Reverse ETL in action: What it is and how it works
 Community Contribution
Community Contribution
Reverse etl is a process that moves enriched, transformed data from centralized warehouses back into operational systems where business users work. Teams in sales, marketing, support, and product operations receive actionable data inside their daily platforms. Unlike traditional etl, which extracts raw data for analysis, reverse etl democratizes access and enables real-time decision-making.
Business users gain timely, accurate data in tools like CRMs and marketing apps.
Data activation accelerates time to value, improves efficiency, and supports continuous monitoring and delivery.
Key Takeaways
Reverse ETL moves cleaned data from central warehouses back into daily business tools like CRMs and marketing apps, enabling teams to make faster, smarter decisions.
This process breaks down data silos and automates workflows, giving sales, marketing, and support teams real-time access to accurate customer information.
Reverse ETL improves business outcomes by syncing data automatically, reducing manual work, and helping teams act quickly on up-to-date insights.
The process includes extracting data from warehouses, transforming it to fit operational systems, loading it into tools, and activating data for immediate use.
By connecting analytics directly to business operations, reverse ETL empowers teams to work efficiently, personalize customer experiences, and drive growth.
Reverse ETL Overview
Definition
Reverse etl represents a modern approach to data integration, where the data warehouse serves as the source and operational systems become the destination. Unlike traditional etl, which extracts data from business applications and loads it into a centralized warehouse, reverse etl inverts this flow. The process moves cleaned and transformed data from the warehouse back into operational tools such as CRMs, marketing automation platforms, and SaaS applications. This inversion of the data integration process enables organizations to operationalize analytics and deliver actionable insights directly to business users.
Census, a leader in the field, defines reverse etl as the process that "syncs data from a system of records like a warehouse to a system of actions like CRM, MAP, and other SaaS apps to operationalize data." This approach closes the loop between analysis and action, ensuring that enriched data reaches the platforms where teams make daily decisions. Reverse etl capabilities allow companies to automate the movement of data, reducing manual intervention and supporting seamless data integration across the business.
Traditional etl pipelines move data from source systems into a data warehouse or data platform. Reverse etl, by contrast, extracts, transforms, and loads data from the warehouse into operational systems. This fundamental shift in the direction of data flow distinguishes reverse etl from conventional etl and highlights its role in enabling real-time, data-driven workflows.
Business Value
Reverse etl delivers measurable business outcomes by making data accessible and actionable within the tools business teams use every day. Companies that implement fully managed reverse etl solutions report significant improvements in operational efficiency and decision-making speed. For example, organizations achieve real-time syncing of product engagement data into CRMs, identify product-qualified leads within sales workflows, and eliminate manual list exports. These benefits drive faster, smarter product-led growth and improve the timing and context for sales outreach.
Reverse etl empowers business teams by automating data syncs and providing real-time access to relevant data within their preferred operational systems. This self-service capability fosters a data-driven culture, allowing teams to explore and analyze data independently without waiting for data teams.
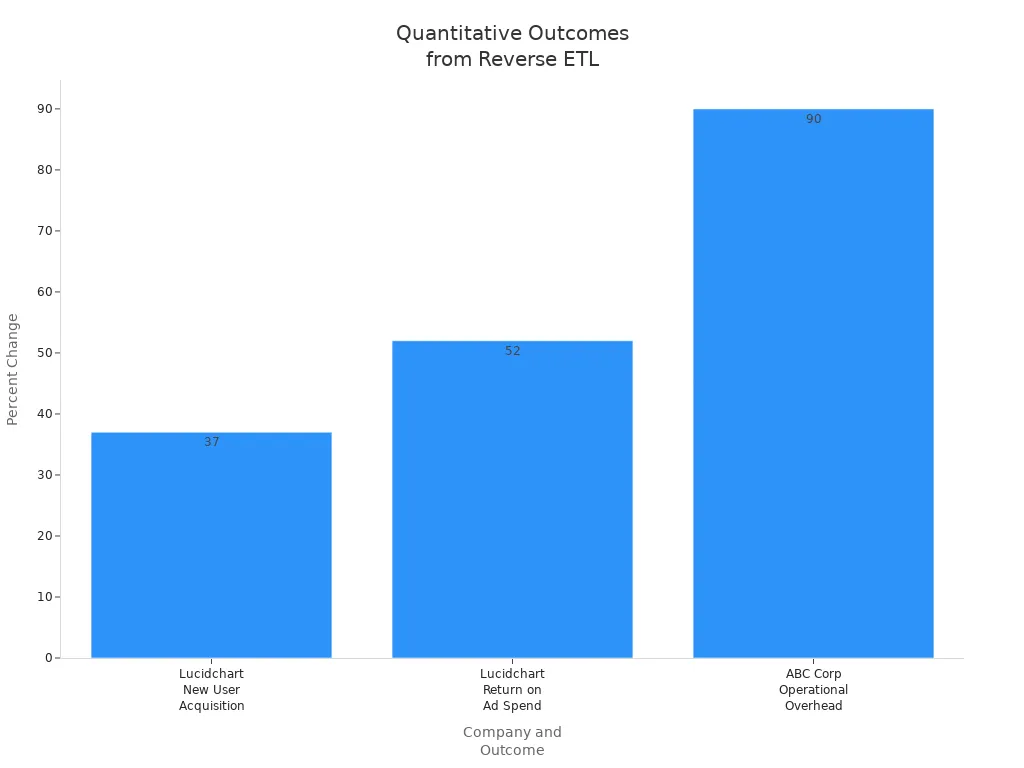
The following table highlights measurable outcomes reported by leading companies:
