Top Benefits and Real-World Uses of Batch Processing
 Community Contribution
Community Contribution
Batch processing delivers significant value for enterprise IT environments in 2025. Over 78% of organizations still depend on batch processing, making it the most widely adopted among data processing methods. Batch processing enables companies to handle large-scale, repetitive, or scheduled workloads efficiently. Enterprises benefit from reduced operational costs, simplified management, and resource optimization.
Batch processing avoids the need for costly hardware upgrades.
It supports vertical and horizontal scaling, which suits massive data integration tasks.
Batch processing remains essential for organizations seeking reliability and cost-effectiveness in handling complex data operations.
Key Takeaways
Batch processing helps companies handle large data tasks efficiently, saving time and reducing costs.
It improves data accuracy by cleaning and validating information before use, which reduces errors.
Batch processing scales easily to manage growing workloads without losing performance.
Many industries like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing rely on batch processing for key operations.
Combining batch processing with real-time systems can balance cost savings and faster data insights.
Benefits of Batch Processing
High Throughput
Batch processing delivers exceptional throughput in large-scale data environments. Organizations rely on this method to process vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently. By grouping tasks and running them during off-peak hours, companies maximize resource utilization and reduce processing times. Automation further enhances throughput by minimizing manual intervention and errors.
Batch processing systems scale to handle growing data volumes without performance loss.
Scheduling tasks based on resource availability allows prioritization of urgent jobs.
Mainframes can process up to 30,000 transactions per second, demonstrating the high throughput capacity of modern batch systems.
Automation and continuous monitoring ensure consistent performance and rapid completion of jobs.
| Metric/Capability | Description |
| Scalability | Ability to handle massive data volumes; platforms like AWS Batch enable seamless distributed scaling |
| Resource Optimization | Efficient CPU and memory usage by grouping tasks into batches, preventing overloads |
| Automation and Scheduling | Jobs run automatically at scheduled times, reducing manual intervention |
| Continuous Performance Monitoring | Real-time insights into processing performance to identify bottlenecks and maintain efficiency |
| Throughput Example | Mainframes processing up to 30,000 transactions per second illustrating high throughput capacity |
Organizations measure throughput improvements by tracking batch processing time, resource utilization, and error rates. They use dashboards and monitoring tools to visualize these metrics and optimize performance. By placing counters and timers at critical points, teams capture accurate throughput data and identify bottlenecks.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most significant benefits of batch processing is its ability to reduce operational costs. Financial services and manufacturing sectors have reported substantial savings by adopting batch processing for routine and large-scale tasks.
| Sector | Batch Processing Applications | Cost Reduction / Efficiency Gains |
| Financial Services | Nightly transaction reconciliation, bulk payment processing, risk analysis reports | Processes over 1 million transactions per night; reduces manual errors by 74%; cuts reconciliation errors by 82%; achieves 40-60% cost reductions through optimized schedules and shared resources |
