Creating Models in CoT Prompting
 Abhishek Kumar
Abhishek Kumar

1. Introduction : What is Chain of Thought?
Imagine asking a student, “What’s 47 × 23?” and they just blurt out “1081.” That’s a correct answer , but you have no idea how they got it.
Now imagine the same student says:
“47 × 23 means 47 × (20 + 3). First, 47 × 20 = 940. Then, 47 × 3 = 141. Adding them gives 1081.”
This second method - explaining the reasoning is Chain of Thought prompting for AI. You guide the model to think step-by-step, which often leads to better, more reliable answers.
2. Why Chain of Thought Works
From decades of studying both human cognition and AI behavior, I can tell you:
Humans reason sequentially - breaking problems into smaller steps reduces error.
AI models mimic patterns in data - when you ask for step-by-step thinking, you align the model’s output with structured reasoning patterns it has seen in training.
Reasoning reduces hallucination - forcing intermediate steps makes it harder for the model to “jump” to wrong conclusions.
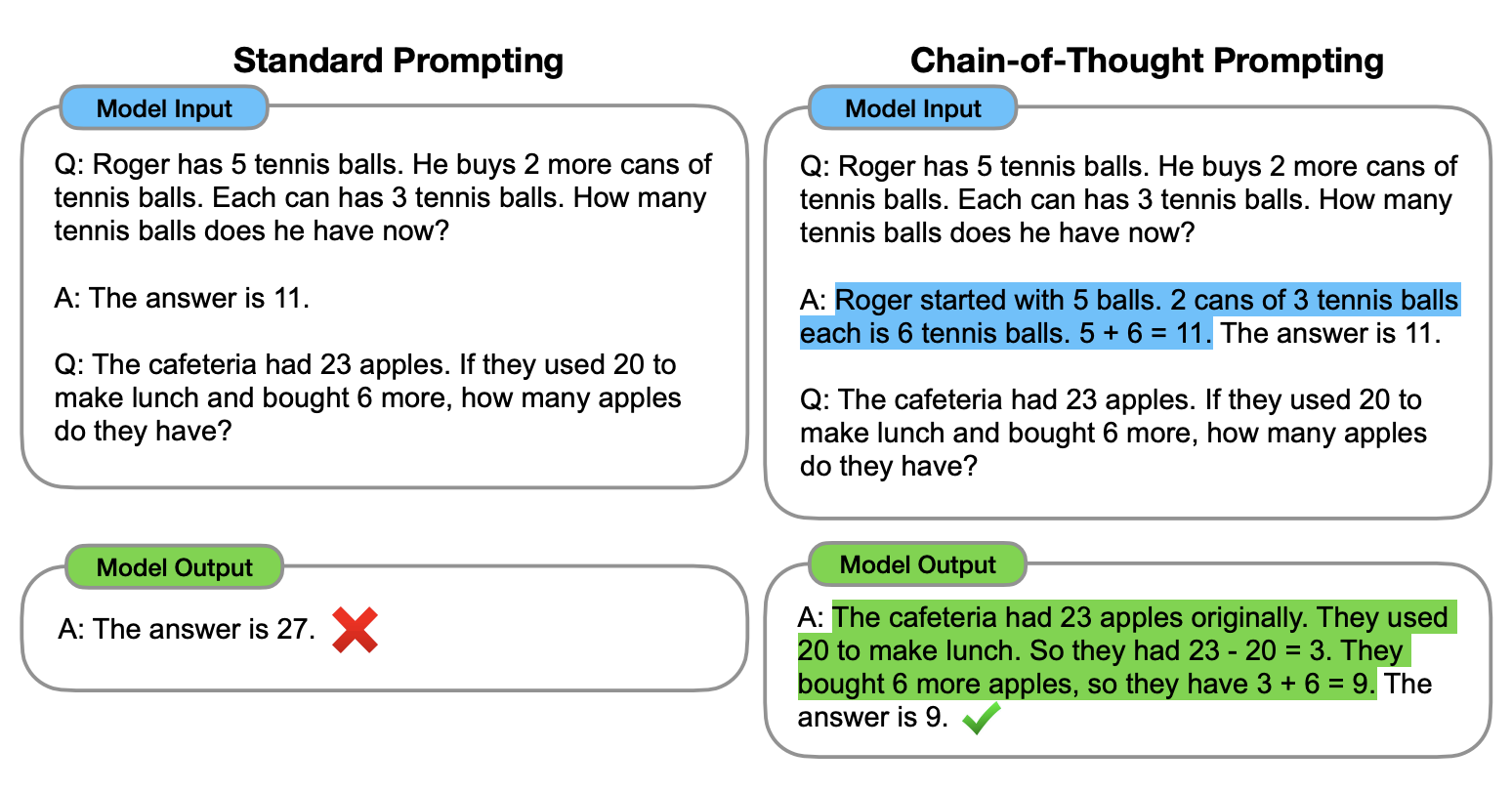
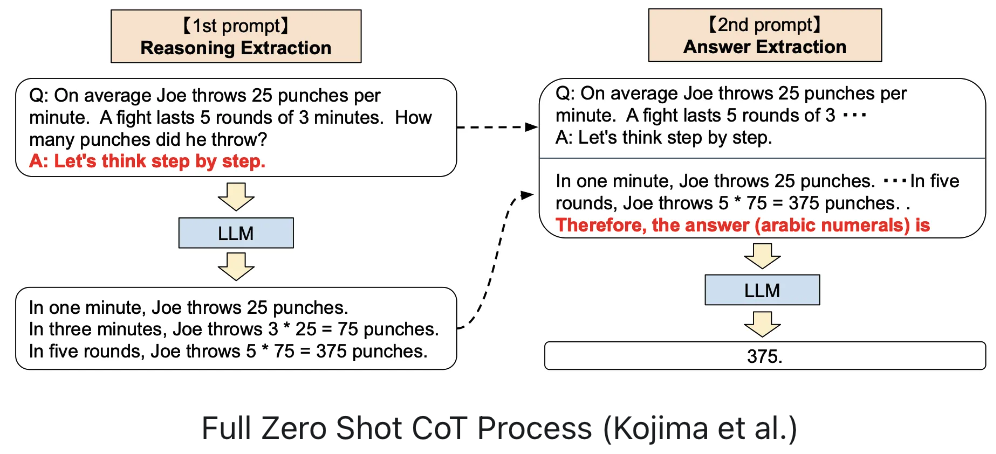
3. The Beginner’s Approach : Zero-shot CoT
Example:
Q: If it’s 3 PM now, what time will it be in 9 hours? Explain step-by-step.
Model:
Step 1: 3 PM + 9 hours = 12 hours later minus 3 hours.
Step 2: 3 PM + 12 hours = 3 AM.
Step 3: 3 AM - 3 hours = 12 AM (midnight).
Answer: 12 AM.
Key tip: Use phrases like
“Let’s think step by step.”
“Show your reasoning before the answer.”
4. Moving to Intermediate : Few-shot CoT
Here, you train the model in-context by giving examples of reasoning before the real question.
Example:
Q: 12 × 4
A: Step 1: 12 × 4 = (10 × 4) + (2 × 4) = 40 + 8 = 48.
Q: 15 × 3
A: Step 1: 15 × 3 = (10 × 3) + (5 × 3) = 30 + 15 = 45.
The model learns the “show steps, then answer” pattern.
5. Advanced Techniques
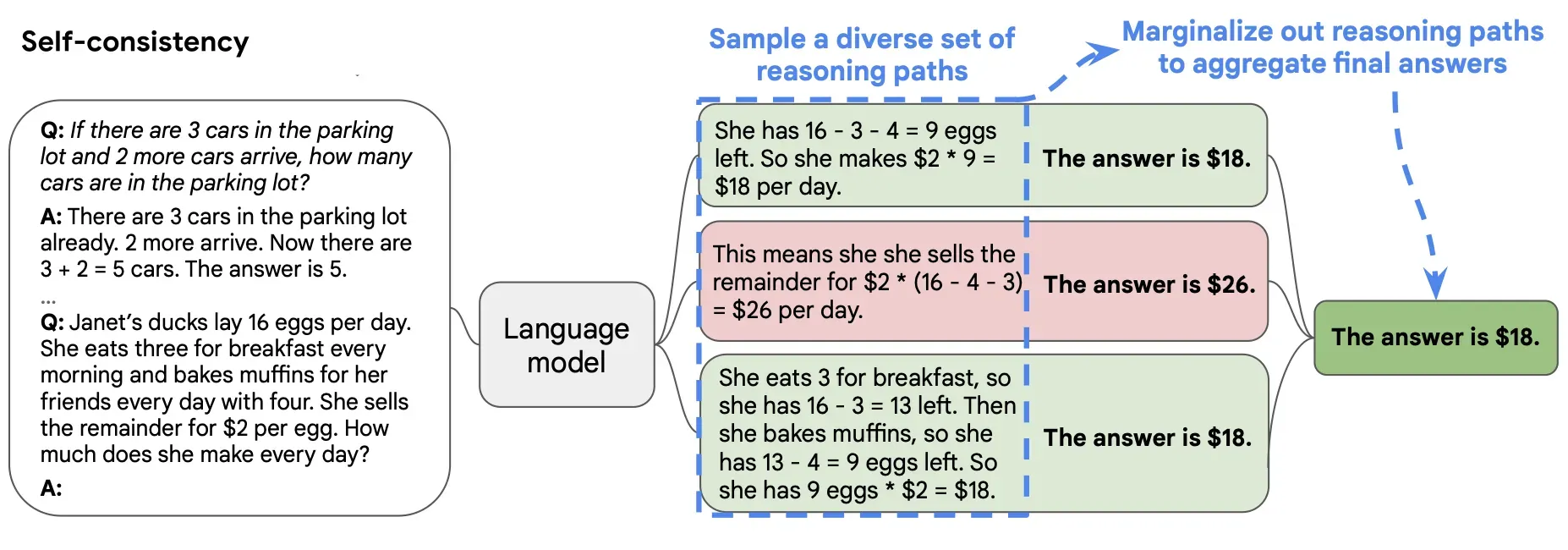
5.1. Self-Consistency + CoT
Instead of one chain of thought, generate multiple reasoning paths and pick the most common answer.