| Company/Use Case | Measurable Outcome | Description |
| Lucidchart | 37% increase in new user acquisition | Syncing product usage data into Salesforce enabled sales reps to better understand account engagement, driving higher acquisition rates. |
| Lucidchart | 52% increase in return on ad spend | Using warehouse-modeled audiences synced to ad platforms improved targeting efficiency and campaign performance. |
| ClickUp | Proactive churn reduction | Churn-risk signals synced into support tools allowed prioritization of at-risk customers before they filed tickets, reducing churn. |
| ABC Corp | 90% reduction in operational overhead | Near real-time updates to Salesforce reduced manual batch updates, improving operational efficiency. |
| ABC Corp | Enhanced decision-making | Sales reps accessed up-to-date model and sales data in CRM, improving lead prioritization. |
| Dreamdata | Improved lead conversion speed | Real-time product engagement data synced into HubSpot enabled timely identification of product-qualified leads, enhancing conversion. |
Reverse etl improves decision-making speed by pushing fresh, actionable data from centralized warehouses into the operational tools business teams use daily. This real-time data availability eliminates delays caused by dependence on data teams for manual extraction. Business users gain the ability to self-serve and act quickly on integrated data. Marketing teams, for example, can build hyper-personalized campaigns by merging product, sales, and support data, enabling faster customer engagement and reducing missed opportunities.
Seamless data integration through reverse etl supports continuous monitoring and delivery. It automates the data integration process, reduces operational overhead, and ensures that business teams always have access to the most current information. Fully managed reverse etl solutions further streamline these workflows, allowing organizations to focus on strategic initiatives rather than pipeline maintenance.
Tip: Reverse etl not only accelerates time to value but also embeds analytics directly into operational workflows, supporting continuous improvement and data-driven growth.
Reverse ETL Process
Reverse ETL transforms the way organizations operationalize analytics by moving enriched data from centralized warehouses into real-time business applications. This process consists of four main stages: extraction, transformation, loading, and data activation. Each stage plays a critical role in enabling real-time workflows, supporting data integration, and driving decision-making in real-time.
Extraction
Extraction marks the first step in the reverse ETL pipeline. Teams extract data from a central repository, most commonly a cloud data warehouse. Popular sources include Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift. These warehouses store vast amounts of analytical data, which reverse ETL tools retrieve to power operational systems such as CRMs, marketing automation platforms, and analytics dashboards.
Data warehouses serve as the primary extraction point for reverse ETL.
The process targets operational business applications like Salesforce, HubSpot, Marketo, Mailchimp, Zendesk, and Intercom.
Extraction enables organizations to activate and operationalize data that would otherwise remain siloed.
Extraction in reverse ETL presents unique challenges. Teams must plan and coordinate between source and target systems. Reading and writing large volumes of data can be resource-intensive, especially in organizations with legacy technology. Efficient data transfer, automation, and frequent updates are essential to ensure timely and accurate delivery to operational systems. Data quality, structure, and security require careful attention to maintain the integrity of the data pipeline.
Note: Extraction from data warehouses demands robust automation and monitoring to ensure that syncs deliver accurate, up-to-date information to business users.