| Manufacturing | Production scheduling, inventory updates, quality control checks | Reduces energy costs by 40%; cuts production downtime by 37%; automates 90% of inventory updates; cloud-native batch architectures reduce infrastructure costs by 65%; AI-driven scheduling cuts processing times by 35% |
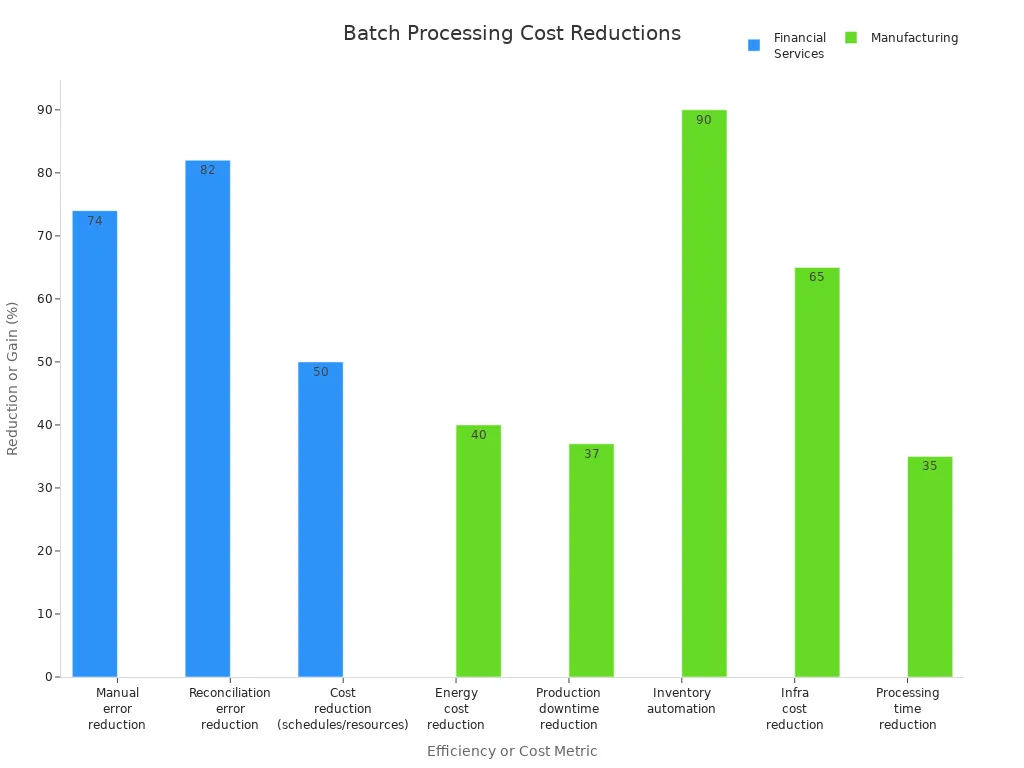
Batch processing allows organizations to schedule jobs during off-peak hours, which reduces the need for expensive hardware upgrades. By optimizing schedules and sharing resources, companies achieve significant cost reductions and improve overall efficiency.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Batch processing optimizes the use of computing resources by scheduling large jobs during periods of low demand. This approach prevents disruption to real-time business activities and reduces operational expenses.
Bulk processing enables more efficient use of memory, disk I/O, and network resources.
Batch jobs can run in the background, improving system performance during critical hours.
Predictable resource demand patterns allow for efficient allocation and cost savings, especially in cloud environments.
The simpler architecture of batch systems reduces maintenance and implementation complexity.
Batch processing creates consistent handling of entire datasets and robust error recovery mechanisms. Unlike streaming systems, which require continuous resource availability, batch processing leverages idle resources and minimizes unnecessary consumption.
Scalability
Scalability remains a core advantage of batch processing. Modern platforms, such as AWS Batch, support both vertical and horizontal scaling, allowing organizations to process massive datasets efficiently.
Event-driven automated scaling adjusts processing resources based on workload, ensuring optimal performance.
Spot instances in cloud environments reduce costs while maintaining processing power.
Parallelism, achieved by partitioning data and distributing workloads, increases throughput and reliability.
Continuous monitoring and modular architectures enable seamless scaling as data volumes grow.
| Processing Type | Scalability | Resource Efficiency and Cost |
| Batch Processing | Utilizes both vertical and horizontal scaling | More resource-efficient and cost-effective for large-scale tasks |
| Real-Time Processing | Primarily depends on horizontal scaling | Requires advanced hardware, leading to higher costs and resource use |
Batch processing platforms define clear service level agreements (SLAs) for throughput, latency, and availability. These metrics help organizations monitor and maintain performance as they scale operations.
Improved Data Accuracy
Batch processing improves data accuracy by enabling comprehensive data transformation, cleaning, and validation before loading information into target systems. Organizations schedule batch jobs during low-traffic periods, which ensures consistency and reduces errors.
Batch processing removes inconsistencies, errors, and duplicates, enforcing data integrity and business rules.
Banks and stock brokerage firms use batch processing to handle millions of transactions, meeting regulatory requirements and minimizing human errors.
The controlled environment of batch processing allows for thorough testing, monitoring, and error handling.
Only clean and accurate data is loaded, which is critical for regulated industries.
Batch processing supports large-scale ETL operations, where accuracy and consistency are essential for compliance and business intelligence.
Reliability
Reliability stands as a hallmark of batch processing, especially in mission-critical applications. Organizations track individual batch job status, processing times, and job completion rates to ensure operational efficiency.
Automated monitoring and alerting workflows check batch job status periodically and notify teams of issues.
Logs capture key fields such as job name, run ID, start and end times, and status for detailed analysis.
