System Prompting - Types and Importance
 Abhishek Kumar
Abhishek KumarBackStory
So, Let’s start with the analogy of - What really is System Prompting
Analogy: Imagine you hire a chef. Before they start cooking, you tell them:“I want Italian food only.”
“No spicy ingredients.”
“Explain each step while cooking.”
That’s exactly what system prompting does - it guides how the AI should behave.
Why is it important
Okay, so we understood the analogy of system prompting . Now, lets see this diagram.

We have all heard about GIGO principle which states - Garbage In, Garbage Out .
This is applicable not only in the real life , but also in the programming world , and so in the Prompting World .
If you will give the bad prompting/ examples , how can you expect that the system will work well ?
Hence ,
System prompting is like giving AI a personality, style, or rulebook before asking it questions. Once you set it, every answer it gives will follow that guide.
Styles of Prompting
Plain or Direct Prompting- The simplest form: you just ask the model a question directly.
Example:
Explain love in simple words. Error 404 lolWorks, but the AI doesn’t have a “role” or strict structure, answers can vary in style, length, or tone.
Instruction-based Prompting (INST / Alpaca style)
Format:
Instruction -> Input -> ResponseOriginated with Alpaca, which adapted ideas from LLaMA and FLAN.
The AI is told exactly what to do, then given the input, then it writes the output.
Structure:
### Instruction: Explain the concept of photosynthesis. ### Input: N/A (or any extra context) ### Response:Use: Best for fine-tuning models to follow clear instructions.
You can read their article - https://crfm.stanford.edu/2023/03/13/alpaca.html
FLAN-style prompting
Used in FLAN-T5 and similar models.(Google)
Focused on instruction-following across a wide variety of tasks.
Often simpler than Alpaca, but same idea: give explicit instructions instead of vague questions.
Works great for zero-shot tasks (asking the model to do things without prior examples).
ChatML (Chat Markup Language)
Designed for chat-based models like GPT.
Adds roles like
system,user,assistant.Widely adopted by all .
Example:
[ {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Explain black holes simply."}, {"role": "assistant", "content": ""} {"role": "developers", "content": ""} {"role": "assistant", "content": ""} ]Why it exists: Helps the AI distinguish who is speaking, keeps conversation context clear, allows multi-turn dialogue naturally.
Types of Prompting
1. Zero-shot prompting
Idea: The model gets no examples - just instructions. It has to answer based on what it already knows.
Example:
Explain why the sky is blue.Use: Quick questions, tasks where you trust the model’s knowledge.
Analogy: You ask a stranger for directions without showing them a map.
2. Few-shot prompting
Idea: You give the model a few examples before asking the real question. This helps it understand the pattern.
Example:
Q: Capital of France? A: Paris Q: Capital of Germany? A: Berlin Q: Capital of Italy? A: Nahii pata bhaiiiii .lolUse: When you want the model to mimic a specific pattern or style.
Analogy: You show the stranger 2-3 maps first, so they understand how to read yours.