Transformation
Transformation converts raw analytical data into a format compatible with operational tools. Most transformations occur inside the data warehouse using SQL or tools like dbt. Teams apply business rules, filter, aggregate, normalize, and reformat data to meet the requirements of target systems.
Filtering, isolating, and reformatting data ensures compatibility with CRMs and marketing platforms.
Aggregation and normalization prepare data for real-time workflows and automation.
Business rules align data with operational needs, such as calculating customer lifetime value or segmenting audiences.
Transformation also improves data quality by catching errors and inconsistencies in near-real-time. Reverse ETL tools detect and handle schema changes, ensuring accurate synchronization and compatibility with operational systems. Deduplication processes remove duplicate records, and validation steps guarantee that only reliable, actionable data enters the next stage of the pipeline.
Tip: Effective transformation ensures that data activation delivers meaningful insights and supports decision-making in real-time.
Loading
Loading involves moving the transformed data into operational systems where business teams can act on it. Reverse ETL typically loads data into CRM platforms, marketing automation tools, customer service helpdesks, and analytics dashboards. Common destinations include Salesforce, Marketo, and Zendesk.
The loading phase automates the transfer of data, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
Teams schedule loads during off-peak hours to minimize disruption and maintain system stability.
Initial full data loads are followed by incremental updates, keeping operational systems current with minimal lag.
Maintaining data integrity during loading is crucial. Rigorous cleansing and validation eliminate errors and inconsistencies. Deduplication ensures that only unique records enter operational tools. Compliance with data protection regulations governs proper data handling. Continuous monitoring, logging, and error handling maintain sync accuracy and reliability throughout the data pipeline.
Callout: Automation and incremental syncs keep operational systems updated with the freshest data, enabling real-time analytics and workflow efficiency.
Data Activation
Data activation represents the strategic process of transforming processed data into actionable business outcomes. Reverse ETL operationalizes analytical outputs by syncing data back into business applications for immediate use. This stage goes beyond simple data movement, integrating insights into operational systems to drive execution and measurement.
| Aspect | Description | Measurement Metrics / Outcomes |
| Data Activation | Strategic process transforming processed data into actionable business outcomes by integrating insights into operational systems. | Success measured by improvements in operational efficiency, customer engagement, and revenue. Metrics include conversion rates, personalization effectiveness, and time-to-insight. |
| Relation to Reverse ETL | Reverse ETL operationalizes analytical outputs by syncing data back into business applications for immediate use, enabling execution phase of data activation. | Enables real-time personalization, predictive alerting, and automated decision-making, contributing to measurable business impact. |
Data activation includes several steps:
Data collection from multiple sources to create unified customer profiles.
Data analysis using advanced analytics and machine learning to generate insights.
Execution by integrating insights into operational systems for immediate action, such as workflow orchestration and automation.
Measurement through continuous feedback, tracking business outcomes like customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Reverse ETL enables real-time workflows by moving enriched data from warehouses into operational data stores. The architecture often starts with a batch load of historical data, followed by continuous incremental syncs using change data capture. This approach keeps operational systems updated with minimal lag, supporting decision-making in real-time. Technologies like Apache Spark and Azure Databricks optimize throughput and scalability, while platforms like Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL provide ultra-low latency for real-time applications.
Real-time data activation bridges the gap between analytics and operations, empowering teams to act on insights instantly and drive measurable business impact.
ETL vs. Reverse ETL
Data Flow
The direction of data flow marks the most fundamental difference between ETL and reverse etl. ETL moves data from multiple source systems into a centralized data warehouse. This process consolidates, cleans, and transforms data for analysis and reporting. In contrast, reverse etl extracts processed data from the warehouse and loads it into operational systems like CRM, marketing automation, or support platforms. This reversed flow enables business teams to act on insights in real time.
| Aspect | ETL Architecture | Reverse ETL Architecture |
| Data Flow Position | Data flows from source to data warehouse via ingestion and sink layers, which are decoupled. | Data flows from data warehouse to external SaaS apps; ingestion and sink layers interact directly in one batch job. |
| Ingestion Layer | Captures incremental updates from source, writes to an ordered message buffer (e.g., Kafka, S3). | Computes changed records using snapshot tables in the warehouse and passes updates directly to sink. |
| Sink Layer | Reads ordered records from buffer, batches them, and loads data in bulk jobs into the warehouse. | Batches records in-memory and calls destination APIs (e.g., Salesforce) with rate limits and timeouts. |
| Ordering & Deduplication | Uses warehouse's analytical power and ingestion timestamps to maintain order and deduplicate records. | Must handle ordering and deduplication without warehouse privileges, requiring robust handling. |
| Error Handling | Tracks sync failures, stores failed records in an error store, retries independently. | Sink classifies failures, passes failed records back to ingestion layer for reprocessing in next runs. |
Note: Reverse etl requires robust handling of ordering, deduplication, and error management due to the complexity of operational system APIs.