Batch processing systems complete jobs within expected timeframes, maintaining the stability of mission-critical applications.
Robust error handling and recovery mechanisms ensure that failures do not disrupt business operations.
Note: Automated monitoring and alerting play a vital role in maintaining the reliability of batch processing systems. Teams receive timely notifications for long-running or failed jobs, which helps prevent negative impacts on essential services.
The benefits of batch processing—high throughput, cost-effectiveness, efficient resource utilization, scalability, improved data accuracy, and reliability—make it indispensable for organizations managing large-scale, repetitive, or scheduled workloads.
Applications of Batch Processing
Data Warehousing
Data warehousing relies on batch processing to consolidate, clean, and transform large volumes of data from multiple sources. Companies schedule ETL jobs to extract, transform, and load data into centralized repositories. These jobs run during off-peak hours, which reduces operational costs and maximizes resource utilization.
Customer billing tasks generate invoices for utilities, telecom, and subscription services.
Inventory management reconciles stock levels and triggers reorder requests.
Report generation produces financial statements, sales reports, and operational metrics.
Batch processing ensures data completeness and accuracy by processing all records in each run. Monitoring systems track performance, errors, and anomalies, maintaining reliability. Job scheduling algorithms optimize task dependencies and resource availability, minimizing downtime and accelerating processing time.
Note: Organizations face challenges such as processing delays, scalability concerns, and complex task dependencies. They address these issues by refining batch schedules and leveraging scalable platforms.
Finance
Financial institutions depend on batch processing for end-of-day reporting, reconciliation, and payroll. Banks automate the handling of large transaction volumes by grouping them into batches, often scheduled overnight.
Batch processing automates multiple transactions as a single group.
It reduces labor and operational costs by minimizing human oversight.
Jobs run regularly outside business hours, requiring minimal manual intervention.
Alerts notify staff if problems occur, ensuring timely resolution.
Batch processing supports efficient end-of-period financial tasks such as payroll and reconciliation.
Automation improves accuracy and frees staff for higher-value duties.
Manual reconciliation often leads to data entry errors and missed transactions. Automation tools import data directly from POS and bank systems, capturing all transactions comprehensively and interpreting data accurately. Standardized processes and real-time alerts enhance the accuracy and speed of financial operations.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use batch processing to automate claims processing and patient record updates. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technology extracts and updates patient records and claims data in batches.
HBF Health in Australia reduced claim turnaround time by 50% through IDP-enabled batch claims processing. Loma Linda University Health improved data accuracy and sped up patient record updates by automating data capture from medical records. St. Vincent’s Health Australia digitized large volumes of patient documents, facilitating easier access and compliance.
Batch processing reduces administrative workload and improves workflow efficiency. Healthcare practices streamline claims submission and enhance revenue cycle management by processing multiple claims simultaneously.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies leverage batch processing for inventory management and production scheduling. ERP scheduling software centralizes production planning, resource allocation, and inventory management.
The software integrates data from sales, inventory, and procurement to plan production runs accurately.
Real-time capacity management automatically adjusts schedules to minimize downtime.
Material reorder alerts prevent shortages and optimize stock levels.
Manufacturers group similar jobs into batches to reduce setup times and improve efficiency. Machines, labor, and materials are assigned to each batch, ensuring optimal use. Sequencing jobs within batches minimizes downtime and meets production priorities. Real-time tracking detects delays or quality issues, while post-production data analysis refines future batch scheduling.
Batch process manufacturing supports industries like food, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals by grouping tasks based on scalable recipes. This method enables precise inventory management, lot traceability, and product consistency.
Retail
Retailers depend on batch processing for sales analytics, inventory updates, and customer intelligence. Batch processes load and clean sales and inventory history data, supporting downstream analytics applications.
Ad hoc batch load processes manage transactional data areas such as sales, inventory receipts, markdowns, and transfers.
Sales reporting automates analysis of sales data to provide insights into sales processes.
Order processing manages order fulfillment, tracks inventory levels, and handles customer information efficiently.
Customer intelligence analyzes sales data to identify buying patterns.
Inventory management automatically tracks stock levels, shipments, and related information.
Promotions and discounts apply in bulk across large product volumes.
Retailers modify staged data directly to correct errors before batch processing, maintaining data accuracy in sales and inventory systems.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications providers use batch processing to manage billing cycles and customer data.
