions
Avoid assuming all inputs are correctly formatted. Always validate inputs before parsing.
Ignoring Exception Details
Exception messages often reveal why parsing fails. For example, an error might indicate that a specific key is missing or malformed.
Skipping API Documentation
Ensure the API's documentation specifies its response format. If not, handle all possible cases (e.g., JSON, plain text, or XML).
5. Conclusion
Handling the String cannot be converted to JSONObject error requires understanding JSON structures, validating inputs, and preparing for unexpected data. With proper preventive measures and robust error handling, you can ensure your application processes JSON data reliably. Have you faced challenges with JSON parsing in Java? Feel free to share your questions or experiences in the comments below!
Read more at : Why ‘String Cannot Be Converted to JSONObject’ Occurs and How to Fix It
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tuanhdotnet directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tuanhdotnet
Tuanhdotnet
I am Tuanh.net. As of 2024, I have accumulated 8 years of experience in backend programming. I am delighted to connect and share my knowledge with everyone.