Tunnelmole: An Open Source Tunneling Tool for Secure and Easy Access
 Robbie Cahill
Robbie Cahill
Tunnelmole: An Open Source Tunneling Tool for Secure and Easy Access
In modern software development, the need to expose a local development server to the public internet is a common and often challenging task. Whether you're testing webhooks, sharing a demo with a client, or debugging a mobile application, you need a reliable way to create a secure bridge from a public URL to your localhost. This is where a tunneling tool becomes an indispensable part of a developer's toolkit.
A tunneling tool creates a secure, outbound connection from your local machine to a remote server, which then proxies public traffic back to your local application. This bypasses the need for complex network configurations like port forwarding, static IP addresses, or firewall rule changes.
This article introduces Tunnelmole, a powerful, open-source tunneling tool designed with developers in mind. We'll explore what it is, its most common use cases, how it works under the hood, and how you can get it up and running in minutes.
What is a Tunneling Tool?
A tunneling tool, at its core, establishes a secure "tunnel" that allows external network traffic to reach a service running on a private network, such as your local development machine. Imagine it as a private, secure hallway that connects a public-facing door (a public URL) directly to your local application's front door (e.g., localhost:3000).
Key characteristics of a tunneling tool include:
- Public URL Generation: It provides a temporary or permanent public HTTPS URL (e.g.,
https://example.tunnelmole.net). - Traffic Forwarding: It captures all requests sent to this public URL and forwards them to a specified
localhostport on your machine. - Security: The connection between your local machine and the public server is encrypted, typically using HTTPS, ensuring that the data in transit is secure.
- NAT and Firewall Traversal: It works without requiring any changes to your router or firewall because it initiates an outbound connection, which is generally permitted by network security policies.
Introducing Tunnelmole: The Open Source Tunneling Tool
Tunnelmole is a simple yet robust tunneling tool that provides all the core functionality developers need to expose local servers securely. It's built with a strong emphasis on simplicity, open-source principles, and flexibility.
As a native NodeJS application, Tunnelmole is lightweight and platform-independent, running seamlessly on Windows, macOS, and Linux. The core philosophy behind Tunnelmole is to provide an essential service that "just works" out of the box, with options for advanced users who require more control.
One of the most significant advantages of Tunnelmole is its commitment to transparency. Both the client and the server are fully open source, which offers several key benefits:
- Trust and Security: You can inspect the source code yourself to understand exactly what the tool is doing with your data. There are no hidden operations or proprietary black boxes.