Batch processing groups multiple payment transactions for efficient processing, validation, and management.
It handles payment, refund, and reversal batches, as well as importing batch files from banks.
Automated billing cycles process large volumes of customer usage data and payments collectively.
Scheduling batch jobs during off-peak hours optimizes resource utilization and system efficiency.
Batch processing improves throughput, accuracy, scalability, fault tolerance, and predictability. Automated, scheduled execution simplifies administration and enables telecom providers to process massive data sets related to customer billing and account management.
Government
Government agencies implement batch processing for payroll, benefits administration, and regulatory reporting.
Payroll systems process thousands of employee payments in scheduled batches, ensuring timely and accurate disbursement.
Benefits administration uses batch processing to update eligibility records and issue payments.
Regulatory reporting consolidates data from multiple departments, generating compliance reports on a regular schedule.
Batch processing supports offline features, billing cycles, and report generation, enabling agencies to meet strict deadlines and maintain data integrity. Automated workflows reduce manual intervention and improve operational efficiency.
Tip: Government organizations benefit from batch processing by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Use Cases
End-of-Day Reporting
Financial institutions rely on batch processing for end-of-day reporting, one of the most common use cases in the industry. Banks process transactions accumulated throughout the day overnight, generating comprehensive reports without the need for real-time systems. Key performance indicators for these batch processing use cases include execution time, resource usage, error rates, and throughput. Monitoring these metrics ensures timely and accurate report delivery. By scheduling jobs during off-peak hours, organizations optimize resources and maintain high data quality.
Execution time tracks how long each batch job takes.
Resource usage monitors CPU, memory, and disk I/O.
Error rates help identify and resolve data issues.
Throughput measures the volume of data processed.
Reliable end-of-day reporting supports compliance and decision-making, making it a critical use case for batch processing.
Billing and Payroll
Large organizations use batch processing to automate billing and payroll, making these essential use cases for operational efficiency. Batch payment processing consolidates thousands of transactions, reducing manual work and minimizing errors such as double payments or missed invoices. Automation tools integrate with accounting and HR systems, validating data and initiating payments on schedule. Compared to manual methods, batch processing significantly lowers error rates and speeds up payouts. Audit trails and access controls further enhance compliance and reliability.
Inventory Updates
Inventory management in retail and manufacturing depends on batch processing for timely and accurate updates. These use cases benefit from batch tracking, which assigns unique identifiers to product groups, enabling traceability and quality control. Electronic batch record systems automate data collection, reduce human error, and support regulatory compliance. By logging movements and monitoring quality, organizations streamline inventory updates and improve operational efficiency.
It provides visibility into product movements.
It supports compliance and quality assurance.
Data Conversion
Data conversion projects represent another important set of use cases for batch processing. Organizations process large volumes of data at scheduled intervals, often using tools like Apache Hadoop. This approach is cost-effective and scalable, making it ideal for migrating data from legacy systems or integrating multiple sources. Batch data ingestion moves information into centralized repositories, overcoming data silos and enabling better decision-making. Automated tools simplify the process, even when handling complex transformations.
Subscription Management
SaaS platforms rely on batch processing for subscription management, a growing category of use cases. Processing customer and transaction data in groups allows for efficient handling of fluctuating workloads. Batch jobs run during off-peak hours, optimizing resource usage and reducing costs. This method improves data quality through validation and cleansing, supports bulk updates, and enables complex reporting. Integration with cloud technologies and AI-driven scheduling further enhances flexibility and performance.
Supply Chain Fulfillment
Logistics companies use batch processing to improve supply chain fulfillment, making it a vital use case for the industry. By grouping orders for picking, packing, and shipping, batch processing reduces travel time, minimizes warehouse congestion, and lowers operational costs. Warehouse management systems enhance visibility and tracking, leading to faster and more accurate deliveries. Proper training and onboarding maximize the benefits, helping companies manage high order volumes and improve customer satisfaction.
Batch processing in these use cases drives efficiency, accuracy, and scalability across industries, supporting both routine operations and strategic growth.
Challenges and Best Practices
Data Latency
Organizations often encounter data latency when using batch processing. Common challenges include bottlenecks in data warehouses, slow ETL pipelines, and delays from collecting and processing data in batches. These issues can impact decision-making and operational efficiency.