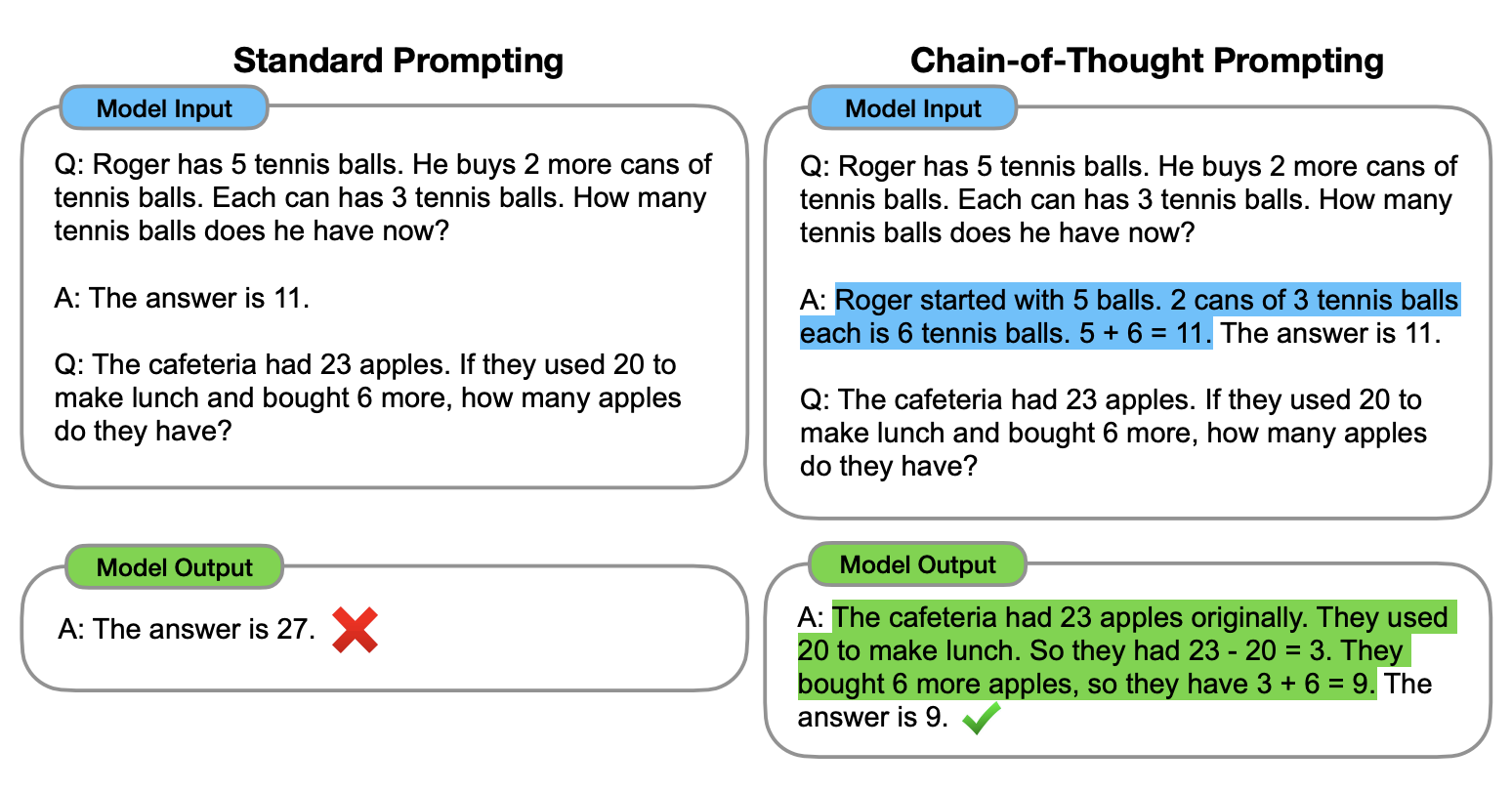
3. Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting
Idea: Ask the model to think step by step before answering. This improves reasoning.
(What you see the recent feature in CHATGPT/ DEEPSEEK - Think Longer) - It uses the same concept
Example:
Solve: 23 + 47 Explain step by step.Model might respond:
Step 1: Add 20 + 40 = 60 Step 2: Add 3 + 7 = 10 Step 3: 60 + 10 = 70Use: Math, logic, multi-step reasoning problems.
Analogy: You ask a student to show their work, not just give the answer.
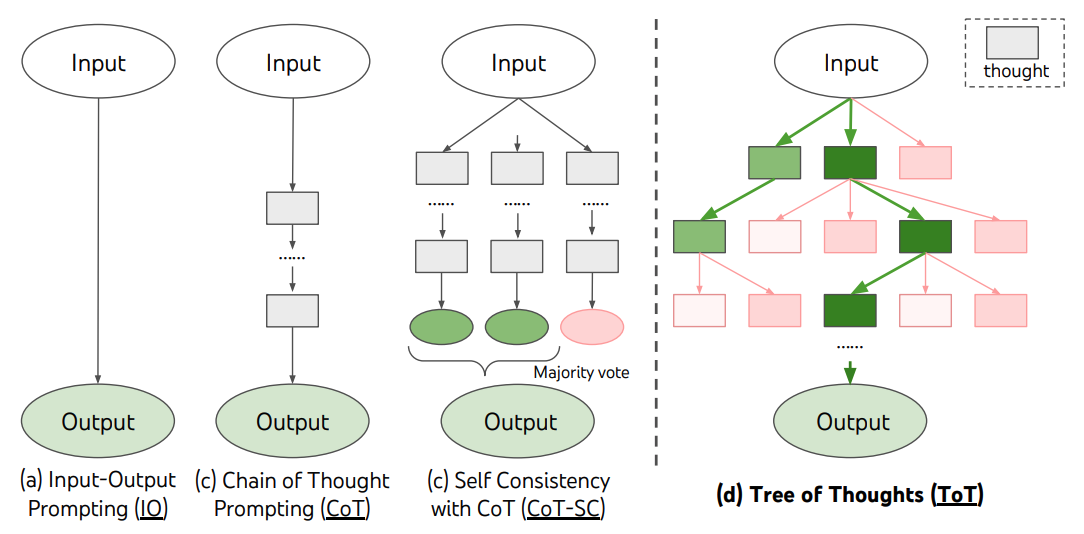
4. Self-Consistency prompting
Idea: Ask the model to generate multiple reasoning paths and pick the most consistent answer.
Example: For a tricky question:
What is the next number in the series: 2, 4, 8, 16, ?The model might generate multiple chains:
Chain 1: Multiply by 2 → 32
Chain 2: Add 2 → 18
Chain 3: Square previous → 256
Then it selects the answer that appears most consistent across chains → 32.
Use: Reduces mistakes, increases accuracy in complex tasks.
Analogy: Ask several experts independently and go with the majority answer.

So, in the end , I want to say that -
“Prompting isn’t about telling AI what to say . it’s about teaching it how to think, one question at a time.”
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Abhishek Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Abhishek Kumar
Abhishek Kumar
I have heart !