Use Cases
ETL and reverse etl serve different business needs. ETL supports analytics, reporting, and data preparation for data engineers and analysts. It creates a single source of truth by consolidating data from various sources. Reverse etl, on the other hand, activates insights by delivering processed data to operational tools for immediate action.
ETL use cases include business intelligence dashboards, historical reporting, and data migration.
Reverse etl enables real-time marketing personalization, syncing customer data to sales tools, and providing support agents with up-to-date insights.
Reverse etl also supports inventory management, HR analytics, and product development by pushing relevant data into daily business applications.
Reverse etl closes the loop between analytics and operations. Business teams can act on the latest data without waiting for manual exports or custom integrations.
Key Differences
Several technical and business differences set ETL and reverse etl apart. ETL focuses on heavy data transformation, cleaning, and aggregation before loading data into a warehouse. Reverse etl performs lighter transformations, mainly formatting data to fit operational systems, since most cleaning happens upstream.
| Aspect | ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) | Reverse ETL |
| Data Flow Direction | Extracts data from source systems, transforms it, and loads into a data warehouse for analysis | Reads data from the data warehouse and writes it back into operational SaaS tools used by business teams |
| Primary Purpose | Supports analytics, reporting, and data migration | Empowers customer-facing teams by operationalizing data in daily tools, breaking down data silos |
| Technical Complexity | Traditional transformations focused on cleaning and structuring data for storage and analysis | More complex transformations to handle destination API quirks, user-friendly UX, and syncing only changes |
| Syncing Challenges | Typically merges data based on timestamps (e.g., updated_at fields) | Requires diffing by comparing current and previous data values, handling failed syncs carefully |
| API Interaction | Loads data into optimized data warehouses with standardized schemas | Writes data to multiple SaaS APIs with different interfaces, rate limits, and update modes |
| Business Impact | Enables data analysts to generate insights from consolidated data | Democratizes data access to non-technical business users, enabling real-time operational workflows |
Reverse etl democratizes data access, allowing business users to leverage data integration for operational efficiency. ETL remains essential for building a reliable foundation for analytics, but reverse etl brings those insights directly into the hands of decision-makers.
Use Cases
Marketing
Marketing teams rely on reverse etl to activate customer data for targeted campaigns and personalized outreach. By operationalizing consolidated customer data from data warehouses, marketers gain access to unified, up-to-date customer data in their preferred tools without heavy IT involvement. This data includes behavioral, demographic, and purchase history, which helps marketers segment leads and identify triggers in the customer journey. Reverse etl complements Customer Data Platforms by providing unified customer profiles and enabling dynamic orchestration for highly personalized, cross-channel marketing experiences. CDPs make data accessible through no-code workflows, improving efficiency and time-to-value.
| Company | Use Case Description | Marketing Impact |
| CrossFit | Used Twilio Segment to unify customer profiles and deliver personalized marketing messages across business areas. | Achieved a 24% increase in registration click rates for a global competition and saved 10–15 hours per campaign through automation. |
| MongoDB | Employed reverse ETL to send timely, personalized product info via live chat, email, and pop-ups to users. | Resulted in a 100x increase in event registration rates and improved ad performance. |
Reverse etl empowers marketing teams to deliver targeted, data-driven campaigns that optimize engagement and ROI.
Sales
Sales teams benefit from reverse etl by accessing real-time customer data directly in CRM systems like Salesforce or HubSpot. Reverse etl syncs data from centralized warehouses into operational tools, allowing sales reps to see product usage stats and prioritized leads without consulting data analysts. This integration transforms static reports into actionable insights, shortening feedback cycles and enabling faster, more informed sales actions. Automated extraction, transformation, and loading of customer interaction data ensure that sales teams always have the most recent and accurate customer data. Change Data Capture detects and syncs changes automatically, eliminating manual exports and reducing engineering overhead. Sales reps engage customers more effectively and prioritize leads with confidence.