Processing bottlenecks arise from heavy data loads and limited storage.
ETL pipelines slow down due to large volumes and complex transformations.
Inherent delays occur because batch processing collects data over time.
To mitigate latency, teams implement stream processing technologies such as Apache Kafka and Apache Flink. Optimizing data querying with indexing and caching also improves performance. Investing in high-performance infrastructure helps avoid bottlenecks and supports faster analysis.
Tip: Combining batch processing with stream processing enables organizations to balance cost efficiency and timely insights.
System Failures
System failures pose significant risks in batch processing environments. Errors may include data corruption, system crashes, or network failures. Effective recovery strategies help maintain data integrity and minimize downtime.
Identify potential errors and design tailored error handling.
Implement retries, alerts, and rollback mechanisms.
Monitor batch processes with continuous alerts and log reviews.
Test error handling by simulating failures.
Establish backup and recovery plans with secure storage.
Use automation tools to reduce human error.
Checkpointing allows batch processing to resume from the last successful point. Robust error handling and persistent job metadata support efficient recovery. Monitoring tools such as Apache Airflow and AWS CloudWatch detect failures promptly, while retry logic manages transient errors.
Security and Compliance
Batch processing systems must comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Organizations conduct security testing, enforce password policies, and use multi-factor authentication. They revoke access for departing employees and maintain incident response plans.
| Compliance Framework | Key Requirements | Measures Implemented |
| HIPAA | Protect PHI, privacy, security | Encryption, access controls, audit logging |
| GDPR | Data minimization, accuracy, confidentiality | Pseudonymization, encryption, lifecycle management |
| SOC 2 | Security, availability, integrity | Firewalls, backup, monitoring, validation |
Batch jobs run in limited windows, reducing exposure. Ongoing operational controls and vendor management streamline compliance. Organizations regularly review procedures to adapt to evolving regulations.
Batch Scheduling
Effective batch scheduling maximizes resource utilization and minimizes conflicts. Teams document automated processes, implement error handling, and test automation before deployment. Continuous monitoring detects issues early.
Consider job dependencies to avoid conflicts.
Design scalable scheduling solutions for growing workloads.
Enforce security controls for automated processes.
Prioritize projects based on urgency and importance.
Review schedules regularly to adapt to changes.
Defining jobs with clear parameters and using priority-based algorithms optimizes execution order and resource allocation.
Integration with Real-Time Systems
Integrating batch processing with real-time systems presents technical challenges. Real-time integration supports instant data syncing and faster decisions but requires complex infrastructure. Batch processing handles bulk operations efficiently but introduces delays.
Managing high data volume and velocity demands scalable infrastructure.
Ensuring data quality requires robust validation and cleansing.
Achieving low latency involves addressing bottlenecks and delays.
Organizations invest in cloud architectures, automated data quality controls, and stream processing technologies to overcome these challenges. Event-driven designs and edge computing further reduce latency and improve performance.
Batch processing continues to drive efficiency and reliability for organizations in 2025. Companies benefit from high throughput, cost savings, and improved data quality across industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Batch processing handles massive data volumes, supports deep analytics, and integrates with modern data lake architectures.
Tools like Apache Spark and Databricks enable scalable, distributed batch processing for ETL, reporting, and machine learning. Organizations should assess their needs and explore hybrid solutions that combine batch processing with real-time systems for optimal results.
FAQ
What is the main difference between batch processing and real-time processing?
Batch processing groups data and processes it at scheduled times. Real-time processing handles data instantly as it arrives. Organizations choose batch processing for large, repetitive tasks and real-time processing for immediate actions.
Which industries benefit most from batch processing?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and government rely on batch processing. They use it for payroll, billing, inventory management, claims processing, and regulatory reporting.
How does batch processing improve data accuracy?
Batch processing validates, cleans, and transforms data before loading it into systems. This method removes errors and duplicates, ensuring that only accurate and consistent data enters business applications.
Can batch processing integrate with cloud platforms?
Yes. Cloud platforms like AWS Batch and Azure Data Factory support batch processing. These platforms offer scalability, automation, and resource optimization for large-scale data workloads.
What tools help monitor batch processing jobs?
Organizations use tools such as Apache Airflow, AWS CloudWatch, and Databricks. These tools provide job scheduling, monitoring, alerting, and error recovery features.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Community Contribution directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