- Flexibility and Self-Hosting: While Tunnelmole offers a convenient hosted service, you have the freedom to host the tunneling server on your own infrastructure. This gives you complete control over your data, security, and domain naming.
- Community Contribution: Being open source means the community can contribute to its development, report issues, and add new features, fostering a collaborative and robust ecosystem.
How Tunnelmole Works
The architecture of Tunnelmole is designed for efficiency and reliability. The process involves a client running on your local machine and a remote server that manages public traffic.
Here is a high-level overview of the process:
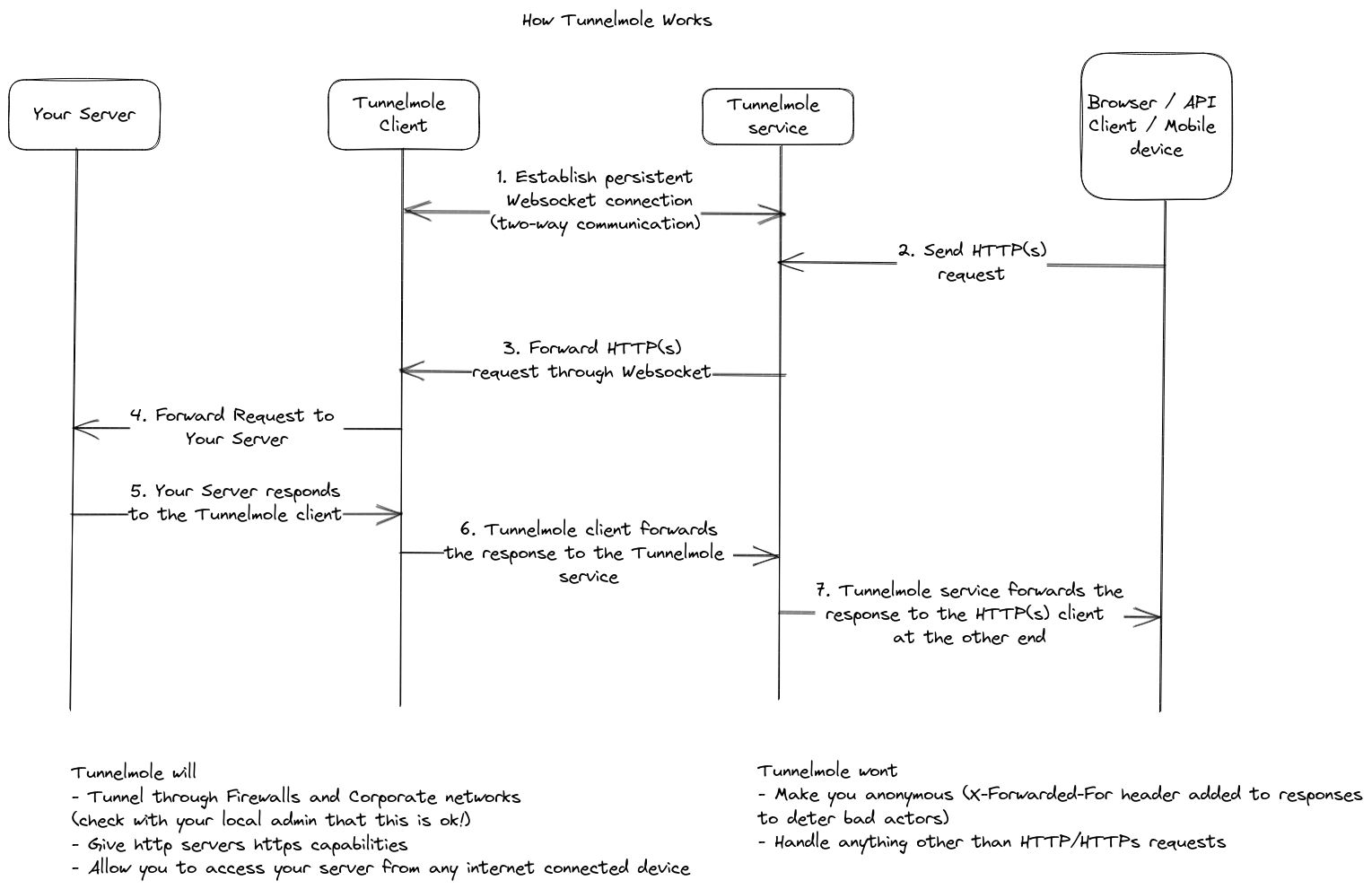
- Initiate Connection: When you run the
tmolecommand on your machine (e.g.,tmole 8080), the Tunnelmole client establishes a secure, persistent connection to the Tunnelmole service host. - Receive Public URL: The Tunnelmole service registers your connection and assigns a unique public URL. It sends this URL back to the client, which displays it in your terminal.
- Receive Public Request: When an external service (like a browser, API client, or webhook provider) sends an HTTP request to your public URL, the request first hits the Tunnelmole service host.
- Forward Request via Tunnel: The service host relays this incoming request through the established tunnel to the Tunnelmole client running on your machine.
- Forward to Local Server: The client receives the request and forwards it to your local web server running on the specified port (e.g.,
http://localhost:8080). - Return Response: Your local application processes the request and sends the response back to the Tunnelmole client. The client then sends this response back through the tunnel to the service host, which, in turn, delivers it to the original requester.
Key Use Cases for a Tunneling Tool
A versatile tunneling tool like Tunnelmole can dramatically boost productivity across various development scenarios.
1. Developing and Testing Webhooks
Webhooks are a cornerstone of modern application integration. Services like Stripe, Shopify, GitHub, and Slack send real-time notifications to a "webhook URL" when certain events occur. For these services to reach your application, the URL must be public and accessible over HTTPS.
Using a tunneling tool is the standard practice for local webhook development. Instead of deploying your code to a staging server for every change, you can run tmole 3000 to get a public HTTPS URL and provide it to the webhook provider. You can then set breakpoints in your local IDE, trigger the webhook, and debug the request live as it hits your machine.
2. Live Mobile App Testing
When developing a mobile app that communicates with a backend API, it's far better to test on a real device than an emulator. Emulators can't replicate real-world network conditions, device-specific quirks, or hardware features.