Customer Success
Customer success teams use reverse etl to access high-quality customer data in real-time within their daily tools. Product usage data flows into CRM and support platforms, allowing managers to identify clients at risk of churning and proactively engage them. Support agents access comprehensive customer data, including previous chats, billing history, and plan details, in ITSM tools like Zendesk. Reverse etl automates repetitive workflows, reduces manual data handling, and enables real-time alerts for at-risk customers. Teams prioritize support tickets, implement proactive retention strategies, and collaborate with sales to reiterate product value. These capabilities streamline workflows, improve decision-making speed, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Data activation through reverse etl empowers teams to work more efficiently, respond faster, and deliver a superior customer experience.
Benefits and Challenges
Advantages
Reverse etl delivers significant advantages for organizations seeking to operationalize their data. Teams keep CRM records enriched and up-to-date with advanced customer scoring and segmentation calculated in data warehouses, overcoming the limitations of traditional CRM systems. Companies update product information in eCommerce platforms automatically, including pricing and personalized recommendations, which boosts customer lifetime value. Inventory data flows back to ERP systems, improving tracking and coordination across tools. Marketing automation becomes more effective as customer purchase data syncs to marketing tools, enabling targeted ads and automated emails based on purchase history. Business teams gain near-real-time access to data in their operational applications, which improves both accuracy and usability.
Enables operational analytics by allowing frontline teams to act on enriched data within daily tools.
Improves sales and marketing effectiveness through up-to-date customer intelligence.
Enhances customer support with a 360-degree view of interactions and history.
Reduces engineering bottlenecks by automating data synchronization.
Bridges the gap between technical teams and business users, supporting smarter decision-making.
Common Issues
Despite its benefits, reverse etl presents several challenges. Ensuring data consistency and quality as data moves back into operational systems requires rigorous checks and ongoing maintenance. Performance impacts on operational systems can occur due to additional data loads. Security and regulatory compliance concerns arise, especially when handling sensitive or regulated data. Large data volumes and throughput demands may lead to performance degradation. Integration complexity increases with diverse data sources and target systems, requiring appropriate connectors and transformation capabilities. Scalability becomes a concern as business needs grow. Teams must also manage deployment, maintenance, monitoring, and alerting to quickly resolve pipeline issues. Robust data governance policies are essential to maintain quality and compliance.
Solutions
Organizations can address these challenges by adopting best practices:
| Challenge | Recommended Solutions and Best Practices |
| Data Integration Complexity | Assess data sources and formats for compatibility, resolve inconsistencies, and use reverse etl tools with pre-built integrations. |
| Privacy & Security | Encrypt data in transit and at rest, use data masking, and implement role-based access control and audit trails. |
| Latency | Implement change data capture to sync only updated data and optimize data models and queries for speed. |
| Scalability | Choose scalable, cloud-based reverse etl tools, apply proper data modeling, and regularly review sync processes. |
Teams should also implement strong data governance, automate repetitive tasks, monitor pipelines continuously, and maintain thorough documentation. Regular testing and continual improvement ensure reliability and efficiency as reverse etl scales with business growth.
Reverse etl transforms how organizations use data. Teams extract, transform, and load data through etl pipelines. Data moves from source systems into warehouses. Data then flows back into operational tools. Data quality improves at every stage. Data-driven workflows become possible. Data activation empowers business users. Data silos disappear. Data supports real-time decisions. Data integration with etl and reverse etl unlocks business value.
Data fuels every step, from etl to activation.
Consider etl and reverse etl to maximize data impact.
FAQ
What types of operational systems can receive data from a warehouse?
Teams can sync information to CRMs, marketing automation platforms, customer support tools, and analytics dashboards. Popular destinations include Salesforce, HubSpot, Marketo, Zendesk, and Intercom.
How often should teams update operational systems with new information?
Most organizations schedule updates hourly or daily. Some use real-time or near-real-time syncs for critical workflows. The frequency depends on business needs and system capabilities.
Does reverse ETL require coding skills?
Many modern platforms offer no-code or low-code interfaces. Data engineers may still configure advanced transformations, but business users can often manage syncs without deep technical knowledge.
How does reverse ETL impact data security?
Teams must follow strict security practices. Encryption, access controls, and audit logs protect sensitive information during transfers. Compliance with regulations remains essential for all data movement.
Can reverse ETL handle large volumes of information?
Scalable cloud-based tools process millions of records efficiently. Incremental syncs and optimized queries help maintain performance as data volumes grow.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Community Contribution directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