This drastically improves accuracy in math, logic, and reasoning-heavy tasks.
How to do it:
Generate 5 possible reasoning chains and pick the most consistent final answer.
The model will “vote” on the most common solution.
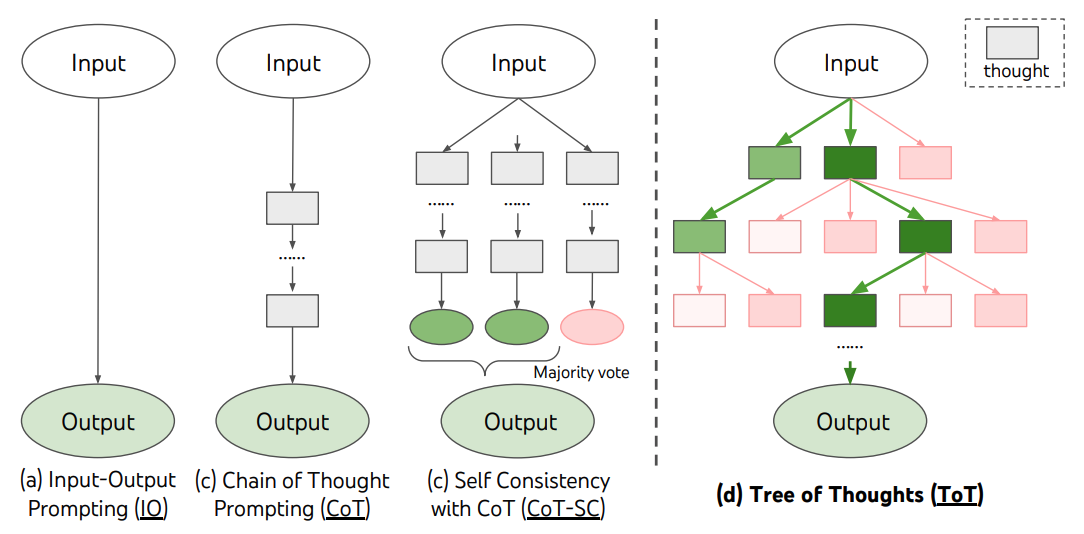
5.2. Tree of Thought (ToT)
A logical extension of CoT.
Instead of one linear chain, the AI explores multiple branches of reasoning , like a decision tree - before picking the best path.
Useful in planning, creative writing, game strategies.
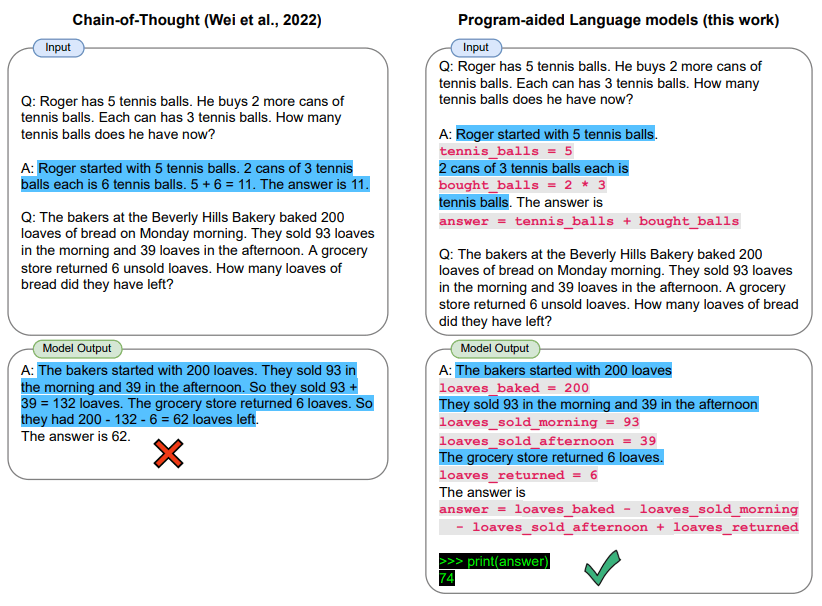
5.3. Program-aided CoT (PaCoT)
Combine CoT reasoning with code execution for calculations.
The model writes the reasoning, uses code to verify, then finalizes the answer.
Example: math problems, data analysis.
6. Real-world Analogy
Think of CoT like assembling IKEA furniture:
Without instructions (no CoT), you might get it right, but it’s a gamble.
With instructions (CoT), each piece fits, and the chance of success skyrockets.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Abhishek Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Abhishek Kumar
Abhishek Kumar
I have heart !