By using a tunneling tool to expose your local backend API, your mobile device can make requests directly to your development machine over the internet. This allows for rapid iteration—make a change to your API, save the file, and immediately test the result on your phone without a redeployment cycle.
3. Sharing Demos with Clients and Colleagues
Have you ever wanted to show a work-in-progress to a client or a product manager without the hassle of a full deployment? A tunneling tool makes this incredibly simple. Just start your local server, run Tunnelmole to get a public URL, and share the link. Your stakeholders can view the live, running application directly from your machine.
This is perfect for agile sprints, user-acceptance testing (UAT), and quick feedback loops.
4. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
Ensuring your web application looks and functions correctly across different devices and operating systems is crucial. With a public URL from Tunnelmole, you can easily open your local site on any device connected to the internet—a different laptop, a tablet, or a friend's computer. This simplifies testing responsive designs and identifying device-specific bugs.
Getting Started with Tunnelmole
Installing and using Tunnelmole is designed to be as straightforward as possible.
Installation
If you have NodeJS (v16.10 or later) installed, the quickest way to get started is by installing Tunnelmole globally via npm:
sudo npm install -g tunnelmole
For users who prefer not to install NodeJS or want a pre-compiled binary, you can use a simple install script for Linux and macOS:
curl -O https://install.tunnelmole.com/xD345/install && sudo bash install
Windows users can download the tmole.exe executable directly from the Tunnelmole website and add it to their system's PATH.
Basic Usage
Using Tunnelmole is a one-step process.
- Start your local web application and take note of its port number (e.g.,
3000,8000,8080). - Open your terminal and run the
tmolecommand followed by the port number.
For example, if your application is running on port 8080, you would run:
tmole 8080
Tunnelmole will connect to the service and print your public URLs:
Your Tunnelmole Public URLs are below and are accessible internet wide. Always use HTTPs for the best security
https://cqcu2t-ip-49-185-26-79.tunnelmole.net ⟶ http://localhost:8080
http://cqcu2t-ip-49-185-26-79.tunnelmole.net ⟶ http://localhost:8080
You can now use the https:// URL in your webhook settings, mobile app, or share it with anyone. All traffic will be securely tunneled to your local server.
Using a Custom Subdomain
For more stable testing environments, you might need a URL that doesn't change every time you start the tool. Tunnelmole supports custom subdomains. If you are using the hosted service, this is a paid feature. Alternatively, if you self-host the Tunnelmole service, you can configure custom domains yourself.
To use a custom subdomain with the CLI, the syntax is:
tmole 8080 as my-cool-app.tunnelmole.net
Programmatic Usage with NodeJS/TypeScript
Tunnelmole can also be integrated directly into your NodeJS projects as an NPM module. This is useful for automating your development workflow.
First, install it as a project dependency:
npm install --save tunnelmole
Then, you can import and run it in your code:
import { tunnelmole } from 'tunnelmole';
// This will start the tunnel and return the public URL
const url = await tunnelmole({
port: 3000
});
console.log(`My app is now public at: ${url}`);
// Example output: My app is now public at: https://idsq6j-ip-157-211-195-169.tunnelmole.net
This approach is perfect for including in npm scripts to start your app and create a public tunnel with a single command.
Self-Hosting: The Ultimate Flexibility
For organizations with strict data privacy requirements or those who want full control over their infrastructure, Tunnelmole's self-hosting capability is a standout feature. Since the Tunnelmole service is also open source, you can deploy it to any server or cloud environment.
Self-hosting provides:
- Complete Data Sovereignty: No traffic ever leaves your own infrastructure.
- Custom Domain Names: Use your own domains and subdomains for your tunnels.
- Unlimited Usage: Avoid any potential rate limits or restrictions of a public service.
- Enhanced Security: Integrate the service directly into your existing security and monitoring infrastructure.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Modern Developers
A reliable tunneling tool is no longer a "nice-to-have"—it's an essential component of an efficient, modern development workflow. It bridges the gap between local development and the public internet, enabling rapid iteration, effective collaboration, and realistic testing.
Tunnelmole stands out as a powerful option in this space due to its simplicity, performance, and unwavering commitment to open-source principles. Whether you need a quick public URL for a single debugging session or a self-hosted, production-grade tunneling solution, Tunnelmole provides the flexibility and control that developers demand.
Give it a try for your next project and experience how a dedicated tunneling tool can streamline your development process.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Robbie Cahill directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
